Kuril Islands dispute
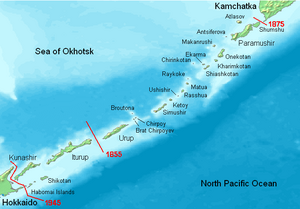
The Kuril Islands dispute (Russian: Спор о принадлежности Курильских островов), also known as the Northern Territories dispute (Japanese: 北方領土問題 Hoppō Ryōdo Mondai), is a dispute between Japan and Russia over sovereignty over the South Kuril Islands. The disputed islands, which were occupied by Soviet forces during the Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation at the end of World War II, are under Russian administration as South Kuril District of the Sakhalin Oblast (Сахали́нская о́бласть, Sakhalinskaya oblast), but are claimed by Japan, which refers to them as the Northern Territories (北方領土 Hoppō Ryōdo) or Southern Chishima (南千島 Minami Chishima), being part of the Nemuro Subprefecture of Hokkaidō Prefecture. The San Francisco Peace Treaty between the Allied Powers[1] and Japan from 1951 states that Japan must give up all claims to the Kuril islands,[2] but it also does not recognize the Soviet Union's sovereignty over the Kuril Islands.[3] Russia maintains that the Soviet Union's sovereignty over the islands was recognized following agreements at the end of the Second World War.[4][5] However, Japan has disputed this claim. The disputed islands are:
- Iturup (Russian: Итуруп)/Etorofu Island (Japanese: 択捉島 Etorofu-tō)
- Kunashir (Russian: Кунашир)/Kunashiri Island (Japanese: 国後島 Kunashiri-tō)
- Shikotan (Russian: Шикотан)/Shikotan Island (Japanese: 色丹島 Shikotan-tō)
- Habomai rocks (Russian: острова Хабомаи ostrova Habomai)/Habomai Islands (Japanese: 歯舞諸島 Habomai-shotō)
Contents |
Background

The first Russo-Japanese agreement to deal with the status of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands is the 1855 Treaty of Shimoda which first established official relations between Russia and Japan. Article 2 of the Treaty of Shimoda, which provided for an agreement on borders, states "Henceforth the boundary between the two nations shall lie between the islands of Etorofu and Uruppu. The whole of Etorofu shall belong to Japan; and the Kurile Islands, lying to the north of and including Uruppu, shall belong to Russia." The islands of Kunashiri, Shikotan and the Habomai Islands, that all lie to the south of Etorofu, are not explicitly mentioned in the treaty and were understood at the time to be a non-disputed part of Japan. The treaty also specified that the island of Sakhalin/Karafuto was not to be partitioned but was to remain under a joint Russo-Japanese condominium.
In a subsequent 1875 Treaty of Saint Petersburg Russia and Japan agreed that Japan would give up all rights to Sakhalin in exchange for Russia giving up all rights to the Kuril Islands in favor of Japan.
The Russo-Japanese war of 1904-1905 was a military disaster for Russia. The 1905 Treaty of Portsmouth, concluded at the end of this war, gave the southern half of the Sakhalin Island to Japan.
Although Japan occupied parts of Russia's Far East during the Russian Civil War following the October Revolution, Japan did not formally annex any of these territories and they were vacated by Japan by the mid-1920s.
There was practically no hostile activity between the USSR and Japan after the Battle of Khalkin Gol ended the Japanese-Soviet Border Wars in 1939 and before the USSR declared war on Japan (Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation) on August 8, 1945. After capturing the islands between August 18 and September 3, 1945, the Soviet Union expelled the Japanese inhabitants two years later.[6]
The modern dispute
World War II agreements
The modern Kuril Islands dispute arose in the aftermath of World War II and results from the ambiguities in and disagreements about the meaning of the Yalta agreement (February 1945), the Potsdam Declaration (July 1945) and the Treaty of San Francisco (September 1951). The Yalta Agreement, signed by the United States, Great Britain and the Soviet Union, stated:
The leaders of the three great powers – the Soviet Union, the United States of America and Great Britain – have agreed that in two or three months after Germany has surrendered and the war in Europe is terminated, the Soviet Union shall enter into war against Japan on the side of the Allies on condition that: [....] 2. The former rights of Russia violated by the treacherous attack of Japan in 1904 shall be restored, viz.: (a) The southern part of Sakhalin as well as the islands adjacent to it shall be returned to the Soviet Union; [....] 3. The Kurile Islands shall be handed over to the Soviet Union.
