Podlaskie Voivodeship
| Podlaskie Voivodeship Województwo podlaskie |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — Voivodeship — | |||||
|
|
|||||
|
|||||
.png) |
|||||
| Coordinates (Białystok): | |||||
| Country | |||||
| Capital | Białystok | ||||
| Counties | |||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 20,180 km2 (7,791.5 sq mi) | ||||
| Population (2006) | |||||
| - Total | 1,197,610 | ||||
| - Density | 59.3/km2 (153.7/sq mi) | ||||
| - Urban | 712,675 | ||||
| - Rural | 484,935 | ||||
| Car plates | B | ||||
| Website | http://www.bialystok.uw.gov.pl | ||||
| * further divided into 118 gminas | |||||
Podlaskie Voivodeship (also known as Podlasie Province, Polish: województwo podlaskie [vɔjɛˈvut͡stfɔ pɔdˈlaskʲɛ] or simply Podlaskie) is a voivodeship (province) in north-eastern Poland. It was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Białystok and Łomża Voivodeships and the eastern half of the former Suwałki Voivodeship, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998. Its capital is Białystok.
Contents |
Etymology
The voivodeship takes its name from the historical region of Podlasie. This name originates from the period when the territory was within the Trakai Voivodeship of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, along the borderline with the Mazovia province, primarily a fief of the Poland of the Piasts and later on part of the Kingdom of Poland of the Jagiellons. Hence pod Lachem would mean "near the Poles", "along the border with Poland".
Transportation
Railways
Passenger Service
Passenger services is provided by two rail service providers:
- PKP Intercity - intercity passengers trains (express, intercity, eurocity, hotel and TLK)
- Przewozy Regionalne - runs only regional passenger trains financed by the voivodeship. Passenger trains are mostly run using electrical multiple units (on electrified lines) or rail buses[1].
Przewozy Regionalne provides service on the following routes:
- Białystok - Sokółka - Augustów - Suwałki
- Białystok - Sokółka - Kuźnica Białystok- Hrodno, Belarus
- Białystok - Warsaw
- Białystok - Mońki - Grajewo - Ełk
- Hajnówka - Czeremcha - Siemiatycze - Siedlce
- Białystok - Bielsk Podlaski - Czeremcha (Connects to Hajnówka - Siedlce service)
Rail Baltica
Rail Baltica is one of the priority projects of the European Union Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T). The project is supposed to link Finland, Baltic States and Poland and also improve the connection between central and eastern Europe and Germany. It requires an upgrade of the existing standard gauge railway from Warsaw–Białystok–Ełk- Sokółka -Trakiszki to 160 km/h[2].
Roadways
| Expressways | National Roads | Voivodeship Roads |
|
|
|
Geography
Varied landscape, shaped in the north of the Baltic glaciation, the rest of the Middle Poland glaciation. The highest peaks are in the north (Rowelska Top - 298 m), where the landscape is dominated by hilly lake district. Lakeland: Zachodniosuwalskie, Wschodniosuwalskie, Ełckie) and sandrowy lake district (Augustów Plain) in the central and southern plains prevail peryglacjalne (plateaus: Kolneńska, Białystok, Wysokomazowiecka, Drohiczynska, Sokólskie Hills, Międzyrzecko łomżyński, Plain Bielsko), varied in wcinającymi not kotlinami and river valleys, lies on the west edge of the outwash plains Kurpiowska. Predominate on the surface of sand, gravel, clay, moraine, and in the valleys and basins of the rivers silt, sand and peat river.
Natural assets
The vast forests and forests (Białowieża, Augustów, Knyszyń, Puszcza Kurpiowska), some of which are the only ones in Europe have retained their original character, you can meet a unique wealth of flora and fauna. The vegetation of the region is extremely rich and diverse, which contributes to the richness of the animal world. Visitors can also see moose, wolves, lynx and bison living in the Bialowieża Forest and Knyszyń Forest.
Podlaskie has the lowest population density of the sixteen Polish voivodeships, and its largely unspoilt nature is one of its chief assets. Around 30% of the area of the voivodeship is under legal protection. The Polish part of the Białowieża Forest biosphere reserve (also a World Heritage Site) is in Podlaskie. There are four National Parks (Białowieża, Biebrza, Narew and Wigry), three Landscape Parks (Knyszyń Forest, Łomża and Suwałki), 88 nature reserves, and 15 protected landscape areas. The voivodeship constitutes a part of the ecologically clean area known as "the Green Lungs of Poland".
