Indo-Pakistani War of 1947
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Indo-Pakistani War of 1947, sometimes known as the First Kashmir War, was fought between India and Pakistan over the region of Kashmir from 1947 to 1948. It was the first of four wars fought between the two newly independent nations. The result of the war still affects the geopolitics of both the countries.
The war was fought within the borders of the former princely state of Kashmir and Jammu by Indian Army, paramilitary and the erstwhile princely state forces opposed by Pakistan Army, paramilitary and local militias from the NWFP. The princely state forces were unprepared for the initial assault of the Pakistani forces, having been deployed thinly on the borders of the princely state for purposes of maintaining border security and deterring militant activity.[6]:19 The state defenses quickly collapsed in the face of the assault, some individuals and units joining the tribal forces. The Pakistani forces referred to themselves as the Azad Kashmir forces (AZK forces), Azad in Urdu meaning liberated or free.
The initial successes by AZK forces were not vigorously pressed, giving an opportunity for India to airlift its forces into Kashmir after the state had acceded to India.[7] With Indian reinforcements opposing AZK forces, the offensive ran out of steam towards the end of 1947, except in the High Himalayas sector where AZK forces made substantial progress until they were turned back at the outskirts of Leh in late 1948. Throughout 1948 many small-scale battles were fought, but none gave a strategic advantage to either side. The Indian Army gradually captured a large area in Rajouri and Poonch and ejected Pakistanis from the Indus valley till Kargil, securing the Dras valley and the Zojila pass. The fronts gradually solidified along what would became known as the Line of Control. A formal cease-fire was declared at 2359 hrs on ni of 1/2 January 1949.[6]:379
Background
Prior to 1815 the area now known as "Jammu and Kashmir" comprised 22 small independent states (16 Hindu and 6 Muhammadan) [8] carved out of territories controlled by the Afghanistan Amir (King) combined with those of local small rulers. These were collectively referred to as the "Panjab Hill States". These small states, ruled by Rajput kings, were vassals of the Mughal Empire since 1757. Following the decline of the Mughals, the hill States fell one by one under the dominance of the Sikhs under Ranjit Singh, who merged them into into a single state to be called the State of Jammu.
The First Anglo-Sikh War (1845–46) was fought between the Sikh Empire, which asserted sovereignty over Kashmir, and the East India Company. In the Treaty of Lahore in 1846, the Sikhs were made to surrender the valuable region (the Jullundur Doab) between the Beas River and Sutlej River and required to pay an indemnity of 1.2 million rupees. Because they could not readily raise this sum, the East India Company allowed the Dogra ruler Gulab Singh to acquire Kashmir from the Sikh kingdom in exchange for making a payment of 750,000 rupees to the East India Company. Gulab Singh became the first Maharaja of the newly formed princely state of Jammu and Kashmir,[9] founding a dynasty, that was to rule the state, the second-largest principality during the British Raj, until India gained its independence in 1947.
Partition of India
Before and after the withdrawal of the British from India in 1947, the princely state of Kashmir and Jammu came under pressure from both India and Pakistan to agree to become part of one of the newly independent countries. According to the instruments of accession relating to the Partition of India, the rulers of princely states were to be given the choice of either acceding to India or Pakistan, or remaining independent. The Maharaja of Kashmir, Hari Singh chose the latter and tried to avoid accession to either country. When British forces ceded responsibility for security to the two dominions, Muslim troops rebelled in the some state force units and alongwith Pashtun tribals from the North West Frontier Province (NWFP), invaded the state, thereby triggering the war.
Fearing that his forces would be unable to withstand the assault, the Maharaja asked for Indian military assistance. India set a condition that Kashmir must accede to India for it to receive assistance. Whereupon the Government of India recognized the accession of the erstwhile princely state to India, and was considered the new Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir, Indian troops were sent to the state to defend it against the Pakistani forces. The legitimacy of this accession is still disputed.
