Skunk
| Skunks | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Striped skunk | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Caniformia |
| Superfamily: | Musteloidea |
| Family: | Mephitidae Bonaparte, 1845 |
| Genera | |
|
Conepatus |
|
Skunks are mammals best known for their ability to secrete a liquid with a strong, foul-smelling odor. General appearance ranges from species to species, from black-and-white to brown or cream colored. Skunks belong to the family Mephitidae[1][2] and to the order Carnivora. There are 10 species of skunks, which are divided into four genera: Mephitis (hooded and striped skunks, two species), Spilogale (spotted skunks, two species), Mydaus (stink badgers, two species), and Conepatus (hog-nosed skunks, four species). The two skunk species in the Mydaus genus inhabit Indonesia and the Philippines; all other skunks inhabit the Americas from Canada to central South America.
Skunks were classified as a subfamily within the family Mustelidae, which includes ferrets, weasels, otters and badgers. However, recent genetic evidence suggests that the skunks are not as closely related to the mustelids as previously thought; they are now classified in their own family.[2]
Contents |
Physical description
Skunk species vary in size from about 15.6 to 37 inches (40 to 94 cm) and in weight from about 1.1 pounds (0.50 kg) (the spotted skunks) to 18 pounds (8.2 kg) (the hog-nosed skunks). They have a moderately elongated body with relatively short, well-muscled legs, and long front claws for digging.
Although the most common fur color is black and white, some skunks are brown or grey, and a few are cream-colored. All skunks are striped, even from birth. They may have a single thick stripe across back and tail, two thinner stripes, or a series of white spots and broken stripes (in the case of the spotted skunk). Some also have stripes on their legs.
Diet
Skunks are omnivorous, eating both plant and animal material and changing their diet as the seasons change. They eat insects and larvae, earthworms, small rodents, lizards, salamanders, frogs, snakes, birds, moles, and eggs. They also commonly eat berries, roots, leaves, grasses, fungi, and nuts.
In settled areas, skunks also seek human garbage. Less often, skunks may be found acting as scavengers, eating bird and rodent carcasses left by cats or other animals. Pet owners, particularly those of cats, may experience a skunk finding its way into a garage or basement where pet food is kept. Skunks commonly dig holes in lawns in search of grubs and worms.
Skunks are one of the primary predators of the honeybee, relying on their thick fur to protect them from stings. The skunk scratches at the front of the beehive and eats the guard bees that come out to investigate. Mother skunks are known to teach this to their young.
Behavior
Skunks are crepuscular and are solitary animals when not breeding, though in the colder parts of their range they may gather in communal dens for warmth. During the day, they shelter in burrows that they dig with their powerful front claws, or in other man-made or natural hollows as the opportunity arises. Both genders occupy overlapping home ranges through the greater part of the year; typically 2 to 4 square kilometres (0.77 to 1.5 sq mi) for females, up to 20 square kilometres (7.7 sq mi) for males.
Skunks are not true hibernators in the winter, but do den up for extended periods of time. However, they remain generally inactive and feed rarely, going through a dormant stage. They often overwinter in a huddle of multiple (as many as twelve) females. Males often den alone. The same winter den is often repeatedly used.
Although they have excellent senses of smell and hearing – vital attributes in a crepuscular omnivore – they have poor vision. They cannot see with any clarity all objects more than about 3 metres (10 ft) away, making them vulnerable to death by road traffic. They are short-lived animals: Fewer than 10% survive for longer than three years.[3]
Reproduction

Skunks typically mate in early spring and are a polygynous species, meaning that (successful) males usually mate with more than one female. Before giving birth (usually in May), the female will excavate a den to house her litter of four to seven kits. They are placental, with a gestation period of about 66 days.[4]
When born, skunk kits are blind, deaf, and covered in a soft layer of fur. About three weeks after birth, their eyes open. The kits are weaned about two months after birth, but generally stay with their mother until they are ready to mate, at about one year of age.
The mother is very protective of her kits and will often spray at any sign of danger. The male plays no part in raising the young and may even kill them.