Japan, as well as the United States, claimed that the Yalta agreement did not apply to the Northern Territories because they were not a part of the Kuril Islands, although U.S. geographers have traditionally listed them as part of the Kuril chain. In a 1998 article in the journal Pacific Affairs, Bruce Elleman, Michael Nichols and Matthew Ouimet argue that the United States never accepted the cession of all the Kuril Islands to the Soviet Union and has maintained from Yalta onwards that it simply agreed at Yalta that Moscow could negotiate directly with Tokyo to come to a mutually acceptable solution, and that the U.S. would support in such a peace agreement the Soviet acquisition of the Kurils.[7] As a key piece of evidence, the same article (page 494 of [7]) quotes an August 27, 1945 letter from Truman to Stalin:"You evidently misunderstood my message [about the Kuril Islands].... I was not speaking of any territory of the Soviet Republic. I was speaking of the Kurile Islands, Japanese territory, disposition of which must be made at a peace settlement. I was advised that my predecessor agreed to support in the peace settlement the Soviet acquisition of those islands."
The Soviet Union and, subsequently, Russia rejected this position. It should be noted that the restoration of the 1904 borders is in paragraph 2, containing sub-paragraphs (a), (b) etc., while the status of the Kurils is covered in a separate 3rd paragraph.
Compared to the Yalta agreement, the text of the Potsdam Declaration contained a more ambiguous passage regarding the Japanese territories: "8. The terms of the Cairo Declaration shall be carried out and Japanese sovereignty shall be limited to the islands of Honshū, Hokkaido, Kyushu, Shikoku and such minor islands as we determine". The islands comprising the Northern Territories are not explicitly included in this list, but the U.S. subsequently maintained, particularly during the preparation of the Treaty of San Francisco, that the phrase "and such minor islands as we determine" could be used to justify transferring the Northern Territories to Japan. The Cairo Declaration of 1943 did not explicitly mention the Kuril Islands but stated: "Japan will also be expelled from all other territories which she has taken by violence and greed".
Japan later claimed that the Cairo Declaration and the Potsdam Declaration, which cites it, did not apply to the Northern Territories on the grounds that they had never belonged to Russia even before the 1904-1905 Russo-Japanese war and had never been claimed by Russia since the establishment of diplomatic relations between Russia and Japan in 1855, and thus they were not among the territories acquired by Japan "by violence and greed".
San Francisco Treaty
A substantial dispute regarding the status of the Kuril Islands arose between the U.S. and the Soviet Union during the preparation of the Treaty of San Francisco in 1951. The Treaty was supposed to be a permanent peace treaty between Japan and the Allied Powers of World War II. By that time the Cold War had already taken hold, and the position of the U.S. in relation to the Yalta and Potsdam agreements had changed considerably. The U.S. had come to maintain that the Potsdam Declaration should take precedence and that strict adherence to the Yalta agreement was not necessary since, in the view of the U.S., the Soviet Union itself violated several provisions of the Yalta agreement in relation to the rights of other countries.[8] The Soviet Union vehemently disagreed[9] and demanded that the U.S. adhere to its promises made to the Soviet Union in Yalta as a condition of the Soviet Union's entry into the war with Japan. A particular point of disagreement at the time was the fact that the draft text of the treaty, while stating that Japan will renounce all rights to Southern Sakhalin and the Kuril islands, did not state explicitly that Japan would recognize the Soviet Union's sovereignty over these territories.