Pakistan was of the view that the Maharaja of Kashmir had no right to call in the Indian Army, because it held that the Maharaja of Kashmir was not a heredity ruler, that he was merely a British appointee. There had been no such position as the "Maharaja of Kashmir" prior to British rule. Hence Pakistan decided to take action, but the Army Chief of Pakistan General Douglas Gracey did not send troops to the Kashmir front and refused to obey the order to do so given by Muhammad Ali Jinnah, Governor-General of Pakistan. Gracey's justified his insubordination by arguing that Indian forces occupying Kashmir represented the British Crown and hence he could not engage in a military encounter with Indian forces. Pakistan finally did manage to send troops to Kashmir but by then the Indian forces had taken control of approximately two thirds of the former principalty. The Gilgit and Baltistan territories were secured for Pakistan by the Gilgit Scouts and the forces of the state of Chitral, another princely state that had acceded to Pakistan.
Operation Gulmarg
The objective of the tribal invasion was to capture control of the Kashmir valley including its principal city, Srinagar, the summer capital of the state (Jammu being the winter capital). The entire was codenamed Operation Gulmarg. Maj Gen Akbar Khan of the Pakistan Army, codename "Jebel Tariq", was made the commander.[6]:18
Deputy Commissioners and Political Agents invited each tribe in the North West Frontier Province to form "lashkars" of upto a thousand men each for invading Jammu and Kashmir for plunder,[6]:18 thereby reversing decades of British policy of restricting tribals to the east of the Durand Line.[7]:32-33 The lashkars were formed at Bannu, Wana, Thal, Kohat and Peshawar and Nowshera where they were armed by the local brigade commanders from army stocks. Two regular army officers, and some soldiers disguised as tribals, were provided to each lashkar as also deserters from State forces as guides. The lashkars were to concentrate at a segregated area near Abbottabad where they would be briefed and dispersed for the various missions.[6]:18
The overall plan for the capture of Jammu and Kashmir was as follows:-
- Ten lashkars would advance along the axis Domel - Baramulla - Srinagar, capture the seat of govt and announce Pakistani rule or accession of the state to Pakistan by a puppet govt. The forces would capture the Srinagar airfield and push southward to secure the Banihal Pass to cut of possible ingress from India.
- Two lashkars would support the main offensive by advancing through the Haji Pir Pass and outflanking the defences from the south while another two laskars did the same from the North through the Nastachhun pass.
- Another force of ten lashkars would infiltrate into Jammu district from Kotli, Mirpur and Sialkot to capture Poonch, Rajauri and expand eastward towards Jammu.
- In consonance with Operation Gulmarg, Pakistani forces comprising regular troops from Gilgit Scouts, tribal lashkars and deserters of State Forces would capture the Northern territories and Ladakh including Gilgit, Skardu , Kargil, Leh and the Shyok/Nubra valleys.
Stages of the war
Initial invasion
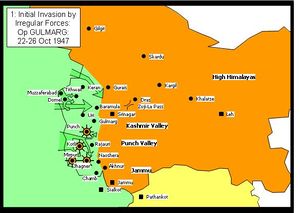
The state forces stationed in the border regions around Muzaffarabad and Domel were quickly defeated by AZK forces (some state forces mutinied and joined the AZK) and the way to the capital was open. Rather than advancing toward Srinagar before state forces could regroup or be reinforced, the invading forces remained in the captured cities in the border region engaging in looting and other crimes against their inhabitants.[10] In the Poonch valley, the state forces retreated into towns where they were besieged.

Indian operation in the Kashmir Valley
After the accession, India airlifted troops and equipment to Srinagar, where they reinforced the princely state forces, established a defense perimeter and defeated the AZK forces on the outskirts of the city. The successful defence included an outflanking manoeuvre by Indian armoured cars. The defeated AZK forces were pursued as far as Baramulla and Uri and these towns were recaptured.
In the Poonch valley, AZK forces continued to besiege state forces.
In Gilgit, the state paramilitary forces (the Gilgit Scouts) joined the invading AZK forces, who thereby obtained control of this northern region of the state. The AZK forces were also joined by troops from Chitral, whose ruler, the Mehtar of Chitral, had acceded to Pakistan.
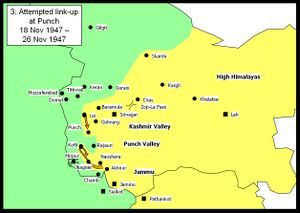
Attempted link-up at Poonch and fall of Mirpur
Indian forces ceased pursuit of AZK forces after recapturing Uri and Baramula, and sent a relief column southwards, in an attempt to relieve Poonch. Although the relief column eventually reached Poonch, the siege could not be lifted. A second relief column reached Kotli, but was forced to evacuate its garrison.