Anal scent glands
The most notorious feature of skunks is their anal scent glands, which they can use as a defensive weapon. They are similar to, though much more developed than, the glands found in species of the Mustelidae family. Skunks have two glands, one on each side of the anus. These glands produce a mixture of sulfur-containing chemicals such as methyl and butyl thiols traditionally called mercaptans, which have a highly offensive smell that can be described as a combination of the odors of rotten eggs, garlic and burnt rubber. The odor of the fluid is strong enough to ward off bears and other potential attackers and can be difficult to remove from clothing. Muscles located next to the scent glands allow them to spray with a high degree of accuracy, as far as 2 to 5 metres (6.6 to 16 ft). The smell aside, the spray can cause irritation and even temporary blindness and is sufficiently powerful to be detected by a human nose anywhere up to a mile downwind. Their chemical defense, though unusual, is effective, as illustrated by this extract from Charles Darwin's Voyage of the Beagle:
We saw also a couple of Zorrillos, or skunks—odious animals, which are far from uncommon. In general appearance the Zorrillo resembles a polecat, but it is rather larger, and much thicker in proportion. Conscious of its power, it roams by day about the open plain, and fears neither dog nor man. If a dog is urged to the attack, its courage is instantly checked by a few drops of the fetid oil, which brings on violent sickness and running at the nose. Whatever is once polluted by it, is for ever useless. Azara says the smell can be perceived at a league distant; more than once, when entering the harbour of Monte Video, the wind being off shore, we have perceived the odour on board the Beagle. Certain it is, that every animal most willingly makes room for the Zorrillo.[5]
Skunks are reluctant to use this weapon, as they carry just enough of the chemical for five or six uses – about 15 cc – and require some ten days to produce another supply. Their bold black and white coloring however serves to make the skunk's appearance memorable. Where practical, it is to a skunk's advantage simply to warn a threatening creature off without expending scent: black and white warning color aside, threatened skunks will go through an elaborate routine of hisses, foot stamping, and tail-high threat postures before resorting to the spray. Interestingly, skunks usually do not spray other skunks, with the exception of males in the mating season. Though they fight over den space in autumn, they do so with teeth and claws.
The singular musk-spraying ability of the skunk has not escaped the attention of biologists. The names of the family and the most common genus (Mephitidae, Mephitis) mean "stench," and Spilogale putorius means "stinking spotted weasel." The word skunk is a corruption of an Abenaki name for them, segongw or segonku, which means "one who squirts" in the Algonquian language.
Most predatory animals of the Americas, such as wolves, foxes and badgers, seldom attack skunks – presumably out of fear of being sprayed. The exception is the great horned owl – the animal's only serious predator – which, like most birds, has a poor-to-nonexistent sense of smell.
Skunks are common in suburban areas. Frequent encounters with dogs and other domestic animals, and the release of the odor when a skunk is run over, have led to many myths about the removal of the skunk odor. Due to the chemical composition of the skunk spray, most of these household remedies are ineffective, with the exception of a peroxide formula or other remedies that break down the thiols.
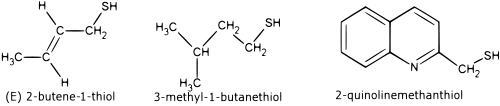
Skunk spray is composed mainly of low molecular weight thiol compounds, namely (E)-2-butene-1-thiol, 3-methyl-1-butanethiol, and 2-quinolinemethanethiol, as well as acetate thioesters of each of these.[6][7] These compounds are detectable by the human nose at concentrations of only 10 parts per billion.[8][9]
Bites
The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recorded 1,494 cases of rabies in skunks in the United States for the year 2006 — about 21.5% of reported cases in all species.[10][11] Skunks trail raccoons as vectors of rabies, although this varies regionally (raccoons dominate along the Atlantic coast and eastern Gulf of Mexico, skunks throughout the Midwest and down to the western Gulf, and in California). Despite this prevalence, all recorded cases of human rabies from 1990–2002 are attributed by the CDC to dogs or bats.
Domestication

The keeping of skunks as pets is legal in only certain U.S. states.[12] Mephitis mephitis, the striped skunk species, is the most social skunk and the one most commonly domesticated. When a skunk is kept as a pet, its scent gland is surgically removed. Typical life spans for domesticated skunks are longer than for wild skunks.