The Treaty of San Francisco was officially signed by 49 nations, including Japan and the United States, on September 8, 1951. Article (2c) states: "Japan renounces all right, title and claim to the Kurile Islands, and to that portion of Sakhalin and the islands adjacent to it over which Japan acquired sovereignty as a consequence of the Treaty of Portsmouth of 5 September 1905." The State Department later clarified that "the Habomai Islands and Shitokan ... are properly part of Hokkaido and that Japan is entitled to sovereignty over them". Britain and the United States agreed that territorial rights would not be granted to nations that did not sign the Treaty of San Francisco, and therefore the islands were not formally recognized as Soviet territory.[7]
The Soviet Union refused to sign the Treaty of San Francisco and publicly stated that the Kuril Islands issue was one of the reasons for its opposition to the Treaty. Japan signed and ratified the San Francisco treaty. However, both the Japanese government and most of the Japanese media currently claim[10] that already at the time of the 1951 San Francisco peace conference, Japan held that the islands of Kunashiri, Etorofu, Shikotan and the Habomai rocks were technically not a part of the Kuril Islands and thus were not covered by the provisions of Article (2c) of the treaty. The timing of this claim is disputed by Russia and by some western historians.[11][12] In a 2005 article in The Japan Times, Gregory Clark writes that official Japanese statements, maps and other documents from 1951 and the statements by the head of the U.S. delegation to the San Francisco conference, John Foster Dulles, make it clear that at the time the San Francisco Treaty was concluded in October 1951, both Japan and the United States considered the islands of Kunashiri and Etorofu to be a part of the Kuril Islands and to be covered by Article (2c) of the Treaty.[13]
The US Senate Resolution of April 28, 1952, ratifying of the San Francisco Treaty, explicitly stated that the USSR had no title to the Kurils[14], the resolution stating:
As part of such advice and consent the Senate states that nothing the treaty [San Francisco Peace Treaty] contains is deemed to diminish or prejudice, in favor of the Soviet Union, the right, title, and interest of Japan, or the Allied Powers as defined in said treaty, in and to South Sakhalin and its adjacent islands, the Kurile Islands, the Habomai Islands, the Island of Shikotan, or any other territory, rights, or interests possessed by Japan on December 7, 1941, or to confer any right, title, or benefit therein or thereto on the Soviet Union.
The USA maintains that until a peace treaty between Japan and Russia is concluded, the disputed Northern Territories remain Japanese territory under Russian military occupation via General Order No. 1.[7]
1956 Soviet-Japanese Joint Declaration and dispute over the composition of the Kuril islands
During the 1956 peace talks between Japan and the Soviet Union, the Soviet side proposed to settle the dispute by returning Shikotan and Habomai to Japan. In the final round of the talks the Japanese side accepted the weakness of its claim to Etorofu and Kunashiri and agreed to settle for return of Shikotan and the Habomais, in exchange for a peace treaty. However, the Americans intervened and blocked the deal.[11][15] The United States warning to Japan that a withdrawal of the Japanese claim on the other islands would mean the United States would keep Okinawa caused Japan to refuse these terms. The United States had asserted that the San Francisco Peace Treaty "did not determine the sovereignty of the territories renounced by Japan," but that "Japan does not have the right to transfer sovereignty over such territories.[14] Nevertheless, on October 19, 1956 in Moscow, the USSR and Japan signed the Soviet-Japanese Joint Declaration. The Declaration ended the state of war between the Soviet Union and Japan, which technically had still existed between the two countries since August 1945.[16] The Joint Declaration did not settle the Kuril Islands dispute, the resolution of which was postponed until the conclusion of a permanent peace treaty between USSR and Japan. However, Article 9 of the Joint Declaration stated: "The U.S.S.R. and Japan have agreed to continue, after the establishment of normal diplomatic relations between them, negotiations for the conclusion of a peace treaty. Hereby, the U.S.S.R., in response to the desires of Japan and taking into consideration the interest of the Japanese state, agrees to hand over to Japan the Habomai and the Shikotan Islands, provided that the actual changing over to Japan of these islands will be carried out after the conclusion of a peace treaty."[17]
The question of whether Etorofu and Kunashiri islands are a part of the Kurils, and thus whether they are covered by Article (2c) of the Treaty of San Francisco, remains one of the main outstanding issues in the Kuril Islands dispute. Based on a 1966 book by a former Japanese diplomat and a member of the 1956 Japanese delegation for the Moscow peace talks, Clark traces the first Japanese claim that Etorofu and Kunashiri islands are not a part of the Kurils to the 1956 negotiations on the Soviet-Japanese Joint Declaration of 1956. The Soviet Union rejected the view at that time, and subsequently, Russia has maintained the same position since then.
Recent developments
The positions of the two sides have not substantially changed since the 1956 Joint Declaration, and a permanent peace treaty between Japan and Russia still has not been concluded.
