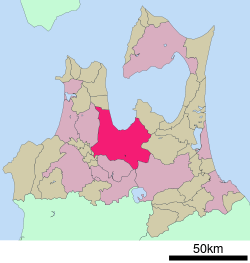
Aomori, Aomori
| Aomori 青森市 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| — Core city — | |||
 |
|||
|
|||
 |
|||
 Aomori
|
|||
| Coordinates: | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Tōhoku | ||
| Prefecture | Aomori Prefecture | ||
| Government | |||
| - Mayor | Hiroshi Shikanai | ||
| Area | |||
| - Total | 824.52 km2 (318.3 sq mi) | ||
| Population (November 1, 2009) | |||
| - Total | 302,068 | ||
| - Density | 366/km2 (947.9/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| City Symbols | |||
| - Tree | Maries' Fir | ||
| - Flower | Rosa rugosa | ||
| - Bird | Ural Owl | ||
| - Insect | Firefly | ||
| Phone number | 017-734-1111 | ||
| Address | 1-22-5 Chūō, Aomori-shi, Aomori-ken 030-8555 |
||
| Website | City of Aomori | ||
Aomori (青森市 Aomori-shi) is the capital city of Aomori Prefecture, in the northern Tōhoku region of Japan. As of 2009, the city had an estimated population of 302,068 and a density of 366 persons per km². Its total area was 824.52 km².
Contents |
History
Aomori literally means blue (or green) forest. The name is generally considered to refer to a small forest on a hill which existed near the town. This forest was often used by fishermen as a landmark. A different theory suggests the name might have been derived from the Ainu language.

The area has been settled extensively since prehistoric times, and numerous Jōmon period sites have been found by archaeologists, the most famous being the Sannai-Maruyama Ruins located just southwest of the city center dating to 5500-4000 BC, and the Komakino site slightly further south dating to around 4000 BC. The large scale of these settlements revolutionized theories on Jōmon period civilization. During the Heian period, the area was part of the holdings of the Northern Fujiwara clan, but remained inhabited by the Emishi people well into the historic period. After the fall of the Northern Fujiwara in the Kamakura period, the territory was part of the domain assigned to the Nambu clan, and into the Sengoku period, it came under the control of the rival Tsugaru clan, whose main castle was located in Namioka. After the start of the Edo period, Aomori was a minor port settlement for Hirosaki Domain called Utō (善知鳥村 Utō-mura). The town was rebuilt in 1626 by Moriyama Yashichirō, under orders of the daimyō, Tsugaru Nobuhira and renamed Aomori, but the name did not come into common use until after 1783.
After the Meiji Restoration the various domains were abolished and replaced with prefectures, a total of six in the territory of modern Aomori prefecture. These were merged into the short-lived Hirosaki Prefecture in July 1871. However, due to the historic enmity between the former Tsugaru territories in the west and the former Nambu territories in the east, the prefectural capital relocated from Hirosaki to the more centrally-located Aomori immediately after the merger and the prefecture was renamed Aomori prefecture on September 23, 1871. However, Aomori was not given town status within Higashitsugaru District until April 1, 1889, and was not designated a city until April 1, 1898.
The Hokkaidō Colonization Office began operations of a ferry service from Aomori to Hakodate in Hokkaidō from 1872. In September 1891, Aomori was connected with Tokyo by rail with the opening of the Tōhoku Main Line. The Ōu Main Line running along the Sea of Japan coast opened in December 1894. The development of modern Aomori was primarily due to its prefectural capital status and the singular importance as the terminus of these rail lines and the Seikan Ferry, which officially opened in 1908. The 8th Division of the Imperial Japanese Army were stationed in Aomori from 1896. In the winter of 1902, 199 of 210 soldiers on a military cold-weather readiness exercise perished while attempting to cross the Hakkōda Mountains from Aomori to Hirosaki in what was later called the Hakkōda Mountains incident.
Much of the town burned down in a large fire on May 3, 1910. The port facilities were expanded in 1924, and the city received its first bus services in 1926. Japan Air Transport began scheduled air services from 1937.
Towards the final stages of World War II, on July 28, 1945 Aomori was subject to an air raid as part of the strategic bombing campaign waged by the United States of America against military and civilian targets and population centers during the Japan home islands campaign. The July 28 bombing claimed 1,767 lives and destroyed 88% of the city.
In the post war period, Aomori rebuilt as the local political and commercial center. The Tsugaru Line railway opened in 1951, and Aomori Airport in 1964. The city was connected to Tokyo by highway in 1979 with the opening of the Tōhoku Expressway. Aomori’s landmark pyramidical Aomori Prefectural Tourist Center opened in 1986. On October 1, 2002, Aomori was proclaimed a core city with increased autonomy from the central government.
On April 1, 2005, Aomori annexed the neighboring town of Namioka.
Geography
Aomori is located in central Aomori Prefecture, between the southern end of Mutsu Bay, which it faces to the north and the Hakkōda Mountains to the south.
