Rigel
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 |
|
|---|---|
| Constellation | Orion |
| Pronunciation | /ˈraɪdʒəl/{normal-en |
| Right ascension | 05h 14m 32.272s[1] |
| Declination | −08° 12′ 05.91″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 0.18[1] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B8Iab[2] |
| U−B color index | −0.66 |
| B−V color index | −0.03 |
| Variable type | Slightly irregular |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 20.7[2] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 1.87[1] mas/yr Dec.: −0.56[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 4.22 ± 0.81 mas |
| Distance | approx. 800 ly (approx. 240 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −6.7 |
| Details | |
| Mass | 17 M☉ |
| Radius | 78[3] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 66,000(bolometric) L☉ |
| Temperature | 11,000 K |
| Other designations | |
|
Rigel, Algebar, Elgebar, β Ori, 19 Ori, HD 34085, HR 1713, HIP 24436, SAO 131907, TD1 4253
|
|
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
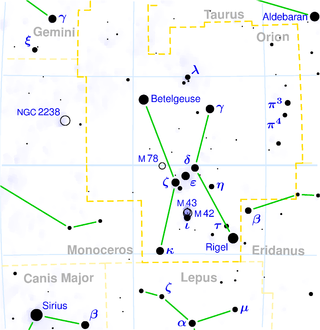
Rigel (β Ori / β Orionis / Beta Orionis) is the brightest star in the constellation Orion and the sixth brightest star in the sky, with visual magnitude 0.18. Although it has the Bayer designation "beta", it is almost always brighter than Alpha Orionis (Betelgeuse).
Contents |
Physical properties
Rigel, a star that is well beyond the current range of accurate parallax measurements; spectroscopic estimates place its distance between 700 and 900 light-years (210 and 280 pc), while Hipparcos's “best guess” is 773 light-years (237 pc), with a margin of error of about 19%.[4] Rigel is a blue supergiant, at 17 solar masses, shining with approximately 85,000 times the luminosity of the Sun.[5] Rigel is the most luminous star in our local region of the Milky Way; the nearest more powerful star is Naos, almost 1,100 light years away in Puppis. The star is so bright that when at 1 astronomical unit from the star, it shines as an unimaginably bright ball with an angular diameter of 35° with magnitude -38. The power flux is 100 MW / m2 which is 10kW / cm2, compared to 1.4kW / m2 for the Sun. which is the same as a few mm from a welding arc so any object will be vaporized (and blown away by the strong stellar wind).
As it is so bright and it is moving through a region of nebulosity, Rigel lights up several dust clouds in its general vicinity, the most notable being the IC 2118 (the Witch Head Nebula).[6] Rigel is also associated with the Orion Nebula, which—while more or less along the same line of sight as the star—is almost twice as far away from Earth. Despite the difference in distance, projecting Rigel's path through space for its expected age brings it close to the nebula. As a result, Rigel is sometimes classified as an outlying member of the Orion OB1 Association, along with many of the other bright stars in that region of the sky; more specifically, it is a member of the Taurus-Orion R1 Association, with the OB1 Association reserved for stars closer to the nebula and more recently formed.[6]
Rigel is variable, in an irregular way common to supergiants, with a range from 0.03 to 0.3 of a magnitude over roughly 22-25 days. The Rigel system is known to be composed of three stars. A fourth star in the system is sometimes proposed, but it is generally considered that this is a misinterpretation of the main star's variability, which may be caused by physical pulsation of the surface.[7]
Spectroscopy
Studies done on Rigel, looking at the Hα lines, have shown a wide variety of configurations. It varies from large emission to large absorption. Current studies are underway to determine if there is a pattern.
