Amersfoort
| Amersfoort | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| — Municipality — | |||
 |
|||
|
|||
 |
|||
| Coordinates: | |||
| Country | Netherlands | ||
| Province | Utrecht | ||
| Area(2006) | |||
| - Total | 63.78 km2 (24.6 sq mi) | ||
| - Land | 62.88 km2 (24.3 sq mi) | ||
| - Water | 0.90 km2 (0.3 sq mi) | ||
| Population (30 November 2008) | |||
| - Total | 143,235 | ||
| - Density | 2,211/km2 (5,726.5/sq mi) | ||
| Source: CBS, Statline. | |||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| - Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Website | www.amersfoort.nl | ||
Amersfoort () is a municipality and the second largest city of the province of Utrecht in central Netherlands. The city is growing quickly but has a well-preserved and protected medieval centre. Amersfoort is one of the largest railway junctions in the country, because of its location on two of the Netherlands' main east-west and north-south rail lines. The town celebrated its 750th birthday in 2009.[1]
Contents |
Population centres
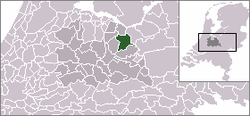
The municipality of Amersfoort consists of the following cities, towns, villages and/or districts: Bergkwartier-Bosgebied, Binnenstad, Hoogland-Hoogland West, Kattenbroek, Kruiskamp-Koppel, Liendert-Rustenburg, Nieuwland, Randenbroek-Schuilenburg, Schothorst, Soesterkwartier, Vathorst-Hooglanderveen Vermeer- en Leusderkwartier, Zielhorst.
History
Hunter gatherers set up camps in the Amersfoort region in the Mesolithic period. Archaeologists have found traces of these camps, such as the remains of hearths, and sometimes microlithic flint objects, to the north of the city.
Remains of settlements in the Amersfoort area from around 1000 BC have been found, but the name Amersfoort, after a ford in the Amer River, today called the Eem, did not appear until the 11th century. The city grew around what is now known as the central square, the Hof, where the Bishops of Utrecht established a court in order to control the "Gelderse vallei" area. It was granted city rights in 1259 by the bishop of Utrecht, Henry I van Vianden. A first defensive wall, made out of brick, was finished around 1300. Soon after, the need for enlargement of the city became apparent and around 1380 the construction of a new wall was begun and completed around 1450. The famous Koppelpoort, a combined land and water gate, is part of this second wall. The first wall was demolished and houses were built in its place. Today's Muurhuizen (wallhouses) Street is at the exact location of the first wall; the fronts of the houses are built on top of the first city wall’s foundations.

The Onze-Lieve-Vrouwentoren tower (The Tower of Our Lady)[2] is one of the tallest medieval church towers in the Netherlands at 98 metres (322 ft). The construction of the tower and the church was started in 1444. The church was destroyed by an explosion in 1787, but the tower survived, and the layout of the church still can be discerned today through the use of different types of stone in the pavement of the open space that was created. It is now the reference point of the RD coordinate system, the coordinate grid used by the Dutch topographical service: the RD coordinates are (155.000, 463.000).
The inner city of Amersfoort has been preserved well since the Middle Ages. Apart from the Onze-Lieve-Vrouwetoren, the Koppelpoort , and the Muurhuizen (Wall-houses), there is also the Sint-Joris church, the canal-system with its bridges, as well as medieval and other old buildings; many are designated as national monuments. In the Middle Ages, Amersfoort was an important centre for the textile industry, and there were a large number of breweries.
In the 18th century the city flourished because of the cultivation of tobacco, but from about 1800 onwards began to decline. The decline was halted by the establishment of the first railway connection in 1863, and, some years later, by the building of a substantial number of infantry and cavalry barracks, which were needed to defend the western cities of the Netherlands. After the 1920s growth stalled again, until in 1970 the national government designated Amersfoort, then numbering some 70,000 inhabitants, as a "growth city". In 2009 the population was 140,000 plus, with an expected 150,000 by 2012.
