Indochina
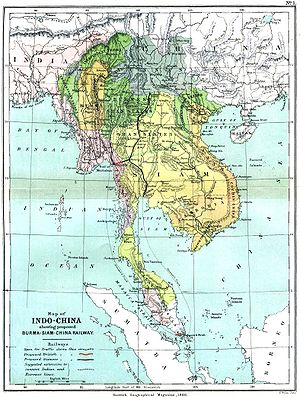
Indochina, or the Indochinese peninsula, is a region in Southeast Asia. It lies roughly east of India, south of China. The name has its origins in the French, Indochine, and was adopted when French colonizers in Vietnam began expanding their territory to bordering countries.
Historically, the countries of mainland Southeast Asia received cultural influence from China and India, but to varying degrees. Some Southeast Asian cultures, such as those of Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar and Thailand are influenced mainly by the culture of India with a smaller influence from the culture of China. Others, such as Vietnam, are more heavily influenced by Chinese culture, with only minor cultural influences from India, largely via the Champa civilization that Vietnam conquered during its southward expansion.
Malaysia and Singapore were at first strongly influenced by Indian culture followed by Islamic influences. Later, Chinese culture becomes a major influence following large numbers of Chinese immigration and settlement.
Today, most of these countries also show pronounced Western cultural influences which began during colonialism of western countries in Southeast Asia.
In a strict sense, Indochina comprises the territory of the former French Indochina:
However, in a wider sense, the cultural region is better described as Mainland Southeast Asia in which sense it also includes:
- Peninsular Malaysia (the southern end of the Malay peninsula excluding the Malay islands)
- Myanmar (formerly Burma—part of British India until 1937)
- Singapore (also considered part of Maritime Southeast Asia if the Johor-Singapore Causeway is not taken into account)
- Thailand (formerly Siam)
Note that the term Sino-Indian is used to describe things relating to India and China. (e.g. Sino-Indian relations).
See also
- ASEAN
- East Indies
- French Indochina
- Malay Peninsula
- Maritime Southeast Asia
- Indochina War
- Indochina Time UTC+7
- Serindia
External links
| This Asia-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||