Ghent
| Ghent Gent (Dutch) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||||
|
||||||
 |
||||||
 Ghent
Location in Belgium
|
||||||
| Sovereign state | ||||||
| Region | ||||||
| Community | ||||||
| Province | ||||||
| Arrondissement | Ghent | |||||
| Coordinates | ||||||
| Area | 156.18 km² | |||||
| Population – Males – Females – Density |
233,120 (2006-01-01) 48.93% 51.07% 1493 inhab./km² |
|||||
| Age distribution 0–19 years 20–64 years 65+ years |
(01 January 2006) 20.92% 61.21% 17.88% |
|||||
| Foreigners | 7.31% (01 July 2005) | |||||
| Unemployment rate | 14.22% (1 January 2006) | |||||
| Mean annual income | €13,617/pers. (2003) | |||||
| Mayor (list) | Daniël Termont (sp.a) | |||||
| Governing parties | sp.a, Open VLD, Pro Gent | |||||
| Postal codes | 9000–9052 | |||||
| Area codes | 09 | |||||
| Website | www.gent.be | |||||
Ghent (English pronunciation: /ˈɡɛnt/; Dutch: Gent, pronounced [ʝɛnt]; French: Gand, pronounced: [ɡɑ̃]; and formerly Gaunt in English) is a city and a municipality located in the Flemish region of Belgium. It is the capital and biggest city of the East Flanders province. The city started as a settlement at the confluence of the Rivers Scheldt and Lys and in the Middle Ages became one of the largest and richest cities of northern Europe. Today it is a busy city with a port and a university.
The municipality comprises the city of Ghent proper and the towns of Afsnee, Desteldonk, Drongen, Gentbrugge, Ledeberg, Mariakerke, Mendonk, Oostakker, Sint-Amandsberg, Sint-Denijs-Westrem, Sint-Kruis-Winkel, Wondelgem and Zwijnaarde. With 237,250 inhabitants in the beginning of 2008,[1] Ghent is Belgium's second largest municipality by number of inhabitants. The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers an area of 1,205 km2 (465 sq mi) and has a total population of 594,582 as of 1 January 2008, which ranks it as the fourth most populous in Belgium.[1][2] The current mayor of Ghent, Daniël Termont, leads a coalition of the sp.a, Open VLD and Pro Gent.
Every year the ten day long "Ghent Festival" (Gentse Feesten in Dutch) is held. About 2 million visitors attend every year.
Contents |
History

Archeological evidence shows human presence in the region of the confluence of Scheldt and Lys going back as far as the Stone Age and the Iron Age.[3] Most historians believe that the older name for Ghent, 'Ganda' is derived from the Celtic word 'ganda' which means confluence[3]. There are no written records of the Roman period but archeological research confirms that the region of Ghent was further inhabited.
When the Franks invaded the Roman territories (from the end of the 4th century and well into the 5th century) they brought their language with them and Celtic and Latin were replaced by Old Dutch.
Around 650 Saint Amand founded two abbeys in Ghent: the Saint Peter Abbey and the St. Bavo's Abbey. The city grew from several nuclei, the abbeys and a commercial centre. Around 800 Louis the Pious, son of Charlemagne, appointed Einhard, the biographer of Charlemagne, as abbot of both abbeys. In 851 and 879 the city was however attacked and plundered twice by the Vikings.
The city recovered and flourished from the 11th century on. Until the 13th century Ghent was the biggest city in Europe after Paris; it was bigger than London, Cologne or Moscow. Within the city walls lived up to 65,000 people. Today, the belfry and the towers of the Saint Bavo Cathedral and Saint Nicholas' Church are just a few examples of the skyline of the period.
The rivers flowed in an area where a lot of land was periodically inundated. These richly grassed 'meersen' ("water-meadows": a word related to the English 'marsh', but not meaning exactly the same: a 'meers' is not permanently under water) were ideally suited for herding sheep, the wool of which was used for making cloth. In fact, Ghent was, during the Middle Ages, the most important city for cloth.