Meanwhile, Mirpur was captured by AZK forces on the 25th of November 1947. Then there was a massacre of Hindus and Sikhs and loot, and more later in Alibeg camp.[11] Around 20 thousand people reported killed, also atrocities on women were reported.[12]
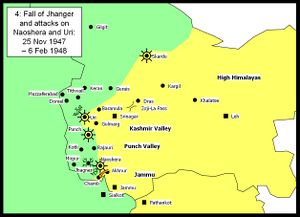
Fall of Jhanger and attacks on Naoshera and Uri
The Pakistani/AZK forces attacked and captured Jhanger. They then attacked Naoshera unsuccessfully. Other Pakistani/AZK forces made a series of unsuccessful attacks on Uri. In the south a minor Indian attack secured Chamb. By this stage of the war the front line began to stabilise as more Indian troops became available.
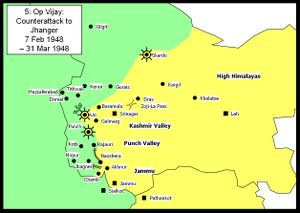
Operation Vijay: counterattack to Jhanger
The Indian forces launched a counterattack in the south recapturing Jhanger and Rajauri. In the Kashmir Valley the Pakistani/AZK forces continued attacking the Uri garrison. In the north Skardu was brought under siege by Pakistani/AZK forces.
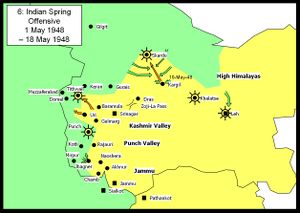
Indian Spring Offensive
The Indians held onto Jhanger against numerous counterattacks from the AZK, who were increasingly supported by regular Pakistani Forces. In the Kashmir Valley the Indians attacked, recapturing Tithwail. The AZK made good progress in the High Himalayas sector, infiltrating troops to bring Leh under siege, capturing Kargil and defeating a relief column heading for Skardu.
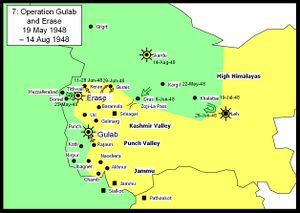
Operations Gulab and Eraze
The Indians continued to attack in the Kashmir Valley sector driving north to capture Keran and Gurais (Operation Eraze)[6]:308-324. They also repelled a counterattack aimed at Tithwal. In the Jammu region, the forces besieged in Poonch broke out and temporarily linked up with the outside world again. The Kashmir State army was able to defend Skardu from the Gilgit Scouts impeding their advance down the Indus valley towards Leh. In August the Chitral Forces under Mata-ul-Mulk besieged Skardu and with the help of artillery were able to take Skardu. This freed the Gilgit Scouts to push further into Ladakh.

Operation Bison
During this time the front began to settle down. The siege of Poonch continued. An unsuccessful attack was launched by 77 Parachute Brigade (Brig Atal) to capture Zoji La pass. Operation Duck, the earlier epithet for this assault, was renamed as Operation Bison by Cariappa. M5 Stuart light tanks of 7 Cavalry were moved in dismantled conditions through Srinagar and winched across bridges while two field companies of the Madras Sappers converted the mule track across Zoji La into a jeep track. The surprise attack on 1 November by the brigade with armour supported by two regiments of 25 pounders and a regiment of 3.7 inch guns, forced the pass and pushed the enemy back to Matayan and later Dras. The brigade linked up on 24 November at Kargil with Indian troops advancing from Leh while the enemy eventually withdrew northwards toward Skardu.[13]:103-127
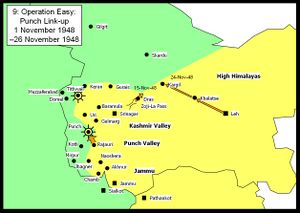
Operation Easy; Poonch link-up
The Indians now started to get the upper hand in all sectors. Poonch was finally relieved after a siege of over a year. The Gilgit forces in the High Himalayas, who had previously made good progress, were finally defeated. The Indians pursued as far as Kargil before being forced to halt due to supply problems. The Zoji La pass was forced by using tanks (which had not been thought possible at that altitude) and Dras was recaptured.