On July 7, 2005, the European Parliament issued an official statement recommending the return of the territories in dispute,[18] which Russia immediately protested.
As late as 2006, Russia's Putin administration offered Japan the return of Shikotan and the Habomais (about 6% of the disputed area) if Japan would renounce its claims to the other two islands, referring to the Soviet-Japanese Joint Declaration of 1956 which promised Shikotan and the Habomais would be ceded to Japan once a peace treaty was signed.[19][20][21]
Japan has offered substantial financial aid to the Kuril Islands if they are handed over. However, by 2007, residents of the islands were starting to benefit from economic growth and improved living standards, arising in particular from expansion in the fish processing industry. As a result, it is thought that islanders are less likely to be won over by Japanese offers of financial support.[22]
On February 6, 2008, Japan Today, an English-language news site in Japan, reported that the Russian president had suggested to Japanese Prime Minister Yasuo Fukuda to finally settle all territorial disputes over the Kuril Islands and had sent him a letter inviting him to come to Russia for discussions.[23]
The dispute over the Kuril Islands was further exacerbated on July 16, 2008, when the Japanese government published new school textbook guidelines directing teachers to say that Japan has sovereignty over the Kuril Islands. The Russian Ministry of Foreign affairs announced on July 18, "[these actions] contribute neither to the development of positive cooperation between the two countries, nor to the settlement of the dispute" and reaffirmed its sovereignty over the islands.[24][25]
Japanese Prime Minister Taro Aso and Russian President Dmitry Medvedev met in Sakhalin on February 18, 2009 to discuss the Kuril Islands issue. Aso said after the meeting that they had agreed to speed up efforts to resolve the dispute so that it would not be left to future generations to find a solution.[26]
Russia has given several concessions to Japan in the dispute. For example, Russia has introduced visa-free trips for Japanese citizens to the Kuril Islands. Japan's fishermen are also allowed to catch sea bioresources in Russia's exclusive economic zone.[27]
However, tensions seem to be rising on both sides as the Russian Head of the Kuril Region has called for dropping the visa free program[28] and Japanese fishermen were fired upon for allegedly fishing illegally in Russian waters.[29]
Current views
Japan's view
Japan's current view of the dispute is given in the official pamphlet of the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs:[30]
- The Cairo Declaration and the Potsdam Declaration did not apply to the Northern Territories because those islands had never belonged to Russia even before 1904-1905.
- Russia had not previously claimed the disputed islands, not in all the time since it began diplomatic relations with Japan in 1855. Therefore the disputed islands could not be considered part of the territories acquired by Japan "by violence and greed".
- The Yalta Agreement "did not determine the final settlement of the territorial problem, as it was no more than a statement by the then leaders of the Allied Powers as to principles of the postwar settlement. (Territorial issues should be settled by a peace treaty.) Furthermore, Japan is not bound by this document, to which it did not agree."[30]
- Russia's 1945 entry into the war against Japan was a violation of the Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact, and the occupation of the islands was therefore a violation of international law. The Soviet Union repudiated the neutrality pact on April 5, 1945, but the pact remained in effect until April 13, 1946.
- Although by the terms of Article (2c) of the 1951 San Francisco treaty, Japan renounced all rights to the Kuril Islands, the treaty did not apply to the islands of Kunashiri, Etorofu, Shikotan and the Habomai rocks since they are not included in the Kuril Islands. Also, the Soviet Union did not sign the San Francisco treaty.
Russia's view
Russia maintains that all the Kuril Islands, including those that Japan calls the Northern Territories, are legally a part of Russia as a result of World War II, and that this acquisition was as proper as any other change of international boundaries following the war.[4] Moscow cites the following basic points:
- The explicit language of the Yalta Treaty gave the Soviet Union a right to the Kurils, and the Soviet Union upheld its own obligations under that treaty.
- The nation of Russia inherited possession of the islands from the former Soviet Union, in accordance with international law.
- The Japanese assertion that the disputed islands are not part of the Kurils is simply a tactic to bolster Tokyo's territorial claim and is not supported by history or geography.
