Berlin Schönefeld Airport
| Berlin-Schönefeld Airport Flughafen Berlin-Schönefeld |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||
 |
|||
IATA: SXF – ICAO: EDDB,  Berlin Schönefeld Airport
|
|||
| Summary | |||
| Airport type | Public | ||
| Operator | Berlin Airports | ||
| Serves | Berlin | ||
| Location | Schönefeld, Brandenburg | ||
| Hub for |
|
||
| Elevation AMSL | 157 ft / 48 m | ||
| Website | |||
| Runways | |||
| Direction | Length | Surface | |
| m | ft | ||
| 07/25 | 3,000 | 9,843 | Asphalt |
| Statistics (2008) | |||
| Passengers | 6,600,000 | ||
| Sources: German AIP at EUROCONTROL[1] | |||
Berlin-Schönefeld Airport (Flughafen Berlin-Schönefeld) (IATA: SXF, ICAO: EDDB) is an international airport located near the town of Schönefeld in Brandenburg, directly at the southern border of Berlin and 18 km (11 mi) southeast[1] of the city centre. Schönefeld was the major civil airport of East Germany (GDR), and the only airport serving East Berlin. Today, it is the smaller of the two Berlin airports.
Schönefeld Airport is situated outside the city proper, unlike Berlin Tegel Airport. Noise pollution is, therefore, less of an issue at Schönefeld. This is the main reason that the airport will be transformed into Berlin-Brandenburg International Airport by 2012.[2]
Schönefeld Airport saw a major increase in passenger numbers over the recent years, which was caused by the opening a base for EasyJet and Germanwings. In 2008, the airport served 6.6 million passengers.
Contents |
History

Berlin-Schönefeld airport was opened on 15 October 1934 to accommodate the Henschel aircraft plant. By the end of the Second World War, over 14,000 aircraft had been built. On 22 April 1945, the airport was occupied by Soviet troops, and the aircraft construction facilities were either dismantled or blown up. By late 1947, the airport's rail link had been repaired and agricultural machinery was built and repaired on the site. In 1946, the Soviet Air Forces moved from Johannisthal Air Field to Schönefeld, including the civil airline Aeroflot. In 1947, the Soviet Military Administration in Germany approved the construction of a civilian airport at the site. Between 1947 and 1990, Schönefeld airport was renamed on several occasions and finally became the main airport of the GDR (Zentralflughafen).
A stipulation of the Four Power Agreement following World War II was a total ban on German carriers' participation in air transport to Berlin, where access was restricted to US, British, French and Soviet airlines. Since Berlin-Schönefeld airport was located outside of the city boundaries of Berlin, this restriction did not apply. Thus, German aircraft of the East German flag carrier Interflug, could use Schönefeld airport, whilst West German Lufthansa was denied access to Berlin-Tegel or Tempelhof airports.
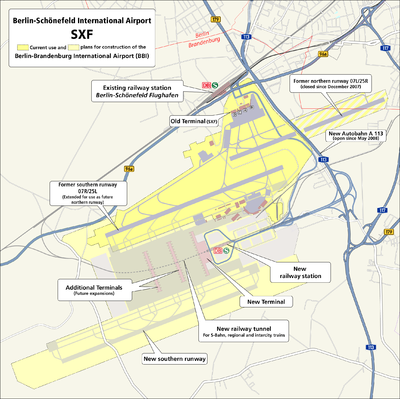
Following the German reunification in 1990, operating three separate airports became increasingly prohibitive, leading the Berlin City Council to pursue a single airport that would be more efficient and would decrease the amount of aircraft noise from the airport within the city. Therefore, it was decided to erect Berlin-Brandenburg International Airport at the current site of Schönefeld Airport, which is scheduled for opening on 30 October 2011. The new airport will share only one runway with the existing one. Most of the old airport, including the terminal and apron areas, is intended to undergo a complete urban redevelopment following its closure.
Terminals, airlines and destinations

Schönefeld Airport has four terminals (A, B, C, D)[3], though this only applies for check-in, as there is only one jointly used airside concourse.