The wool-industry, originally established at Bruges, created the first European industrialized zone in Ghent in the High Middle Ages. The mercantile zone was so highly-developed that wool had to be imported from Scotland and England. This was one of the reasons for Flanders' good relationship with Scotland and England. Ghent was the birthplace of John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster. The trade with England (but not Scotland) suffered significantly during the Hundred Years' War.
The city recovered in the 14th century, while Flanders was united with neighbouring provinces under the Dukes of Burgundy. High taxes led to a rebellion and eventually the Battle of Gavere in 1453, in which Ghent suffered a terrible defeat at the hands of Philip the Good. Around this time the center of political and social importance in the Low Countries started to shift from Flanders (Bruges–Ghent) to Brabant (Antwerp–Brussels), although Ghent would continue to play an important role.

In 1500 Juana of Castile gave birth to Charles V, who became Holy Roman Emperor and King of Spain. Although native to Ghent, he punished the city after the 1539 Revolt of Ghent and obliged the city's nobles to walk in front of the emperor barefoot with a noose (Dutch: strop) around the neck; since this incident, the people of Ghent have been called "Stroppendragers" (noose bearers). The Saint Bavo Abbey was abolished, torn down, and replaced with a fortress for Spanish troops. Only a small portion of the abbey was spared demolition.
The late 16th and the 17th century brought devastation because of the Religious wars. At one time Ghent was a Calvinistic republic, but eventually the Spanish army reinstated Catholicism. The wars ended the role of Ghent as a center of international importance. In 1745 the city was captured by French forces during the War of the Austrian Succession before being returned to Austria following the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle.
In the 18th and 19th century the textile industry flourished again in Ghent. In 1800 Lieven Bauwens, having smuggled the plans out of England, introduced the first mechanical weaving machine on the European continent.
Ghent was also the site of the signing of the Treaty of Ghent which formally ended the War of 1812 between Britain and the United States. After the battle of Waterloo Ghent became a part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands for 15 years. In this period Ghent established its own university (1817) and a new connection to the sea (1824–27).
After the Belgian Revolution, with the loss of port access to the sea for more than a decade, the local economy collapsed and the first Belgian trade-union originated in Ghent. In 1913 there was a World exhibition in Ghent. As a preparation for these festivities, the Sint-Pieters railway station was completed in 1912.
Geography
Municipality
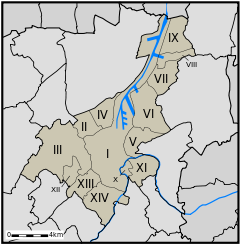
After the 1965 and 1977 fusions the city is made up of:
- I Ghent
- II Mariakerke
- III Drongen
- IV Wondelgem
- V Sint-Amandsberg
- VI Oostakker
- VII Desteldonk
- VIII Mendonk
- IX Sint-Kruis-Winkel
- X Ledeberg
- XI Gentbrugge
- XII Afsnee
- XIII Sint-Denijs-Westrem
- XIV Zwijnaarde
Neighbouring municipalities
- Wachtebeke
- Lochristi
- Destelbergen
- Melle
- Merelbeke
- De Pinte
- Sint-Martens-Latem
- Deinze
- Nevele
- Lovendegem
- Evergem
- Zelzate
Tourism

Architecture
|
Historical centre of Ghent – from left to right: Old post office, Saint-Nicholas Church, Belfry, and Saint Bavo Cathedral.
|

Ghent at Night
|

Riverside in Ghent
|
Much of the city's medieval architecture remains intact and is remarkably well preserved and restored. Its centre is the largest carfree area in Belgium. Interesting highlights are the Saint Bavo Cathedral with the Ghent Altarpiece, the belfry, the Gravensteen castle, and the splendid architecture along the old Graslei harbour. Ghent established a nice blend between comfort of living and history – it is not a city-museum. The city of Ghent houses also three béguinages and numerous churches, among which the Saint-James' church, the Saint-Nicolas' church and the Saint Michael's church are the most beautiful examples.