Russia has said it is open to a negotiated "solution" to the island dispute while declaring that the legality of its own claim to the islands is not open to question.[31] In other words, Japan would first have to recognize Russia's right to the islands and then try to acquire some or all of them through negotiations.
Public attitudes
In Russia most of the population, as well as the mass media, strongly oppose any territorial concessions to Japan.[32] A common view[32] is that Russia won the Kuril Islands during World War II and is entitled to keep them regardless of the prior history of the disputed territories. Many [32] believe that taking these islands away from Japan was a just reward for Russia's sacrifices during World War II and for Russia's agreement to enter the war against Japan at the request of its allies. The attitudes of the Russian public have hardened in the 2000s. According to a July 2009 poll conducted by the All-Russian Public Opinion Research Center (VTsIOM), 89% of respondents were against territorial concessions to Japan in the Kuril Islands dispute, compared to 76% from a similar poll in 1994.[33]
In Japan, there are various private groups cooperating with local and national government to encourage the Japanese people to push for the return of the islands. One man whose family was evicted from the islands, Kenjiro Suzuki[34], heads the Tokachi branch of the League of Chishima Habomai Islands Residents (Chishima is the Japanese name for the Kuril Islands).[35] In 2008, the main organization had a budget of approximately 187 million yen ($1.7 million US$).[36]
According to a New York Times opinion column, the legal base of the Japanese claim to the islands is "quite weak". The Japanese claim is the result of a bizarre negotiating mix up in the 1956 talks for resuming diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union.[15]
See also
- Kuril Islands
- Soviet-Japanese relations and Russo-Japanese relations
- Foreign relations of Japan
- Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1875)
- All-Russian Committee for Defence of Kuriles
- Ainu people
References and footnotes
- ↑ Article 25 of The San Francisco Peace Treaty defines the Allied Forces as “the States at war with Japan, […] provided that in each case the State concerned has signed and ratified the Treaty. […] the present Treaty shall not confer any rights, titles or benefits on any State which is not an Allied Power as herein defined; nor shall any right, title or interest of Japan be deemed to be diminished or prejudiced by any provision of the Treaty in favour of a State which is not an Allied Power as so defined.” The Allied powers were Australia, Canada, Ceylon, France, Indonesia, the Kingdom of the Netherlands, New Zealand, Pakistan, the Republic of the Philippines, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, and the United States of America. The Soviet Union refused to sign the treaty.
- ↑ "The history of the Kuril Islands Dispute". RIA Novosti. 1 May 2009. http://en.rian.ru/analysis/20090501/121506723.html. Retrieved 2009-07-09.
- ↑ Text of Gromyko's Statement on the Peace Treaty.New York Times, page 26, September 9, 1951
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 “Japan’s undermining of Russian sovereignty not tolerated” – Medvedev
- ↑ (Russian) "О проблеме мирного договора в российско-японских отношениях". Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 22 July 2005. http://www.ln.mid.ru/ns-vnpop.nsf/osn_copy/511967C89F5D135EC325704300315459. Retrieved 2009-07-26.
- ↑ K. Takahara, Nemuro raid survivor longs for homeland. Japan Times, September 22, 2007. Accessed August 3, 2008
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Bruce A. Elleman, Michael R. Nichols and Matthew J. Ouimet, A Historical Reevaluation of America's Role in the Kuril Islands Dispute, Pacific Affairs, Vol. 71, No. 4 (Winter, 1998-1999), pp. 489-504
- ↑ Text of Dulles Reply to the Soviet Charges Against Japanese Peace Treaty; THE PRESIDENT ARRIVING TO OPEN PEACE CONFERENCE, New York Times, September 4, 1951; from page 3: "Charge: [...] Likewise, the Treaty States that southern Sakhalin and the Kurile Islands are to be detached from Japan but does not state, as previously promised by the United States, that these territories should be handed over to the Soviet Union. Reply: [...] As regards South Sakhalin and the Kurile Islands, the treaty carries out the provisions of the Potsdam surrender terms, the only agreement by which Japan and the Allied powers as a whole are bound. So long as other governments have rights under the Yalta Agreement which the Soviet Union has not fulfilled, there is at least question as to whether the Soviet Union can, "with clean hands", demand the fulfillment of the parts of that agreement it likes".
