Perimeter
A perimeter is a path that surrounds an area. The word comes from the Greek peri (around) and meter (measure). The term may be used either for the path or its length - it can be thought of as the length of the outline of a shape. The perimeter of a circular area is called circumference.
Contents |
Practical uses


Calculating the perimeter has considerable practical applications. The perimeter can be used to calculate the length of fence required to surround a yard or garden. The perimeter of a wheel (its circumference) describes how far it will roll in one revolution. Similarly, the amount of string wound around a spool is related to the spool's perimeter.
Formulas
| shape | formula | variables |
|---|---|---|
| circle |  |
where 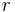 is the radius. is the radius. |
| triangle | 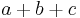 |
where 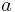 , , 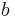 and and 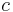 are the lengths of the sides of the triangle. are the lengths of the sides of the triangle. |
| square | 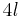 |
where 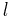 is the side length is the side length |
| rectangle | 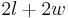 |
where 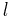 is the length and is the length and 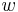 is the width is the width |
| equilateral polygon | 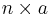 |
where 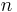 is the number of sides and is the number of sides and 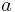 is the length of one of the sides. is the length of one of the sides. |
| regular polygon | 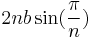 |
where 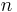 is the number of sides and is the number of sides and 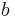 is the distance between center of the polygon and one of the vertices of the polygon. is the distance between center of the polygon and one of the vertices of the polygon. |
| general polygon | 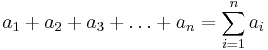 |
where 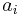 is the length of the is the length of the 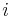 -th (1st, 2nd, 3rd ... n-th) side of an n-sided polygon. -th (1st, 2nd, 3rd ... n-th) side of an n-sided polygon. |
Perimeter is about the distance around all of a shape for e.g. circle , the perimeter around a circle is called a circumference . Perimeters for more general shapes can be calculated as any path with 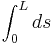 where
where 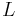 is the length of the path and
is the length of the path and 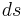 is an infinitesimal line element. Both of these must be replaced with other algebraic forms in order to be solved: an advanced notion of perimeter, which includes hypersurfaces bounding volumes in
is an infinitesimal line element. Both of these must be replaced with other algebraic forms in order to be solved: an advanced notion of perimeter, which includes hypersurfaces bounding volumes in 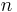 -dimensional euclidean spaces can be found in the theory of Caccioppoli sets.
-dimensional euclidean spaces can be found in the theory of Caccioppoli sets.
See also
- Isoperimetric inequality
- Circumference
- Caccioppoli set
- Pythagorean Theorem
- Wetted perimeter
External links