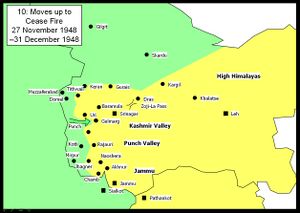
Moves up to cease-fire
At this stage Indian Prime Minister Jawahar Lal Nehru decided to ask UN to intervene. A UN cease-fire was arranged for the 31 December 1948. A few days before the cease-fire the Pakistanis launched a counter attack, which cut the road between Uri and Poonch. After protracted negotiations a cease-fire was agreed to by both countries, which came into effect. The terms of the cease-fire as laid out in the UNCIP resolution.[14] of August 13, 1948 were adopted by the UN on January 5, 1949. This required Pakistan to withdraw its forces, both regular and irregular, while allowing India to maintain minimum strength of its forces in the state to preserve law and order. On compliance of these conditions a plebiscite was to be held to determine the future of the territory. In all, 1,500 soldiers died on each side during the war[15] and Pakistan was able to acquire roughly two-fifths of Kashmir, including five of the fourteen eight thousanders plus peaks of the world, while India maintained the remaining three fifths of Kashmir, including the most populous and fertile regions.
See also
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Official Government of India Statement giving numbers of KIA - Parliament of India Website. It is believed that this figure only gives the Indian Army casualties and not the State Forces.
- ↑ JAK Rifles KIA
- ↑ Indian Army-Martyrs Home Page
- ↑ Library of Congress Country Studies
- ↑ Battle Casualties of Azad Kashmir Regiment during 1947-1948
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Prasad, S.N.; Dharm Pal (1987). History of Operations In Jammu and Kashmir 1947-1948. New Delhi: History Department, Ministry of Defence, Government of India. (printed at Thomson Press (India) Limited). pp. 418..
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Sen, Maj Gen L. P. (1969). Slender Was the Thread: Kashmir Confrontation 1947-48. New Delhi: Orient Longman. pp. 308. ISBN 0861316924. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=lYHXmx4cOUsC. Retrieved 4 August 2010.
- ↑ History of the Panjab Hill States By J. Hutchinson, J.P. Vogel
- ↑ Srinagar www.collectbritain.co.uk.
- ↑ I Indo-Pakistani War, 1947-1949 By Tom Cooper Air Combat Information Group October 29, 2003
- ↑ Mirpur 1947- the Untold Story
- ↑ Kashmir, Storm Center of the World
- ↑ Sinha, Lt. Gen. S.K. (1977). Operation Rescue:Military Operations in Jammu & Kashmir 1947-49. New Delhi: Vision Books. pp. 174. ISBN 81-7094-012-5. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=SMwBAAAAMAAJ. Retrieved 4 August 2010.
- ↑ Resolution adopted by the United Nations Commission for India and Pakistan on 13 August 1948
- ↑ Global security
Bibliography
- Major sources
- Ministry of Defence, Government of India. Operations In Jammu and Kashmir 1947-1948. (1987). Thomson Press (India) Limited, New Delhi. This is the Indian Official History.
- Lamb, Alastair. Kashmir: A Disputed Legacy, 1846-1990. (1991). Roxford Books. ISBN 0-907129-06-4.
- Praval, K.C. The Indian Army After Independence. (1993). Lancer International, ISBN 1-897829-45-0
- Sen, Maj Gen L.P. Slender Was The Thread: The Kashmir confrontation 1947-1948. (1969). Orient Longmans Ltd, New Delhi.
- Vas, Lt Gen. E. A. Without Baggage: A personal account of the Jammu and Kashmir Operations 1947-1949. (1987). Natraj Publishers Dehradun. ISBN 81-85019-09-6.
- Other sources
- Cohen, Lt Col Maurice. Thunder over Kashmir. (1955). Orient Longman Ltd. Hyderabad
- Hinds, Brig Gen SR. Battle of Zoji La. (1962). Military Digest, New Delhi.
- Sandhu, Maj Gen Gurcharan. The Indian Armour: History Of The Indian Armoured Corps 1941-1971. (1987). Vision Books Private Limited, New Delhi, ISBN 81-7094-004-4.
- Singh, Maj K Brahma. History of Jammu and Kashmir Rifles (1820–1956). (1990). Lancer International New Delhi, ISBN 81-7062-091-0.
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
