Portofino
| Portofino | |
|---|---|
| — Comune — | |
| Comune di Portofino | |
 |
|
 Portofino
|
|
| Coordinates: | |
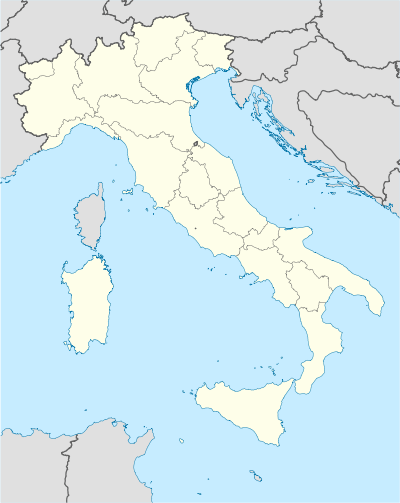
| Country | Italy |
| Region | Liguria |
| Province | Genoa (GE) |
| Government | |
| - Mayor | Giorgio Devoto |
| Area | |
| - Total | 2.6 km2 (1 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 4 m (13 ft) |
| Population (31 October 2006)[1] | |
| - Total | 521 |
| - Density | 200.4/km2 (519/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Portofinesi |
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) |
| - Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) |
| Postal code | 16034 |
| Dialing code | 0185 |
| Patron saint | St. George |
| Saint day | First Sunday in April |
| Website | Official website |


Portofino (Ligurian: Portofin) is a small Italian fishing village, comune and tourist resort located in the province of Genoa on the Italian Riviera. The town crowded round its small harbour is considered to be among the most beautiful Mediterranean ports.
Contents |
History
According to Pliny the Elder, Portofino was founded by the Romans and named Portus Delphini, or Port of the Dolphin, because of the large number of dolphins that inhabited the Tigullian Gulf.


The village is mentioned in a diploma from 986 by Adelaide of Italy, which assigned it to the nearby Abbey of San Fruttoso di Capodimonte. In 1171, together with the neighbouring Santa Margherita Ligure, it was included in Rapallo's commune jurisdiction. After 1229 it was part of the Republic of Genoa. The town's natural harbour supported a fleet of fishing boats, but was somewhat too cramped to provide more than a temporary safe haven for the growing merchant marine of the Republic of Genoa.
In 1409 Portofino was sold to the Republic of Florence by Charles VI of France, but when the latter was ousted from Genoa the Florentine gave it back. In the 15th century it was a fief of families such as the Fieschi, Spinola, Adorno and Doria.
In 1815 it became part of the Kingdom of Sardinia and, from 1861, of the unified Kingdom of Italy.
In the late 19th century, first British, then other Northern European aristocratic tourists began to visit Portofino, which they reached by horse and cart from Santa Margherita Ligure. Aubrey Herbert (1880–1923) was one of the more famous Englishmen to maintain a villa at Portofino. Eventually more expatriates built expensive vacation houses, and by 1950 tourism had supplanted fishing as the town's chief industry, and the waterfront was a continuous ring of restaurants and cafés.
Main sights
- Statue of "Christ of the Abyss", put underwater on August 29, 1954 in the small bay at a depth of 17 metres. This statue was placed to protect fishermen and scuba divers and in memory of Duilio Marcante. Sculpted by Guido Galletti, it represents a benedictory Christ who is looking up towards the sky with open arms as a sign of peace.
- Castello Brown (16th century).
- Church of St. Martin (Divo Martino, 12th century).
- Church of St. George, housing some saints' relics.
- Oratory of Santa Maria Assunta, in Gothic style.
Other
Portofino has inspired a re-creation of the sea side town around the harbour at Tokyo DisneySea in Chiba, Japan, a full scale replication, in authentic detail at the Portofino Bay Resort at Universal Orlando Resort in Orlando, USA which opened in September 1999. Additionally the Gulf Harbour development on the Hibiscus Coast, New Zealand[2] and also Reston in VA, USA. On Top Gear, Richard Hammond raced James May from Portofino to Saint-Tropez in the South of France. Hammond was in a Ferrari Daytona while May was in a speedboat. May eventually won the race by a very small margin.
Twin towns
 Kinsale, Ireland
Kinsale, Ireland Palma de Mallorca, Spain
Palma de Mallorca, Spain Nelson, England, UK
Nelson, England, UK
See also
- Cervara Abbey
- Paraggi
References
- Notes
- ↑ All demographics and other statistics: Italian statistical institute Istat.
- ↑ Gulf Harbour Portofino Model
External links
- Portofino travel guide from Wikitravel
- Comune di Portofino official website
- Portofino Natural Park
- Portofino Marine Protected Area
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