Second World War
Since Amersfoort was the largest garrison town in the Netherlands before the outbreak of the Second World War, with eight barracks, the whole population of then 43,000 was evacuated ahead of the expected invasion by the Germans in May 1940. After four days of battle, the population was allowed to return.
There was a functioning Jewish community in the town, at the beginning of the war numbering about 700 people. Half of them were deported and killed, mainly in Auschwitz and Sobibor. In 1943, the synagogue, dating from 1727, was severely damaged on the orders of the then Nazi-controlled city government. It was restored and opened again after the war, and has been served since by a succession of rabbis.
There was a concentration camp near the city of Amersfoort during the war. The camp, officially called Polizeiliches Durchgangslager Amersfoort (Police Transit Camp Amersfoort), better known as Kamp Amersfoort, was actually located in the neighbouring municipality of Leusden. After the war the leader of the camp, Joseph Kotälla, was sentenced to death.
Origin of Keistad (Boulder-city)

The nickname for Amersfoort, Keistad (boulder-city), originates in the Amersfoortse Kei, a 9-tonne (19,842 lb) boulder that was dragged from the Soest moors into the city in 1661 by 400 people because of a bet between two landowners. The people got their reward when the winner bought everyone beer and pretzels. Other nearby towns then nicknamed the people of Amersfoort Keientrekker (boulder-dragger/puller). This story embarrassed the inhabitants, and they buried the boulder in the city in 1672, but after it was found again in 1903 it was placed in a prominent spot as a monument. The fact is there are not many boulders in the Netherlands, so its a bit of an icon. It is regularly stolen as a prank.
Culture
Museums
- The Mondriaan House: birthplace of the painter Piet Mondriaan. Exhibits a lifesize reconstruction of his workshop in Paris. Some temporary shows and work by artists inspired by the painter.
- Flehite: historic, educational and temporary exhibitions behind a splendid facade. The museum closed in 2007 due to asbestos contamination. It was refurbished and reopened in May 2009.
- Zonnehof: small elegant modernist building designed by Gerrit Rietveld on an eponymous square just south of the centre with temporary exhibitions of mostly contemporary art.
- Armando Museum: Work by the painter Armando (who lived in Amersfoort as a child) in a renovated church building. Mostly temporary exhibitions. (Most of the church and the art on exhibition was destroyed in a fire on 22 October 2007).[3]
- Dutch Cavalry Museum
- Culinary Museum
- Kunsthal KADE[4]
Sports
Amersfoort had its own professional football (soccer) club named HVC. It was founded on 30 July 1973, but disbanded on 30 June 1982 because of financial problems. It also hosted the riding part of the modern pentathlon event for the 1928 Summer Olympics.
Other
The city has a zoo, DierenPark Amersfoort, which was founded in 1948.
Transport

Bus
Bus services are provided by 2 firms: Connexxion and Veolia. Connexxion provides services in town and to some destinations in the province of Utrecht, while Veolia offers connections to the province of Gelderland.
Rail
Amersfoort has three railway stations:
- Amersfoort, the main station, which has trains to Enschede, Rotterdam, Den Haag, Amsterdam and Leeuwarden/Groningen
- Amersfoort Schothorst, to the north of Amersfoort station.
- Amersfoort Vathorst, to the north of Amersfoort Schothorst.
Road
Two major motorways pass Amersfoort:
- to the north, the A1 motorway (Amsterdam - Apeldoorn)
- to the east, the A28 motorway (Utrecht - Groningen)
Water
The the river Eem (pronounced roughly "aim") begins in Amersfoort, and the town has a port for inland water transport. The Eem connects to the nearby Eemmeer (Lake Eem). The Valleikanaal drains the eastern Gelderse Vallei and joins with other sources to form the Eem in Amersfoort.