In the nineteenth century Ghent's most famous architect, Louis Roelandt, built the university hall Aula, the opera house and the main courthouse. Highlights of modern architecture are the university buildings (the Boekentoren or Book Tower) by Henry Van de Velde. There are also a few theatres from diverse periods.
The beguinages, as well as the belfry and adjacent cloth hall, were recognized by UNESCO as World Heritage Sites in 1998 and 1999.
Museums
Important museums in Ghent are the Museum voor Schone Kunsten (Museum of Fine Arts), with paintings by Hieronymus Bosch, Peter Paul Rubens, and many Flemish masters; the SMAK or Stedelijk Museum voor Actuele Kunst (City Museum for Contemporary Art), with works of the 20th century, including Joseph Beuys and Andy Warhol; and the Designmuseum with masterpieces of Victor Horta and Le Corbusier. The Huis van Alijn (House of the Alijn family) was originally a beguinage and is now a museum for folk art where theatre and puppet shows for children are presented. The Museum voor Industriële Archeologie en Textiel or MIAT displays the industrial strength of Ghent with recreations of workshops and stores from the 1800s and original spinning and weaving machines that remain from the time when the building was a weaving mill. The new STAM museum, about the history of the city, will open in 2010.
Restaurants and culinary traditions
As most Belgian cities, Ghent offers a rich variety of local and foreign cuisine. The city centre and quarter called "Patershol" has a huge concentration of restaurants. The "Sleepstraat" a little bit further north houses a number of Turkish restaurants and food bars. By contrast, restaurants are rather sparse beyond the "historic centre".
In Ghent and other regions of East-Flanders, bakeries sell a donut-shaped bun called a "mastel" (plural "mastellen"), which is basically a bagel. "Mastellen" are also called "Saint Hubert bread", because on the Saint's feast day, which is 3 November, the bakers bring their batches to the early Mass to be blessed. Traditionally, it is thought that blessed mastellen immunize against rabies.
As with many areas of northern Belgium the diet centres around hearty stews and soups. Flemish beef stew (stoverij) is available almost everywhere as is "Waterzooi", a local stew originally made from freshwater fish caught in the rivers and creeks of Ghent, but nowadays often made with chicken instead of fish. It is usually served nouvelle-cuisine-style, and will be supplemented by a large pot on the side.
The city promotes a meat-free day on Thursdays called Donderdag Veggiedag[4][5] with vegetarian food being promoted in public canteens for civil servants and elected concillors, in all city funded schools, and promotion of vegetarian eating options in town (through the distribution of "veggie street maps"). This campaign is linked to the recognition of the detrimental environmental effects of meat production, which the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization has established to represent nearly one-fifth of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Festivities
The city is host to some big cultural events such as the Gentse Feesten, I Love Techno, "10 Days Off" musical festival, Flanders International Film Festival Ghent (with the World Soundtrack Awards) and the Gent Festival van Vlaanderen. Also, every five years, a huge botanical exhibition (Gentse Floraliën) takes place in Ghent, attracting numerous visitors to the city.
The International Festival van Vlaanderen, which had its 50th celebration in 2008, is one of the fastest growing music festivals in Europe. Yearly it opens with the OdeGand City festivities that takes place on the second Saturday of September. Some 50 concerts takes place in diverse locations throughout the medieval inner-city and some 250 internationally acclaimed virtuosi performs. The new Festival MADE dimension of the festival introduces in its program both the innovative experiments of local artists and feature the original version of Mozart's Kleine Nacht Music. Since 2002, the festivities have begun with the now renowned OdeGand street festival that takes Classical Music to every corner of the city, even onto the boats on the canals where spectators get 'live' classical rides. The whole of the medieval town of Ghent turns classical in September, and although the Festival has something of the exuberance of a 'Night of the Proms', it is many notches higher on the scales of inventiveness and quality. Other major Flemish cities follow suit with similar events during Festival Time, all of which form part of the International Festival (Antwerp with Laus Polyphoniae; Bruges with MAfestival; Brussels with KlaraFestival; Limburg with Basilica, Mechelen and Brabant with Novecento and Transit).