Domesticated skunks can legally be kept as pets in the UK. However, the Animal Welfare Act 2006[13] has made it illegal to remove their scent glands (it is considered to be a cosmetic operation), thus making them impractical as pets. Many owners abandon skunks in the wild when they discover that vets will no longer perform the operation to remove their scent glands.[14]
Classification
Arranged alphabetically.[15]
- Family Mephitidae
- Genus: Conepatus
- Conepatus chinga – Molina's Hog-nosed Skunk
- Conepatus humboldtii – Humboldt's Hog-nosed Skunk
- Conepatus leuconotus – American Hog-nosed Skunk
- Conepatus semistriatus – Striped Hog-nosed Skunk
- Genus: Mephitis
- Mephitis macroura – Hooded Skunk
- Mephitis mephitis – Striped Skunk
- Genus: Mydaus
- Mydaus javanensis – Indonesian or Javan Stink Badger (Teledu)
- Mydaus marchei – Palawan Stink Badger
- Genus: Spilogale
- Spilogale angustifrons – Southern Spotted Skunk
- Spilogale gracilis – Western Spotted Skunk
- Spilogale putorius – Eastern Spotted Skunk
- Spilogale pygmaea – Pygmy Spotted Skunk
- Genus: Conepatus
See also
- Skunk oil
References
- ↑ Don E. Wilson & DeeAnn M. Reeder (2005). Mammal Species of the World. A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0801882210.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Dragoo and Honeycutt; Honeycutt, Rodney L (1997). "Systematics of Mustelid-like Carnvores". Journal of Mammalogy (Journal of Mammalogy, Vol. 78, No. 2) 78 (2): 426–443. doi:10.2307/1382896. http://jstor.org/stable/1382896.
- ↑ http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Mephitis_mephitis.html
- ↑ "Skunks Management Guidelines". UC Davis IPM. http://www.ipm.ucdavis.edu/PMG/PESTNOTES/pn74118.html.
- ↑ Darwin, Charles (1839). Voyage of the Beagle. London, England: Penguin. ISBN 0-14-043268-X. http://www.gutenberg.org/etext/3704. Retrieved June 27, 2006.
- ↑ Wood W. F., Sollers B. G., Dragoo G. A., Dragoo J. W. (2002). "Volatile Components in Defensive Spray of the Hooded Skunk, Mephitis macroura". Journal of Chemical Ecology 28 (9): 1865. doi:10.1023/A:1020573404341.
- ↑ William F. Wood. "Chemistry of Skunk Spray". Dept. of Chemistry, Humboldt State University. http://users.humboldt.edu/wfwood/chemofskunkspray.html. Retrieved July 27, 2010.
- ↑ William F. Wood (1999). "The History of Skunk Defensive Secretion Research". Chem. Educator 4 (2): 44–50. doi:10.1007/s00897990286a. http://chemeducator.org/sbibs/s0004002/spapers/420044ww.pdf.
- ↑ Aldrich, T.B. (1896). "A chemical study of the secretion of the anal glands of Mephitis mephitica (common skunk), with remarks on the physiological properties of this secretion.". J. Exp. Med. 1 (2): 323–340. doi:10.1084/jem.1.2.323. PMID 19866801. PMC 2117909. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2117909/pdf/323.pdf.
- ↑ Blanton J.D., Hanlon C.A., Rupprecht C.E. (2007). "Rabies surveillance in the United States during 2006". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 231 (4): 543. doi:10.2460/javma.231.4.540. PMID 17696853.
- ↑ "Rabies Surveillance US 2006". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. http://www.cdc.gov/rabies/docs/rabies_surveillance_us_2006.pdf.
- ↑ List of states
- ↑ "Animal Welfare Act 2006" (PDF). http://www.opsi.gov.uk/ACTS/acts2006/pdf/ukpga_20060045_en.pdf. Retrieved December 5, 2009.
- ↑ Lesley Tate (August 18, 2008). "Escaped skunk causes a stink". Craven Herald & Pioneer. http://www.cravenherald.co.uk/news/news_index/display.var.2435207.0.escaped_skunk_causes_a_stink.php.
- ↑ Wilson, Don E.; Reeder, DeeAnn M., eds (2005). Mammal Species of the World (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2 vols. (2142 pp.). ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. http://www.bucknell.edu/msw3/browse.asp?id=14001521.
External links
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||