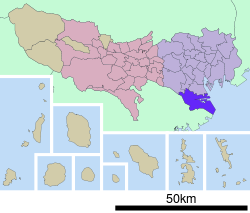
Ōta, Tokyo
| Ōta 大田 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| — Special ward — | |||
| 大田区 · Ōta City | |||
 |
|||
|
|||
 |
|||
 Ōta
|
|||
| Coordinates: | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Kantō | ||
| Prefecture | Tokyo | ||
| Government | |||
| - Mayor | Tadayoshi Matsubara | ||
| Area | |||
| - Total | 59.46 km2 (23 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2008) | |||
| - Total | 677,341 | ||
| - Density | 11,360/km2 (29,422.3/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| Website | Ōta | ||

Ōta (大田区 Ōta-ku) is one of the 23 special wards of Tokyo, Japan. As of 2008, the ward has an estimated population of 677,341 and a density of 11,360 persons per km². The total area is 59.46 km², the largest of the 23 special wards.
Ōta's hub is situated around the two Kamata Stations (JR Kamata and Keikyu Kamata) where the Ōta Ward Office and central Post Office can be found.
Contents |
History
The ward was founded on March 15, 1947 merging the old wards of Ōmori and Kamata.
Tokyo International Airport (Haneda Airport, HND), now the main domestic airport for the Greater Tokyo Area, began with the establishment of Haneda Airfield in 1931 in the town of Haneda, Ebara District of Tokyo Prefecture. In 1945, it became Haneda Army Air Base under the control of the United States Army. In the same year, the Occupation ordered the expansion of the airport, evicting people from the surroundings on 48 hours' notice. With the end of the occupation, the Americans returned part of the facility to Japanese control in 1952, completing the return in 1958. Haneda Airport in Ōta was the major international airport for Tokyo, and handled traffic for the Tokyo Olympics.
Ōta has a sister city relationship with Salem, Massachusetts. The discovery of a shell mound in Ōmori, one of the forerunners of Ōta, by Edward S. Morse, director of the museum in Salem, occasioned the tie. Ōta has a friendship link with Chaoyang District, Beijing, People's Republic of China.
Politics and government
The city is run by a city assembly of 50 elected members. The current mayor is Tadayoshi Matsubara.
- Ōta local election, 2007
Geography
The southernmost of the 23 special wards, Ōta borders the special wards of Shinagawa, Meguro and Setagaya stand to the north, and Kōtō lies to the east. Across the Tama River in Kanagawa Prefecture is the city of Kawasaki, forming the boundaries to the south and west.
Landmarks
- Ikegami Honmonji, a Buddhist temple founded by Nichiren in the 13th century
- Ōmori Shell Mound site
- Senzoku Pond, where Nichiren is said to have washed his feet. The grave of Katsu Kaishu is nearby.
Transportation
Air
- Tokyo International Airport
Rail
- JR East Keihin-Tōhoku Line: Ōmori, Kamata Stations
- Keikyū
- Main Line: Heiwajima, Ōmorimachi, Ume Yashiki, Keikyū-Kamata, Zoshiki, Rokugo-dote Stations
- Airport Line: Keikyū-Kamata, Kojiya, Otorii, Anamori Inari, Tenkubashi, Haneda Kuko Stations
- Tokyu Corporation
- Tōkyū Tōyoko Line: Den-en-chōfu, Tamagawa Stations
- Tōkyū Ikegami Line: ten stations
- Tōkyū Tamagawa Line: Tamagawa, Numabe, Unoki, Shimo-Maruko, Musashi-Nitta, Yaguchi no Watashi, Kamata Stations (entire line)
- Tōkyū Ōimachi Line: Kita-Senzoku Station
- Tokyo Monorail: Ryutsu Center, Showajima, Seibijo, Tenkubashi, Shin Seibijo, Haneda Kuko Dai 1 Biru, Haneda Kuko Dai 2 Biru Stations
- Toei Asakusa Line: Magome, Nishi-Magome Stations
Highway
- Shuto Expressway
- No. 1 Haneda Route (Edobashi JCT - Iriya)
- B Bayshore Route (Namiki - Kawasaki-ukishima JCT)
- National highways
- Route 1
- Route 15
- etc.