Neighbouring municipalities
- Kuroishi, Goshogawara, Towada, Hirakawa
- Kitatsugaru District – Itayanagi
- Minamitsugaru District – Fujisaki
- Higashitsugaru District – Hiranai, Yomogita
- Kamikita District – Shichinohe
Climate
Aomori has a cold maritime climate with short cool summers, and very severe winters. The city and its surrounding area are renowned for its heavy snowfall, which is said to be the heaviest among all Japanese cities. In February 1945 the city recorded a maximum snow cover of 209 cm, with a temperature of minus 24.7 deg C recorded in February 1931. In contrast, Sapporo's heaviest snowfall occurred in 1939, and that was only 164 cm. The particularly heavy snow is caused by several winds that collide around the city. This makes the air rise and cool, resulting in rapid and thick cloud formation and precipitation.
In summer, a cool wind called Yamase frequently blows from the east, which sometimes results in extremely cool weather and poor harvests. Additionally, thick fogs are often observed in mountainous areas in the summer. Due to this fog, flights to Aomori Airport are often canceled.
| Climate data for Aomori | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Source: 気象庁[1] | |||||||||||||
Economy
Aomori serves as the regional commercial center for central Aomori prefecture. Agriculture and commercial fishing form only 4% of the city economy, with manufacturing forming 16.2% and the service sector forming 78.2%.
Transportation
Airports
- Aomori Airport - (established in 1964 with international flights from 1995) is about a 30 minute drive from the city, with bus service available. There are flights to Tokyo, Osaka, Nagoya Sapporo, and Seoul, South Korea.
Railways
- East Japan Railway Company - Tōhoku Main Line
- Aomori, Higashi-Aomori, Koyanagi, Yadamae, Nonai, Asamushi-Onsen
- East Japan Railway Company - Ōu Main Line
- Aomori – Shin-Aomori, Tsugaru-Shinjō, Tsurugasaka, Daishaka, Namioka
- East Japan Railway Company - Tsugaru Line
- Aomori, Aburakawa, Tsugaru-Miyata, Okunai, Hidariseki, Ushirogata, Nakasawa
- Hokkaidō Railway Company - Tsugaru Kaikyō Line
Highways
- Tōhoku Expressway
- Aomori Expressway
- National Route 4 (Japan)
- Japan National Route 7
- Japan National Route 101
- Japan National Route 103
- Japan National Route 280
- Japan National Route 394

Seaports
The Seikan Ferry operates ferries to Hakodate. It takes about four hours to go by ferry from Aomori to Hakodate. The ferry was initially run by the Ministry of Railroads but was later taken over by Japanese National Railways. From 1908 to 1988 the ferry served as the primary transport between the island of Honshū and the northern island of Hokkaidō. In March 1988, the Seikan Tunnel opened up, travelling under the Tsugaru Strait, this quickly replaced the slow-moving ferry as the primary transportation between the two islands.
Sightseeing
Aomori Nebuta is a famous festival performed from August 2 to August 7 every year. Besides this, major attractions of Aomori include ruins, museums, and mountains. The Hakkōda Mountains have good locations for trekking with hot spas (onsen), such as Sukayu Onsen.
- Asamushi Onsen
- Munakata Shiko Memorial Museum of Art
- Aomori City Forestry Museum
- Aomori Prefectural Folk Museum
- Aomori City History and Folk Arts Museum
- Nebuta-no-sato Museum
- Sannai-Maruyama Ruins
- Asamushi Aquarium
Sport
Aomori has hosted several international curling events, two in 2003 (including the Asian Winter Games), and the local women's "Team Aomori" was selected to represent Japan at the 2006 Winter Olympics in Turin, Italy [1] and at the 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver, Canada. From March 17 - 25, 2007, Aomori hosted the World Women's Curling Championships[2].
Education
Aomori is the only prefectural capital in Japan which has no national university, instead, nearby Hirosaki became the site for the prefecture's highest educational facility.
Universities and colleges
High schools
|
Junior high schools
|
Notables from Aomori
- Noriko Awaya - singer
- Takaharu Furukawa - archer
- Takanori Hatakeyama - professional boxer
- Yuji Hayami- science-fiction writer
- Shigeru Izumiya – entertainer
- Yaho Kitabatake - children's fiction writer
- Ichiro Kojima - photographer
- Keizo Miura - skier
- Yuichiro Miura - skier
- Shiko Munakata - woodblock artist
- Hitoshi Saito - judoka
- Kyoichi Sawada - photographer
- Akimitsu Takagi - crime fiction writer
- Bushuyama Takashi - sumo wrestler
- Kiyoshi Tanabe - professional boxer
- Shūji Terayama - modern artist
- Takanosato Toshihide sumo wrestler
- Akiko Yano - singer–songwriter
- Daisuke Matsuzaka - Baseball player
Sister city relations
 - Hakodate, Hokkaidō – since 1989
- Hakodate, Hokkaidō – since 1989 - Kecskemét, Bács-Kiskun County, Hungary – since 1994
- Kecskemét, Bács-Kiskun County, Hungary – since 1994 - Pyeongtaek, Gyeonggi-do, South Korea – since 1995
- Pyeongtaek, Gyeonggi-do, South Korea – since 1995 – Dairen, Liaoning, China – since 2004
– Dairen, Liaoning, China – since 2004
References
External links
- Official website in Japanese
- Official website in English
- The 5th Winter Asian Games AOMORI 2003
- Sannai-Maruyama Site official website
- Pictures of Aomori, Japan ( Aomori city, Aomori Bay Bridge )
- Photos, report and advice about Nebuta Matsuri, Aomori's famous festival (one of the most famous festivals in Japan)
|
||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