Climate
| Białystok, Poland | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart () | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Podlaskie is the coldest region of Poland, located in the very northeast of the country near the border with Belarus and Lithuania. The region has a continental climate which is characterized by high temperatures during summer and long and frosty winters . The climate is affected by the cold fronts which come from Scandinavia and Siberia. The average temperature in the winter ranges from -15°C (5°F) to -4°C (24.8°F)[3].
Culture
Podlaskie is the most diverse of all Polish voivodships. The area has been inhabited for centuries by members of different nations and religions: Belarusians, Lithuanians, Ukrainians, Russyns, Gypsies, Tatars, Jews and Filipons.
Many places of religious worship remain:
- An 18th-century former Carmelite monastery on Wigry Lake
- A former jesuit monastery complex in Drohiczyn
- Christ's Transfiguration Orthodox church on the Holy Mount of Grabarka
- Saint Nicolaus the Miracle Worker Orthodox church in Białystok
- A 17th-century synagogue in Tykocin
- The oldest Polish mosque in Kruszyniany
Historical Locations
Middle Ages
- St.. Michael and John the Baptist in Łomża (1504–1526)
Renaissance
- The ruins of the castle in Tykocin[ (15th century)
- The Jewish cemetery in Tykocin (16th century)
- Monastery of the Annunciation in Suprasl (16th to 18th centuries)
Baroque
- Dominican Convent of the Visitation of the Blessed Virgin Mary Church in Sejny (1610–1619)
- Old Parish Church in Białystok (1617–1626)
- Synagogue (1642) and the Talmud house in Tykocin (18th century)
- Trzewiczkowych Carmelite Monastery with the Church of Our Lady of Mount Caramel in Bielsk Podlaski (mid-17th century)
- Branicki Palace in Białystok (the 17th and 18th centuries)
- Summer residence Branicki in Choroszcz (1752–1759)
- Holy Trinity Church in Tykocin (1742–1750)
- Church of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary in Siemiatycze (1719–1727)
- Monastery of the Dominican church of St. And St. John the Baptist. Stephen Martyr in Choroszcz (mid-18th century)
- Capuchin Monastery in Łomża (1770–1798)
- Old Town Hall in Bielsk Podlaski (1776–1780)
- Sokółki Palace in Pawłowiczch near Sokółka
- Synagogue in Orla
- Bernardine Monastery in Tykocin (1771–1791)
- The team Stawiski Franciscan monastery (17th - 19th century)
Classicism
- Basilica. Birth of the Virgin and St. Nicholas in Bielsk Podlaski (1780)
- Cathedral of St.. Nicholas in Białystok (1843–1846)
- Church of Sts. Kolnie Anne (1834–1839)
- Co-cathedral of St. Alexander in Suwałki (1825)
- Classical brick mansion in Little Płock (1835)
- Church of Sts. Anthony in Sokółka (1848)
- Cemetery Cathedral in Łomża
- Synagogue in Kolno (second half. 18th century)
19th century
- Lubomirski Palace in Białystok (second half. 19th century)
- Hasbacha Palace in Białystok (the late 19th century)
- The palace and park in Buchholtzów Suprasl (1892–1903)
- Team Becker factory in Białystok (nineteenth and early 20th century)
- The fence and gate parafialno-municipal cemetery in Kolno (1809)
- Church in the Parish and (the first half. 19th century)
- Catholic Parish in Grabowie (the first half. 19th century)
- The Jewish cemetery in Kolno (1817)
- The Jewish cemetery in Stawiski (the first half. 19th century)
- Parish Church p.w. St. Adalbert in m (the first half. 19th century)
- The team mail Stawiski (II quarter of the 19th century)
- Neo-Baroque bell tower at the church brick church. St. Anne Kolnie (1862)
- Buildings of the monastery of SS. Benedictine in Łomża (1863)
- Church of the Assumption in Łomża (1877)
- Roman Catholic Cemetery in Porytem (second half. 19th century)
- Church of the Holy Trinity in Zambrów (1879)
- Church of the Holy Trinity in Grajewo (1882)
- Church of Sts. John the Baptist in Wysokie Mazowiecki (1888)
