Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a partially-permeable membrane down a water potential gradient.[1] More specifically, it is the movement of water across a partially permeable membrane from an area of high water potential (low solute concentration) to an area of low water potential (high solute concentration). It is a physical process in which a solvent moves, without input of energy, across a semipermeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations.[2] Osmosis releases energy, and can be made to do work[3]. Osmosis is a passive process, like diffusion.
Net movement of solvent is from the less-concentrated (hypotonic) to the more-concentrated (hypertonic) solution, which tends to reduce the difference in concentrations. This effect can be countered by increasing the pressure of the hypertonic solution, with respect to the hypotonic. The osmotic pressure is defined to be the pressure required to maintain an equilibrium, with no net movement of solvent. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity.
Osmosis is important in biological systems, as many biological membranes are semipermeable. In general, these membranes are impermeable to organic solutes with large molecules, such as polysaccharides, while permeable to water and small, uncharged solutes. Permeability may depend on solubility properties, charge, or chemistry, as well as solute size. Water molecules travel through the plasma cell wall, tonoplast (vacuole) or protoplast in two ways, either by diffusing across the phospholipid bilayer directly, or via aquaporins (small transmembrane proteins similar to those in facilitated diffusion and in creating ion channels). Osmosis provides the primary means by which water is transported into and out of cells. The turgor pressure of a cell is largely maintained by osmosis, across the cell membrane, between the cell interior and its relatively hypotonic environment.[4]
Contents |
Basic explanation
Osmosis may occur when there is a partially permeable membrane, such as a cell membrane. When a cell is submerged in water, the water molecules pass through the cell membrane from an area of low solute concentration (outside the cell) to one of high solute concentration (inside the cell); this is called osmosis. The cell membrane is selectively permeable, so only necessary materials are let into the cell and wastes are left out.[4]
When the membrane has a volume of pure water on both sides, water molecules pass in and out in each direction at the exact same rate; there is no net flow of water through the membrane.
In a solution, the concentration of water is dilluted (or lowered) by the presence of solute particles. If there is a solution on one side, and pure water on the other, there will be a higher concentration of water molecules on the pure water side of the membrane. Therefore, water molecules pass through the membrane from the pure water side toward the solution side more frequently than from the solution side going to the pure water side. This will result in a net flow of water to the side with the solution. Assuming the membrane does not break, this net flow will slow and finally stop as the pressure on the solution side becomes such that the movement in each direction is equal: dynamic equilibrium. This could either be due to the water potential on both sides of the membrane being the same, or due to osmosis being inhibited by factors such as pressure potential or osmotic pressure.
Osmosis can also be explained using the notion of entropy, from statistical mechanics. Suppose a permeable membrane separates equal amounts of pure solvent and a solution. Since a solution possesses more entropy than pure solvent, the second law of thermodynamics states that solvent molecules will flow into the solution until the entropy of the combined system is maximized. Notice that, as this happens, the solvent loses entropy while the solution gains entropy. Equilibrium, hence maximum entropy, is achieved when the entropy gradient becomes zero, and dissolution takes place.
Pure water is more ordered than water in a solution; thus, from an entropic standpoint it takes some net energy to move a water molecule from a disordered solution and "pack it in" with pure water. This is the same explanation as to why the disordered air does not spontaneously separate and order into oxygen and nitrogen, it would take energy for this to happen. Additionally, particle size has no bearing on osmotic pressure, as this is the fundamental postulate of colligative properties.[5]
Examples of osmosis

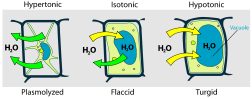
Osmotic pressure is the main cause of support in many plants. The osmotic entry of water raises the turgor pressure exerted against the cell wall, until it equals the osmotic pressure, creating a steady state.
When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water in the cells moves to an area higher in solute concentration and the cell shrinks, and in doing so, becomes flaccid. This means the cell has become plasmolysed - the cell membrane has completely left the cell wall due to lack of water pressure on it; the opposite of turgid.
Also, osmosis is responsible for the ability of plant roots to draw water from the soil. Since there are many fine roots, they have a large surface area, and water enters the roots by osmosis.
Osmosis can also be seen when potato slices are added to a high concentration of salt solution. The water from inside the potato moves to the salt solution, causing the potato to shrink and to lose its 'turgor pressure'. The more concentrated the salt solution, the bigger the difference in size and weight of the potato slice.