- ↑ Text of Gromyko's Statement on the Peace Treaty.New York Times, September 9, 1951; From page 26: "The Soviet delegation has already drawn the attention of the conference to the inadmissibility of the situation under which the draft peace treaty with Japan fails to state that Japan should recognize the sovereignty of the Soviet Union over the southern part of Sakhalin and the Kurile Islands. The draft is in flagrant contradiction with the obligations assumed by the United States and Great Britain with regard to these territories under the Yalta Agreement."
- ↑ The convoluted case of the coveted Kurils. By Kosuke Takahashi. Asia Times. November 25, 2004. "Japan and the Allied Powers, including the US and the UK, signed the peace treaty in San Francisco in 1951, when the Soviet Union participated but did not sign the treaty. At the conference, Japan renounced the "Kuril Islands", excluding Etorofu, Kunashiri, Shikotan, or Habomai islands, which Japan claimed had always been Japanese territories and wished to claim them after the war."
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Kimie Hara, 50 Years from San Francisco: Re-Examining the Peace Treaty and Japan's Territorial Problems. Pacific Affairs, Vol. 74, No. 3 (Autumn, 2001), pp. 361-382. Available online at J-STOR.
- ↑ Northern Territories dispute highlights flawed diplomacy. By Gregory Clark. Japan Times, March 24, 2005.
- ↑ Northern Territories dispute highlights flawed diplomacy. By Gregory Clark. Japan Times, March 24, 2005. "Japanese materials at the time -- Foreign Ministry maps, statements by former Prime Minister Shigeru Yoshida at San Francisco and in his later memoirs, and newspaper reports all make it clear that Etorofu and Kunashiri were most definitely included. The chief U.S. negotiator for the San Francisco treaty, Secretary of State John Foster Dulles, agreed. Asked at San Francisco to define the territory of the Kurils, he said only that the Habomais might be excluded (at the time there were suggestions that Shikotan might be part of the Kurils). More was to follow. Questioned in the Diet on October 19, 1951, over whether the word "Kurils" as used in the treaty included Etorofu and Kunashiri, the head of the Foreign Ministry Treaties Bureau, Kumao Nishimura, said unambiguously that both the northern Chishima and southern Chishima (Etorofu and Kunashiri) were included."
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 James E. Goodby, Vladimir I. Ivanov, Nobuo Shimotomai, '"Northern territories" and beyond: Russian, Japanese, and American Perspectives, Praeger Publishers, 1995
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Clark, Gregory (July 18, 1992). "Tokyo's Claim to the Kurils Is Shaky". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/1992/07/18/opinion/18iht-edcl_0.html. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ↑ Texts of Soviet-Japanese Statements; Peace Declaration Trade Protocol, page 2, New York Times, October 20, 1956; available for fee from the New York Times electronic archive.
- ↑ "Texts of Soviet-Japanese Statements; Peace Declaration Trade Protocol." New York Times, page 2, October 20, 1956. Subtitle: "Moscow, October 19. (UP) - Following are the texts of a Soviet-Japanese peace declaration and of a trade protocol between the two countries, signed here today, in unofficial translation from the Russian".
- ↑ European Parliament resolution on relations between the EU, China and Taiwan and security in the Far East #15 [1]
- ↑ Soviet-Japanese joint declaration of 1956 — full text in Russian at Wiki
- ↑ declaration of 1956, official Japan site — full text in Russian
- ↑ declaration of 1956, Japan embassy — full text in Russian
- ↑ Islands disputed with Japan feel Russia's boom
- ↑ Japan expects the Kuril Islands return :: In Depth :: Russia International :: Russia-InfoCentre
- ↑ Russia hopes to solve territorial dispute with Japan by strengthening trust, Xinhua News Agency, Accessed 19 July 2008
- ↑ Japanese schoolbooks to claim Russia's Southern Kuril Islands, RussiaToday, Accessed 19 July 2008
- ↑ Japan, Russia discuss islands row
- ↑ "Japan’s statements on Kurils have no legal force - envoy". ITAR-TASS. 8 July 2009. http://www.itar-tass.com/eng/level2.html?NewsID=14126572&PageNum=47. Retrieved 2009-07-09.
- ↑ "Russia might drop visa-free exchange with Japan". ITAR-TASS. 8 July 2009.