Economy
The port of Ghent, in the north of the city, is the third largest port of Belgium. It is accessed by the Ghent-Terneuzen Canal, which ends near the Dutch port of Terneuzen on the Western Scheldt. The port houses, among others, big companies like Sidmar, Volvo Cars, Volvo Trucks, Volvo Parts, Honda, and Stora Enso.
The Ghent University and a number of research oriented companies are situated in the central and southern part of the city.
As the biggest city of East-Flanders, Ghent has many hospitals, schools and shopping streets.
Tourism is increasingly becoming a major employer in the local area.
Transport
As one of the largest cities in Belgium, Ghent has a highly developed transportation system.
- By car the city is accessible by two of the country's main roads:
- In addition Ghent also has two ringways:
- The R4: connects the outskirts of Ghent with each other and the surrounding villages, and also leads to the E40 and E17 roads.
- The R40: connects the different downtown quarters with each other, and provides access to the main avenues.
- The municipality of Ghent comprises five train stations:
- Gent-Sint-Pieters Station: an international train station with connections to Bruges, Brussels, Antwerp, Kortrijk, other Belgian towns and Lille. The station also offers a direct connection to Brussels Airport.
- Gent-Dampoort Station: an intercity train station with connections to Sint-Niklaas, Antwerp, Kortrijk and Eeklo.
- Gentbrugge Station: a regional train station in between the two main train stations, Sint-Pieters and Dampoort.
- Wondelgem Station: a regional train station with connections to Eeklo once an hour.
- Drongen Station: a regional train station in the village of Drongen with only a limited number of trains a day.
- Ghent has an extensive web of public transport lines, operated by De Lijn:
- Ghent Tram (see pictures below):
- Line 1: Flanders Expo - Sint-Pieters-Station - Korenmarkt (city centre) - Evergem
- Line 21: Zwijnaardebrug - UZ - Sint-Pieters-Station - Zonnestraat (city centre) - Zuid - Melle Leeuw
- Line 22: Zwijnaardebrug - UZ - Sint-Pieters-Station - Zonnestraat (city centre) - Zuid - Gentbrugge
- Line 4: Sint-Pieters-Station - Muide - Korenmarkt (city centre) - Zuid - Moscou
- Ghent Tram (see pictures below):
-
- City buses (see picture below):
- Line 3: Mariakerke - Korenmarkt (city centre) - Dampoort-Station - Gentbrugge (former Trolleybus (see picture below))
- Line 5: Van Beverenplein - Sint-Jacobs (city centre) - Zuid - UZ - Zwijnaarde
- Line 6: Watersportbaan - Zuid - Dampoort-Station - Wondelgem - Mariakerke
- Line 8: Zuid - University - Sint-Pieters-Station - Blaarmeersen
- Line 9: Mariakerke - Malem - Sint-Pieters-Station - Gentbrugge
- Line 17/18: Drongen - Korenmarkt (city centre) - Dampoort-Station - Oostakker
- Line 38/39: Blaarmeersen - Korenmarkt (city centre) - Dampoort-Station - Sint-Amandsberg
- At Sint-Pieters-Station and the Zuid bus station there are several regional buses as well.
- City buses (see picture below):
When arriving in Ghent, it is best to leave cars in Park & Ride zones next to the road. The actual city centre is a car free area, and parking is difficult and expensive in the city. On weekends, night buses provide free transportation through the night.
|
Low floor tram vehicle (type: HermeLijn) |
Former trolleybus |
Regional bus |
Sports
In the Belgian first football division Ghent is represented by K.A.A. Gent. Another Ghent football club is KRC Gent-Zeehaven, playing in the Belgian fourth division.