- The main building is the original part of the airport. It houses check-in for Terminals A and B. Terminal A features check-in counters A01-A18, with the largest user being Ryanair. Terminal B, in a side wing, was originally reserved for transit passengers to and from West Berlin, who took advantage of cheaper air fares and package tours arranged by an East German travel agency. Nowadays, it is used exclusively by easyJet (check-in counters B20-B29), which gave it the name easyJet-Terminal.
- Terminal C was originally built to accommodate flights to Israel. It was reconfigured in 2008 and now handles sightseeing trips and flights in connection with special events.[4] Some flights are operated on a vintage raisin bomber DC-3.
- Terminal D was opened in December 2005 due to rapidly growing passenger numbers. Being nearly identical to Terminal C at Tegel Airport, it features check-in counters D40-D57, which are mainly used by Condor and Germanwings.
The airside consists of three jet bridges as well as several walk-boarding aircraft stands located at Pier 3a, an extension that was opened in 2005.
Schönefeld Airport is served by the following scheduled airlines:[5]
| Airlines | Destinations | Check-in |
|---|---|---|
| Aer Lingus | Dublin | D |
| Aeroflot | Moscow-Sheremetyevo | A |
| Air Algérie | Algiers [seasonal] | A |
| Air Berlin | Antalya [seasonal], Djerba [seasonal], Hurghada [seasonal], Monastir [seasonal], Palma de Mallorca | A |
| Air VIA | Burgas [seasonal], Varna [seasonal] | D |
| Belavia | Minsk | A |
| Bremenfly | Tel Aviv | D |
| Bulgarian Air Charter | Burgas [seasonal], Varna [seasonal] | D |
| Condor | Agadir, Antalya [seasonal], Corfu [seasonal], Dalaman [seasonal], Fuerteventura, Heraklion [seasonal], Hurghada, Kos [seasonal], Larnaca, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Palma de Mallorca [seasonal], Sharm el-Sheikh, Tenerife-South | D |
| Dubrovnik Airline | Dubrovnik [seasonal] | D |
| EasyJet | Basel/Mulhouse, Liverpool, London-Gatwick, London-Luton | A |
| EasyJet | Athens, Barcelona, Bristol, Brussels, Budapest, Cagliari, Copenhagen, Dubrovnik, Geneva, Glasgow-International, Heraklion, Ibiza, Lisbon, Madrid, Málaga, Milan-Malpensa, Naples, Nice, Olbia, Palma de Mallorca, Paris-Orly, Pisa, Rome-Ciampino, Thessaloniki, Venice-Marco Polo | B |
| EgyptAir | Cairo | A |
| El Al | Tel Aviv | D |
| Eurocypria Airlines | Larnaca | A |
| Germanwings | Bastia, Bucharest-Băneasa, Cologne/Bonn, Dubrovnik, Heraklion, Istanbul-Sabiha Gökçen [resumes 3 July], Izmir, Moscow-Vnukovo, Munich, Pristina, Split, Stockholm-Arlanda, Stuttgart, Zadar, Zagreb, Zweibrücken | D |
| Hamburg International | Olbia [seasonal], Palma de Mallorca [seasonal] | A |
| Iceland Express | Reykjavik-Keflavik | A |
| Icelandair | Reykjavik-Keflavik [seasonal] | A |
| Israir Airlines | Tel Aviv | D |
| Middle East Airlines | Beirut [seasonal] | A |
| Norwegian Air Shuttle | Bergen, Oslo-Gardermoen, Oslo-Rygge, Stavanger | D |
| Nouvelair | Djerba, Monastir [both seasonal] | A |
| Pegasus Airlines | Ankara, Antalya, Istanbul-Sabiha Gökçen | A |
| Rossiya | St Petersburg | A |
| Ryanair | Bremen, Dublin, East Midlands, Edinburgh, Hahn, Kaunas, London-Stansted, Málaga, Milan-Orio al Serio, Oslo-Rygge, Stockholm-Skavsta, Weeze | A |
| Sky Airlines | Antalya | A |
| SunExpress | Antalya, Bodrum [seasonal], Istanbul-Sabiha Gökçen, Izmir | A |
| Syrian Air | Aleppo, Damascus, Vienna | A |
| Tunisair | Djerba, Monastir, Tunis | A |
| Turkish Airlines | Istanbul-Sabiha Gökçen | A |
Cargo airlines
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| FedEx Feeder operated by Air Contractors | Paris-Charles de Gaulle |
| West Air Sweden | Cologne/Bonn |
Public transport
- Schönefeld Airport is served by Berlin Schönefeld Flughafen railway station, a short walking distance away from the airport terminal. Berlin S-Bahn lines S9 and S45 each run every twenty minutes. The RE AirportExpress train is the only direct link to the city centre of Berlin. It runs every 30 minutes, and stops at the most important stations of Berlin, including Berlin Ostbahnhof, Alexanderplatz, Friedrichstrasse, Central Station (after 30 minutes), and Zoologischer Garten railway station.