In unusual environments, osmosis can be very harmful to organisms. For example, freshwater and saltwater aquarium fish placed in water of a different salinity than that to which they are adapted to will die quickly, and in the case of saltwater fish, dramatically. Another example of a harmful osmotic effect is the use of table salt to kill leeches and slugs.
Suppose an animal or a plant cell is placed in a solution of sugar or salt in water.
- If the medium is hypotonic — a dilute solution, with a higher water concentration than the cell — the cell will gain water through osmosis.
- If the medium is isotonic — a solution with exactly the same water concentration as the cell — there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane.
- If the medium is hypertonic — a concentrated solution, with a lower water concentration than the cell — the cell will lose water by osmosis.
Essentially, this means that if a cell is put in a solution which has a solute concentration higher than its own, then it will shrivel up, and if it is put in a solution with a lesser solute concentration than its own, the cell will expand and burst.
Chemical gardens demonstrate the effect of osmosis in inorganic chemistry.
Factors
Osmotic pressure
As mentioned before, osmosis may be opposed by increasing the pressure in the region of high solute concentration with respect to that in the low solute concentration region. The force per unit area, or pressure, required to prevent the passage of water through a selectively permeable membrane and into a solution of greater concentration is equivalent to the osmotic pressure of the solution, or turgor. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the property depends on the concentration of the solute, but not on its identity.
Osmotic gradient
The osmotic gradient is the difference in concentration between two solutions on either side of a semipermeable membrane, and is used to tell the difference in percentages of the concentration of a specific particle dissolved in a solution.
Usually the osmotic gradient is used while comparing solutions that have a semipermeable membrane between them allowing water to diffuse between the two solutions, toward the hypertonic solution (the solution with the higher concentration). Eventually, the force of the column of water on the hypertonic side of the semipermeable membrane will equal the force of diffusion on the hypotonic (the side with a lesser concentration) side, creating equilibrium. When equilibrium is reached, water continues to flow, but it flows both ways in equal amounts as well as force, therefore stabilizing the solution.
Variation
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a separation process that uses pressure to force a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that retains the solute on one side and allows the pure solvent to pass to the other side. More formally, it is the process of forcing a solvent from a region of high solute concentration through a membrane to a region of low solute concentration by applying a pressure in excess of the osmotic pressure.
Forward osmosis
Osmosis may be used directly to achieve separation of water from a "feed" solution containing unwanted solutes. A "draw" solution of higher osmotic pressure than the feed solution is used to induce a net flow of water through a semipermeable membrane, such that the feed solution becomes concentrated as the draw solution becomes dilute. The diluted draw solution may then be used directly (as with an ingestible solute like glucose), or sent to a secondary separation process for the removal of the draw solute. This secondary separation can be more efficient than a reverse osmosis process would be alone, depending on the draw solute used and the feedwater treated. Forward osmosis is an area of ongoing research, focusing on applications in desalination, water purification, water treatment, food processing, etc.
See also
- Active Transport
- Diffusion
- Homeostasis
- Ion trapping
- Osmoprotectant
- Osmoregulation
- Osmotic shock
- Osmotic power
- Plasmolysis
- Salinity gradient power
- Water potential
- Brining
- Reverse osmosis plant
References
- ↑ Haynie, Donald T. (2001). Biological Thermodynamics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 130–136. ISBN 0521795494.
- ↑ "Osmosis". http://www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/e22/22c.htm.
- ↑ "Statkraft to build the world's first prototype osmotic power plant". http://www.statkraft.com/pro/press/Press_releases/2007/Statkraft_to_build_world_s_first_osmotic_power_plant.asp.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Maton, Anthea; Jean Hopkins, Susan Johnson, David LaHart, Maryanna Quon Warner, Jill D. Wright (1997). Cells Building Blocks of Life. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall. pp. 66–67.
- ↑ Borg, Frank (2003). "What is osmosis? Explanation and understanding of a physical phenomenon". Jyväskylä University, Chydenius Institute, Karleby, Finland. pp. 1–39. http://arxiv.org/abs/physics/0305011v1.
External links
- Osmosis simulation in Java
- NetLogo Osmosis simulation for educational use (Java Applet for fast PCs)
- NetLogo Osmosis simulation for educational use (Java Applet, runs also on slow PCs)
- An Osmosis Experiment