- ↑ "Fired on Japanese fishing vessels may have intentionally trespassed into Russian waters". Mainichi Daily News. 2 February 2010.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Japan's Northern Territories (Pamphlet). Japan Ministry of Foreign Affairs website.
- ↑ Russia stands firm in territorial dispute with Japan. RIA Novosti. July 2, 2008.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 Russians Want to Keep the Kuril Islands. By E. Vovk. The Public Opinion Foundation Database. November 25, 2004
- ↑ Sergey Borisov. ROAR: “Trusting relationship unlikely to solve main problem for Russia-Japan”. Russia Today, September 8, 2009.
- ↑ 抑留55年目の回顧〜「シベリア抑留関係展示会」【3】
- ↑ Tokachi branch of the League of Chijima Habomai Islands Residents: 2008 16th Regular Meeting Proposals (paper document in Japanese)「支部長 鈴木 健二郎」
- ↑ http://www.koueki.jp/disclosure/ta/chishima-habomai/0.pdf
Further reading
- Hasegawa, Tsuyoshi. Racing the Enemy: Stalin, Truman, and the Surrender of Japan. Harvard University Press, 2005. ISBN 0-674-01693-9.
- Stephan, John J. The Kuril Islands Russo-Japanese Frontier in the Pacific. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1974. ISBN 0-19-821563-0
- Kimie Hara, 50 Years from San Francisco: Re-Examining the Peace Treaty and Japan's Territorial Problems. Pacific Affairs, Vol. 74, No. 3 (Autumn, 2001), pp. 361-382. Available online at J-STOR.</ref>
External links
- South Kuriles/Northern Territories:A Stumbling-block in Russia-Japan Relations, history and analysis by Andrew Andersen, Department of Political Science, University of Victoria, May 2001
- Chishima: Frontiers of San Francisco (A documentary film about Kuril Island dispute.)
- Japan's Northern Territories (Japanese government website)
- The convoluted case of the coveted Kurils analysis by Kosuke Takahashi (November 25, 2004)
- Northern Territories dispute highlights flawed diplomacy by Gregory Clark (Economist), Japan Times (March 24, 2005)
- Creative thinking on the Kurils analysis by Kosuke Takahashi (April 20, 2005)
- Akaha and Vassilieva, "Lessons for Improved Japan - Russia Relations", Asahi Shimbun, June 20, 2005, Monterey Institute of International Studies
- Little known facts in history of the dispute (in Russian).
- Russian view on the history of the dispute (in Russian)
- Takahara, Kanako (September 22, 2007). "Nemuro raid survivor longs for homeland" (Newspaper article). Japan Times. http://search.japantimes.co.jp/cgi-bin/nn20070922w1.html. Retrieved 2008-02-01.
| Type | Territory | Currently Administered by | Claimants |
| Land: | Aksai Chin | ||
| Baekdu Mountain | |||
| Heixiazi / Bolshoy Ussuriysky (Eastern part)2 | |||
| Indo-Bangladesh enclaves3 | |||
| Kachin State | |||
| Kashmir3 | |||
| Kayin State | |||
| Korean Peninsula and its adjacent islands3 | |||
| Mainland China | |||
| North Borneo (Sabah)2 | |||
| Outer Mongolia2 | |||
| Pamir Mountains3 | |||
| Patani | |||
| Shan State | |||
| Sixty-Four Villages East of the River2 | |||
| South Tibet (now Arunachal Pradesh of India) | |||
| Tannu Uriankhai (now Tuva Republic of Russia)2 | |||
| Trans-Karakoram Tract | |||
| Wa State | |||
| Islands and Waters: | Diaoyutai / Senkaku Islands | ||
| Kinmen | |||
| Kori Creek2 | |||
| Liancourt Rocks | |||
| Macclesfield Bank | |||
| Matsu | |||
| Paracel Islands | |||
| Pedra Branca, Middle Rocks, and South Ledge | |||
| Pratas Islands | |||
| Scarborough Shoal | |||
| Socotra Rock | |||
| Southern Kuril Islands | |||
| Spratly Islands3 | |||
| Taiwan and Penghu2 | |||
| Notes: | 1Government in exile/exiled group. 2Inactive dispute. 3Divided among multiple claimants. |
||