- The airport is linked by local BVG bus lines 162 (towards Adlershof) and 171 (towards Neukölln)[6]. At night, the underground replacement N7 bus is available. A dedicated DB express bus runs to Berlin Südkreuz.[7]
- Taxis take around 30 minutes to get to the city centre.
Accidents and incidents
- On 14 August 1972, an Ilyushin Il-62 aircraft of Interflug (registration DM-SEA) enroute to Burgas Airport crashed shortly after take-off from Schönefeld Airport near Königs Wusterhausen, killing all 156 passenger and crew onboard. See Interflug Flight DM-SEA [sic].
- On 22 November 1977, a Tupolev Tu-134 aircraft of Interflug (registration DM-SCM) crashed upon landing at Schönefeld Airport due to a falsely configured autopilot. There were no fatalities under the 74 passenger and crew, but the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.[8]
- On 19 August 1978, a LOT flight from Gdansk Airport to Schönefeld (carried out on a Tupolev Tu-134, registration SP-LGC) was hijacked and forced to land at Tempelhof Airport in West Berlin, thus having been used as a means for escaping the Eastern Bloc. In these cases, perpetrators were usually not charged by Western authorities.[9]
- On 12 December 1986, an Aeroflot Tupolev Tu-134 (registration CCCP-65795) coming from Minsk Airport crashed in Berlin-Bohnsdorf on its approach towards Schönefeld airport, after having attempted to land on a runway that was temporary blocked for construction work, killing 72 of the 82 passengers and crew onboard. [10]
- On 17 July 1989, an Ilyushin Il-62 aircraft of Interflug (registration DDR-SEW) bound for Moscow crashed shortly after take-off into a field near the airport and caught fire. 21 people onboard as well as one person on the ground were killed. The East German authorities feared an act of sabotage due to the anniversary of the 17 June 1953, which lead to a delayed aid for injured people. West German rescuers offering help were denied access to the scene. The cause for the accident was later given as a jammed rudder due to a construction failure.[11]
- On 28 March 2000, a Boeing 737-300 of Germania (registration D-AGES) operating a charter flight on behalf of LTU from Tenerife South Airport to Berlin-Schönefeld was the subject of an attempted hijack in mid-flight. A passenger forced his way into the cockpit, where he attacked the pilot, leading to a sudden loss of altitude. The perpetrator was restrained and the flight continued to Berlin.[12]
- On 19 June 2010, Douglas DC-3 D-CXXX of Berlin Air Services crashed shortly after take off on a local sightseeing flight.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 EAD Basic
- ↑ The future lies in Schoenefeld
- ↑ Schönefeld Airport layout
- ↑ Event and Show Terminal C
- ↑ Schönefeld Airport timetable. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
- ↑ Berlin bus lines. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
- ↑ Express bus schedule form Schönefeld Airport to Südkreuz. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
- ↑ Interflug accident of 1977 at the Aircraft Accident Database. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
- ↑ LOT highjacking at the Aircraft Accident Database. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
- ↑ Aeroflot accident of 1986 at the Aviation Accident Database. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
- ↑ Interflug accident of 1989 at the Aviation Accident Database. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
- ↑ Germania attempted highjacking at the Aircraft Accident Database. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
External links
- Berlin Airports website
- Berlin Brandenburg Homepage
- local public transportation map (PDF)
- Current weather for EDDB at NOAA/NWS
- Accident history for SXF at Aviation Safety Network
|
|||||