Rigel is surrounded by a shell of expelled gas, perhaps shed by its pulsations, stellar wind, or both; the issue remains unsolved.[6]
System
Rigel has been a known visual binary since at least 1831, when it was first measured by F. G. W. Struve. Though Rigel B is not particularly faint at magnitude 6.7, its closeness to Rigel A — which is over 500 times brighter — makes it a challenging target for telescopes smaller than 150 mm (5.9 in).[7] At Rigel's estimated distance, Rigel B is separated from its primary by over 2200 AU; not surprisingly, there has been no sign of orbital movement, though they share the same proper motion.[6][7]
Rigel B is itself a spectroscopic binary system, consisting of two main sequence stars that orbit their center of gravity every 9.8 days. The stars both belong to the spectral class B9V; Rigel B is the more massive of the pair, at 2.5 versus 1.9 solar masses.[6][7]
There was long-running controversy in the late 19th and early 20th century over the possible visible binarity of Rigel B. A number of experienced observers claimed to see it as a double, while others were unable to confirm it; indeed, the proponents themselves were sometimes unable to duplicate their results. Observations since have ruled out the likelihood of a visible companion to Rigel B.[6][7]
Etymology and cultural significance
The star's name comes from its location at the "left foot" of Orion. It is a contraction of Riǧl Ǧawza al-Yusra, this being Arabic for "Left Foot of the Central One". Another Arabic name is رجل الجبار riǧl al-ǧabbār, "the foot of the great one" (giant, conqueror, etc.), which is also the source of the variant name Algebar. It also has the alternative traditional names Algebar or Elgebar, but these are rarely used.
It is known as 参宿七 (Shēnxiù Qī, "The Seventh of the Three Stars") in Chinese. The name is due to the fact that the Asterism of Three Stars was originally composed of just three stars, all of them in the girdle of the Orion. Later, four more stars were added to this asterism, but the name remained unchanged.
In Japan, this star was called Genji-boshi (源氏星) (suggestion from the white flag of Genji clan)[8][9], "the Star of Genji clan" or Gin-waki, (銀脇), "the Silver (Star) beside (Mitsu-boshi)."
In stellar navigation, Rigel is one of the most important navigation stars, since it is bright, easily located and equatorial, which means it is visible all around the world's oceans.
Rigel was known as Yerrerdet-kurrk to the Wotjobaluk koori of southeastern Australia, and held to be the mother-in-law of Totyerguil (Altair). The distance between them signified the taboo preventing a man from approaching his mother-in-law.[10]
See also
- List of largest known stars
- Hypergiant
- Giant star
- Blue supergiant
- List of stellar angular diameters
- List of most luminous stars
- List of brightest stars
- List of most massive stars
- Lists of stars
- Rigel in fiction
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "SIMBAD Astronomical Database". Results for Rigel from The Hipparcos Catalogue. http://webviz.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR?-source=+Hipparcos&-c=Rigel. Retrieved 2008-04-12.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "SIMBAD Astronomical Database". Results for Rigel. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/Simbad. Retrieved 2008-04-10.
- ↑ "Star". NASA. November 29, 2007. http://www.nasa.gov/worldbook/star_worldbook.html. Retrieved 2009-06-24. "Rigel is much larger at 78 solar radii"
- ↑ Calculated in this way: 0.81 / 4.22 * 100 = 19.2
- ↑ Kaler, James. "Rigel". http://www.astro.uiuc.edu/~kaler/sow/rigel.html. Retrieved 2007-02-04.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Jedicke, Peter; Levy, David H. (1992). "Regal Rigel". The New Cosmos. Waukesha: Kalmbach Books. pp. 48–53.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Burnham, Robert, Jr. (1978). Burnham's Celestial Handbook. New York: Dover Publications. pp. 1300.
- ↑ "Daijirin" p.815 ISBN:4385139024
- ↑ Hōei Nojiri "Shin seiza jyunrei" p.19 ISBN: 9784122041288
- ↑ Mudrooroo (1994). Aboriginal mythology : an A-Z spanning the history of aboriginal mythology from the earliest legends to the present day. London: HarperCollins. p. 142. ISBN 1855383063.
External links
- Rigel
- Image of Rigel from APOD
|
|||||||||||||||||