Every year the Six Days of Flanders, a six-day track cycling race, is held in Ghent. It takes place in the Kuipke velodrome.
The city also hosts an annual track and field meet at the Flanders Sports Arena: the Indoor Flanders meeting. It is one of the IAAF's foremost indoor track and field events and two-time Olympic champion Hicham El Guerrouj set a world record at the event in 1997.
Famous people

See also: Notable people from Ghent
- Saint Bavo, patron saint of Ghent (589–654)
- Saint Livinus of Ghent, (580–657)
- Henry of Ghent, scholastic philosopher (c. 1217–1293)
- Jacob van Artevelde, statesman and political leader (c. 1290–1345)
- John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster (1340–1399)
- Jan van Eyck, painter (c. 1385–1441)
- Hugo van der Goes, painter (c. 1440–1482)
- Jacob Obrecht, composer of the Renaissance (c. 1457–1505)
- Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Karel V, Charles Quint (1500–1558)
- Cornelius Canis, composer of the Renaissance, music director for the chapel of Charles V in the 1540s–1550s
- Daniel Heinsius, scholar of the Dutch Renaissance (1580–1655)
- Caspar de Crayer, painter (1582–1669)
- Frans de Potter, writer, (1834–1904)
- Jan Frans Willems, writer (1793–1846)
- Joseph Guislain, physician (1797–1860)
- Hippolyte Metdepenningen, lawyer and politician (1799–1881)
- Louis XVIII of France was exiled in Ghent during the Hundred Days in 1815
- Charles John Seghers, Jesuit clergyman and missionary (1839–1886)
- Victor Horta, Art Nouveau architect (1861–1947)
- Maurice Maeterlinck, poet, playwright, essayist, recipient of the Nobel Prize in Literature (1862–1949)
- Frans Rens, writer, (1805–1874)
- Leo Baekeland, chemist and inventor of Bakelite (1863–1944)
- Pierre Louÿs, poet and romantic writer (1870–1925)
- Marthe Boël, feminist (1877–1956)
- Karel van de Woestijne, writer (1878–1929)
- Corneille Jean François Heymans, physiologist and recipient of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1892–1968)
- Gustave Van de Woestijne, painter (1881–1947)
- Suzanne Lilar, essayist, novelist, and playwright (1901–1992)
- Jean Daskalidès, gynecologist and founder of Leonidas chocolates (1922–1992)
- Willy De Clercq, liberal politician and European Commissioner (1927–)
- Jacques Rogge, International Olympic Committee President (1942–)
- Gabriel Ríos, musician
- Cédric Van Branteghem, sprinter athlete
- Soulwax, electronic/rock band: brothers David and Stephen Dewaele
- Xavier Henry, shooting guard for the NBA's Memphis Grizzlies
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
|
|
See also
- List of Mayors of Ghent
References
- Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Statistics Belgium; Werkelijke bevolking per gemeente op 1 januari 2008 (excel-file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, as of 1 January 2008. Retrieved on 2008-10-19.
- ↑ Statistics Belgium; De Belgische Stadsgewesten 2001 (pdf-file) Definitions of metropolitan areas in Belgium. The metropolitan area of Ghent is divided into three levels. First, the central agglomeration (agglomeratie) with 278,457 inhabitants (2008-01-01). Adding the closest surroundings (banlieue) gives a total of 423,320. And, including the outer commuter zone (forensenwoonzone) the population is 594,582. Retrieved on 2008-10-19.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "History of Ghent". www.gent.be. http://www.gent.be/gent/english/history/gesch01.htm. Retrieved 2006-05-05.
- ↑ "Ghent's veggie day: for English speaking visitors" on Vegetarisme.be
- ↑ "Belgian city plans 'veggie' days" on BBC News (2009-05-12).
- ↑ Gent van A tot Z: Zustersteden.
External links
- Official website, (Dutch)
- Official Tourist website, (Dutch) (English) (French) (German) (Spanish)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||