Conjunctiva
| Conjunctiva | |
|---|---|
 |
|
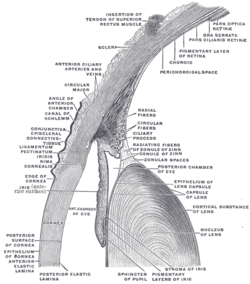
| The upper half of a sagittal section through the front of the eyeball. (Label for 'Conjunctiva' visible at center-left.) | |
 |
|
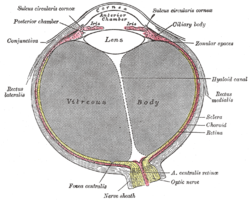
| Horizontal section of the eyeball. (Conjunctiva labeled at upper left.) | |
| Gray's | subject #227 1026 |
| Artery | lacrimal artery, anterior ciliary arteries |
| Nerve | lacrimal nerve |
| MeSH | Conjunctiva |
The conjunctiva (plural = conjunctivas or conjunctivae) is a clear mucous membrane consisting of cells and underlying basement membrane that covers the sclera (white part of the eye)and lines the inside of the eyelids. It is made up of rare stratified columnar epithelium.
Contents |
Function
It helps lubricate the eye by producing mucus and tears, although a smaller volume of tears than the lacrimal gland.[1] It also contributes to immune surveillance and helps to prevent the entrance of microbes into the eye.
Gross anatomy
The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts:
| Part | Area |
|---|---|
| Palpebral or tarsal conjunctiva | lines the eyelids |
| Fornix conjunctiva | where the inner part of the eyelids and the eyeball meet, the palpebral conjunctiva is reflected at the superior fornix and the inferior fornix to become the bulbar conjunctiva. It is loose and flexible, allowing the free movement of the lids and eyeball. An ophthalmologist or optometrist can insert eye drops into the lower eyelid space. The substance works its way up the surface of the eyeball and diffuse into the internal eye. [2] |
| Bulbar or ocular conjunctiva | covers the eyeball, over the sclera. This region of the conjunctiva is bound tightly and moves with the eyeball movements. |
Diseases and disorders
Disorders of the conjunctiva and cornea are a common source of eye complaints.
The surface of the eye is exposed to various external influences and is especially suspectible to trauma, infections, chemical irritation, and allergic reactions.
The conjunctiva is best known because of its inflamed state, conjunctivitis (more commonly known as pinkeye).
Conjunctival irritation is one of the adverse health effects that can take place after overexposure to VOCs (Volatile organic compounds).
See also
- Pinguecula
- Pterygium
- Rougine
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage
Additional images
 Sagittal section through the upper eyelid. |
References
- ↑ London Place Eye Center (2003). Conjunctivitis. Retrieved July 25, 2004.
- ↑ Eye, human Encyclopaedia Britannica
External links
- Medicinenet.com (1999). Conjunctiva. Retrieved July 25, 2004.
- MedEd at Loyola medicine/pulmonar/images/anatomy/eyeli.jpg
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| This eye article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |