U
|
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Latin alphabet | |||||
| Aa | Bb | Cc | Dd | ||
| Ee | Ff | Gg | Hh | ||
| Ii | Jj | Kk | Ll | Mm | Nn |
| Oo | Pp | Rr | Ss | Tt | |
| Uu | Vv | Ww | Xx | Yy | Zz |
U is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet. Its name in English (![]() /ˈjuː/) is pronounced u;[1] the plural is ues, though this is rare.[2]
/ˈjuː/) is pronounced u;[1] the plural is ues, though this is rare.[2]
Contents |
History
The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details.
During the late Middle Ages, two forms of "v" developed, which were both used for its ancestor u and modern v. The pointed form "v" was written at the beginning of a word, while a rounded form "u" was used in the middle or end, regardless of sound. So whereas valor and excuse appeared as in modern printing, "have" and "upon" were printed haue and vpon. The first distinction between the letters "u" and "v" is recorded in a Gothic alphabet from 1386, where "v" preceded "u". By the mid-1500s, the "v" form was used to represent the consonant and "u" the vowel sound, giving us the modern letter "u". Capital "U" was not accepted as a distinct letter until many years later.[3]
Usage
U is commonly associated with the close back rounded vowel [u] found in many languages. This form is colloquially termed the "long u" in English.
In English there is also a "short U", which in most dialects of English is an open-mid back unrounded vowel [ʌ].
Codes for computing
| NATO phonetic | Morse code |
| Uniform |
 |
 |
 |
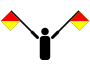
| Signal flag | Flag semaphore | Braille |
In Unicode the capital U is codepoint U+0055 and the lowercase u is U+0075.
The ASCII code for capital U is 85 and for lowercase u is 117; or in binary 01010101 and 01110101, correspondingly.
The EBCDIC code for capital U is 228 and for lowercase u is 164.
The numeric character references in HTML and XML are "U" and "u" for upper and lower case respectively.
See also
|
References
- ↑ "U" Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1989); Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged (1993)
- ↑ Brown & Kiddle (1870) The institutes of English grammar, p 19.
Ues is the plural of the name of the letter; the plural of the letter itself is U's, Us, u's, or us. - ↑ Pflughaupt, Laurent (2008). Letter by Letter: An Alphabetical Miscellany. trans. Gregory Bruhn. Princeton Architectural Press. pp. 123–124. ISBN 9781568987378. http://books.google.com/books?id=63Qnbt2CMiMC&pg=PA124. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
| Aa | Bb | Cc | Dd | Ee | Ff | Gg | Hh | Ii | Jj | Kk | Ll | Mm | Nn | Oo | Pp | Rr | Ss | Tt | Uu | Vv | Ww | Xx | Yy | Zz | |
|
Letter U with diacritics
history • palaeography • derivations • diacritics • punctuation • numerals • Unicode • list of letters • ISO/IEC 646 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||