Economy
.jpg)

The following companies have their headquarters in Ōta.
- Air Japan and Air Nippon Network (subsidiaries of All Nippon Airways, at Tokyo International Airport)[1][2]
- Alps Electric Corporation
- Canon[3]
- Gakken Co., Ltd., school textbook publisher
- Ikegami, manufacturer of broadcast equipment
- Namco, game maker[4]
- Sega[5]
- Skymark Airlines, at Tokyo International Airport[6]
- Toyoko Inn, in the Kamata district of Ōta[7][8]
Former operations
Prior to the merger with Japan Airlines,[9] Japan Air System had its headquarters by Tokyo International Airport in Ōta.[10] In 2000 All Nippon Airways was headquartered by Tokyo International Airport in Ōta.[11] In 2002 Air Nippon was headquartered on the 5th floor of the Utility Center Building (ユーティリティセンタービル Yūtiriti Sentā Biru) by Tokyo International Airport in Ōta.[12] Before its dissolution, Galaxy Airlines was headquartered in the ARC Building on the airport grounds.[13]
Education
Colleges and universities
- Aeronautical Safety College
- Toho University Omori Campus
- Tokyo Institute of Technology: the Ōokayama Campus straddles the boundary with Meguro
Primary and secondary schools
Ōta operates public elementary and junior high schools. Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education operates public high schools.
Public high schools in Ōta include:
- Den Enchofu High School [1]
- Kamata High School [2]
- Mihara High School [3]
- Omori High School [4]
- Ota Shingaku High School [5]
- Rokugoh Technical High School [6]
- Tsubasa High School [7]
- Yukigaya High School [8]
Private high schools include Tokyo High School.
Libraries
The city operates several libraries, including:[14]
- Ota Library (the main library)
- Hamatake Library
- Haneda Library
- Ikegami Library
- Kamata Library
- Kamata Ekimae Library
- Kugahara Library
- Magome Library
- Omori East Library
- Omori South Library
- Omori West Library
- Rokugo Library
- Senzokuike Library
- Shimomaruko Library
- Tamagawa Library
See also
References
- ↑ "Company Guide." Air Japan. Retrieved on May 19, 2009.
- ↑ "会社概要." Air Nippon Network. Retrieved on May 20, 2009.
- ↑ "Corporate Profile." Canon. Retrieved on January 13, 2009.
- ↑ "Company Profile." Namco. Retrieved on March 16, 2010.
- ↑ "Corporate." Sega. Retrieved on January 13, 2009.
- ↑ "About Us." Skymark Airlines. Retrieved on May 7, 2009.
- ↑ "Company Profile." Toyoko Inn. Retrieved on January 13, 2009.
- ↑ "Company History." Toyoko Inn. Retrieved on January 13, 2009.
- ↑ "A tale of many tails: the merger of Japan Airlines and Japan Air System makes perfect business sense, but commonality of equipment is a different matter." Air Transport World. April 1, 2003. Retrieved on May 19, 2009.
- ↑ "COMPANY INFORMATION." Japan Air System. Retrieved on January 13, 2009.
- ↑ "Corporate Information." All Nippon Airways. April 8, 2000. Retrieved on May 19, 2009.
- ↑ "会社案内." Air Nippon. February 7, 2002. Retrieved on May 20, 2009.
- ↑ "Head Office & Regional Office Information." Galaxy Airlines. Retrieved on May 20, 2009.
- ↑ "Libraries." City of Ota. Retrieved on January 13, 2009.
External links
- Ōta official website in Japanese
- The Toho University web site in English
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