Local government

The municipal council of Amersfoort consists of 39 seats, which are divided as follows:[5] [6]
- VVD - 6 seats (6 seats in 2006)
- PvdA - 6 seats (10 seats in 2006)
- CDA - 4 seats (5 seats in 2006)
- GroenLinks - 5 seats (4 seats in 2006)
- ChristenUnie - 3 seats (3 seats in 2006)
- SP - 2 seats (3 seats in 2006)
- D'66 - 5 seats (not represented in 2006)
- Burger Partij Amersfoort - 7 seats (5 seats in 2006)
- TON - 1 seat (not represented in 2006)
- Jouw Amersfoort - not represented (3 seats in 2006)
- NCPN (Nieuwe Communistische Partij Nederland - not represented (not represented in 2006)
- Lijst 10 (Lashkari)- not represented (not exisiting in 2006)
The city has a court of first instance (kantongerecht) and a regional chamber of commerce.
Economy
The city is a main location for several international companies:
- Yokogawa, an electrical engineering and software company, it's European headquarters is located in Amersfoort.
- Nutreco, animal feed and human foodstuffs
- Arcadis, international consultants and engineers in infrastructure and environment, 14,000 employees
- DHV, consultants and engineers.
- Golden Tulip Hospitality Group, international hotel chain Golden Tulip Hotels, Inns and Resorts.[7]
It also has a number of non-profit associations and foundations:
- VEH, the largest home-owners association in the Netherlands; with 700,000 members, it is also the largest in the world
- NVA, the national association of insurance agents
- the KNLTB, the Dutch national lawn-tennis association.
Notable residents of Amersfoort
- See also People from Amersfoort
- Paulus Buys (1531–1594) – Grand Pensionary
- Johan van Oldenbarnevelt (1547–1619) – statesman
- Piet Mondriaan (1872–1944) – painter
- Willem Sandberg (1897–1984) – graphic designer, Stedelijk Museum director
- Johannes Heesters (1903) – actor, singer and entertainer
- Ben Pon (1936) – sports car racing driver
- Ben Pon (senior) – car importer and developer of the Volkswagen Type 2
- Loet Geutjes (1943) – water polo player
- Feike de Vries (1943) – water polo player
- Anke Rijnders (1956) – swimmer
- Frank Drost (1963) – swimmer
- Jan Wagenaar (1965) – water polo player
- Arie van de Bunt (1969) – water polo goalkeeper
- Ton van Heugten, (1945–2008) – former sidecarcross world champion
- Victor Kaisiepo, (1948-2010) – advocate for West Papuan self-determination.[8]
- Jeff de Neeling, Football player
- Joop Kasteel, Professional Fighter and Bodybuilder
- Father Roderick Vonhögen, – television host, podcaster, founder of the Star Quest Production Network
Sister cities
See also
- Rusthof cemetery
References
Notes
- ↑ "Home Page" (in Dutch). Amersfoort 750. http://www.amersfoort750.nl/. Retrieved 24 January 2009.
- ↑ "Onze Lieve Vrouwentoren". SkyscraperCity. http://www.skyscrapercity.info/100.php?id=4&bid=1185. Retrieved 26 March 2008.
- ↑ "Armando Museum fire". Armandomuseum.nl. 22 October 2007. http://www.armandomuseum.nl. Retrieved 4 November 2007.
- ↑ Kunsthalkade.nl
- ↑ "Zetelverdeling en stemaantallen" (in Dutch). Gemeente Amersfoort. http://www.amersfoort.nl/smartsite.shtml?id=157252. Retrieved 26 March 2008.
- ↑ "Verkiezingsuitslag(stemaantalen en zetelverdeling 3 maart 2010" (in Dutch). Gemeente Amersfoort. http://www.amersfoort.nl/smartsite.shtml?id=219256. Retrieved 26 April 2010.
- ↑ "Contact". Golden Tulip Hospitality Group. http://corporate.goldentulip.com/contact/default.aspx?Language=EN. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ↑ "Papuan activist Kaisiëpo dies". Radio Netherlands Worldwide. 2010-01-31. http://www.rnw.nl/english/article/papuan-activist-kaisiëpo-dies. Retrieved 2010-02-20.
External links
- AmersfoortYourWay Tourist information and hotel bookings
- Amersfoort, City with a Heart
|
|||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
|||||