- Building Seminar in Łomża(1866)
- Town Hall in Łomża (1822–1823)
- Numerous monuments Street. Dwornej in Łomża
- Manor in Wojnówce
- Basilica of the Assumption in Białystok (1900–1905, neo-Gothic)
- The Church of St.Adalbert in Białystok (1906–1912)
- The Church of St. Rocha in Białystok (1926–1947, modernist)
- Church of the Sacred Heart of Jesus in Augustów (1905–1911 eclectic)
- The Church of Our Lady of Częstochowa and St. Casimir in Mońkach (1921–1935)
- Saints' Church of the Apostles Peter and Paul in Łapach (1918–1927)
- Fortress in Osowcu
- A Polish Tatars' (Islam in Poland) wooden mosque and a Muslim cemetery in the village of Bohoniki
Economy
General Economic Indicators
The following are general economic indicators for Podlaskie[4]:
- Population (as of 30 September 2009) - 1190735
- Average paid employment in enterprise sector (November 2009) - 95896
- Average monthly gross wages and salaries in enterprise sector (November 2009) - 2813,05 zł
- Unemployment rate (as of the end of November 2009) - 12,0%
- Dwellings completed (November 2009) - 661
- Procurement of milk (November 2009) - 126,8 mln l
- National economy entities in the REGON register, excluding persons tending private farms (as of the end of November 2009) - 89654
According to REGON register in the year 2002 there were around 95 thousand companies registered in Podlaskie region (97 % of them in private sector), dealing with;
- Trade and servicing – 33.2 %
- Providing services to real estates and companies – 11.8 %
- Construction – 10.5%
- Industrial processing – 9.7 %
- Transport 8.3%
- Agriculture, hunting and forestry 4.5%
Agriculture
Arable land constitutes around 60% of the total area of the region – most of which is ploughland (around 40%), forests, meadows and pastures. Over 120 000 farms are registered, roughly half of which are small farms of 1–5 ha and medium-sized farms of 5–10 ha. The smaller farms prefer intensive production (gardening, orcharding), whereas the larger ones engage in cattle and crop production. The cattle-raising farms are mainly oriented towards milk production.
The natural conditions of the region are conducive to the development of organic growing, which at present is practised by around 100 farms. Over 600 farms in the region offer agritourist services.[5]
Government
The voivodeship's seat is the city of Białystok. Like all voivodeships, it has a government-appointed Provincial Governor[6] (Polish: wojewoda), as well as an elected Regional Assembly (sejmik) and of the executive elected by that assembly, headed by the voivodeship marshal (marszałek województwa). Administrative powers and competences are statutorily divided between these authorities.
Cities and towns
The voivodeship contains 39 cities and towns. These are listed below in descending order of population (according to official figures for 2006[7] ):
|
|
Administrative division
Podlaskie Voivodeship is divided into 17 counties (powiats): 3 city counties and 14 land counties. These are further divided into 118 gminas.
The counties are shown on the numbered map and detailed in the table beside it.
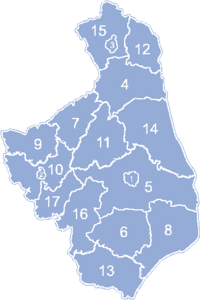
| English and Polish names |
Area (km²) |
Population (2006)[7] |
Seat | Other towns | Total gminas |
| City counties | |||||
| 102 | 295,210 | 1 | |||
| 65 | 69,234 | 1 | |||
| 33 | 63,572 | 1 | |||
| Land counties | |||||
| Białystok County powiat białostocki |
2,985 | 136,797 | Białystok * | Łapy, Czarna Białostocka, Wasilków, Choroszcz, Supraśl, Michałowo, Zabłudów, Tykocin, Suraż | 15 |
| Sokółka County powiat sokólski |
2,054 | 72,424 | Sokółka | Dąbrowa Białostocka, Krynki, Suchowola | 10 |
| Bielsk County powiat bielski |
1,385 | 60,047 | Bielsk Podlaski | Brańsk | 8 |
| Wysokie Mazowieckie County powiat wysokomazowiecki |
1,288 | 59,719 | Wysokie Mazowieckie | Ciechanowiec, Szepietowo | 10 |
| Augustów County powiat augustowski |
1,658 | 58,966 | Augustów | Lipsk | 7 |
| Łomża County powiat łomżyński |
1,354 | 50,887 | Łomża * | Nowogród, Jedwabne | 9 |
| Grajewo County powiat grajewski |
967 | 50,120 | Grajewo | Szczuczyn, Rajgród | 6 |
| Siemiatycze County powiat siemiatycki |
1,460 | 48,603 | Siemiatycze | Drohiczyn | 9 |
| Hajnówka County powiat hajnowski |
1,624 | 48,130 | Hajnówka | Kleszczele | 9 |
| Zambrów County powiat zambrowski |
733 | 44,798 | Zambrów | 5 | |
| Mońki County powiat moniecki |
1,382 | 42,960 | Mońki | Knyszyn, Goniądz | 7 |
| Kolno County powiat kolneński |
940 | 39,676 | Kolno | Stawiski | 6 |
| Suwałki County powiat suwalski |
1,307 | 35,136 | Suwałki * | 9 | |
| Sejny County powiat sejneński |
856 | 21,331 | Sejny | 5 | |
| * seat not part of the county | |||||
Historical units
The following is a partial list of political subdivisions in which part or all of current day Podlaskie Voivodeship was wholly or partially contained within:
| Years | Historical Political Unit | Area of present Voivodeship | ||
| East/South Areas |
West Areas |
North Areas |
||
| 1998 1989 |
Third Polish Republic | Białystok Voivodeship | Łomża Voivodeship | Suwałki Voivodeship |
| 1989 1975 |
People's Republic of Poland | Białystok Voivodeship | Łomża Voivodeship | Suwałki Voivodeship |
| 1975 1952 |
Białystok Voivodeship | |||
| 1952 1945 |
Republic of Poland | Białystok Voivodeship | ||
| 1945 1944 |
Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic | Belastok Voblast | ||
| Republic of Poland | Provisional Committees | |||
| 1944 1941 |
Nazi Germany | Bezirk Bialystok | East Prussia | |
| 1941 1939 |
Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic | Belastok Voblast | ||
| Nazi Germany | East Prussia | |||
| 1939 1938 |
Second Polish Republic | Białystok Voivodeship | Warsaw Voivodeship | Białystok Voivodeship |
| 1938 1918 |
Białystok Voivodeship | |||
| 1918 1915 |
German Empire | Bialystok-Grodno District | Lithuania District | |
| Kingdom of Poland | TBD | |||
- Russian Empire
- Grodno Governorate (1842–1915)
- Belostok Oblast (1807–1842)
- Kingdom of Poland (Congress Poland)
Kingdom of Prussia
- Białystok Department (1795–1807)
- Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
- Podlaskie Voivodeship (1569–1795)
- Grand Duchy of Lithuania
- Podlaskie Voivodeship (1513–1569)
- Trakai Voivodeship
- Duchy of Trakai
- Duchy of Lithuania
- Kingdom of Poland
- Duchy of Masovia
- Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia
- Galicia–Volhynia (Land of Berestia)
- Kievan Rus
- Yotvingia
External links
- Radzilow Web Page
- Szczuczyn Web Page
- Wizna Web Page
- VisitBiałystok.com
- (Polish) Podlaski Urząd Wojewódzki Official website
- Natural tourism (birdwatching) in Podlasie
- Topographical maps 1:50 000
References
- ↑ "Przewozy Regionalne". http://www.przewozyregionalne.pl/. Retrieved 23 January 2010.
- ↑ Feasibility study on Rail Baltica railways (by the EU)
- ↑ "Weatherbase: Historical Weather for Białystok, Poland". http://www.weatherbase.com/weather/weather.php3?s=59221&refer=. Retrieved 22 January 2010.
- ↑ "Statistical Office in Białystok". http://www.stat.gov.pl/bialystok/index_ENG_HTML.htm. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- ↑ "Podlaski Urząd Wojewódzki - Podlasie Voivodeship Office" (in Polish). 2007. http://www.bialystok.uw.gov.pl/PUWMCMS/Tlumaczenia/polski.htm.
- ↑ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) Agreement Article XI, Coordination with Polish Authorities" (in Polish). 2007-12-31. http://www.msz.gov.pl/Agreement,regarding,the,placement,in,Poland,of,anti-ballistic,defensive,missile,interceptors,20825.html.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Central Statistical Office (GUS) Population: Size and Structure by Administrative Division" (in Polish). 2007-12-31. http://www.stat.gov.pl/gus/45_655_PLK_HTML.htm.
|
||||||||||
|
|||||||


