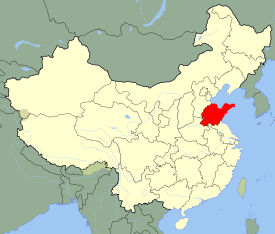
Weihai
| Weihai 威海 |
|
|---|---|
| — Prefecture-level city — | |
| 威海市 | |
 Weihai, Shandong , China |
|
 |
|
| Country | China |
| Province | Shandong |
| County-level divisions | 4 |
| Township-level divisions | 66 |
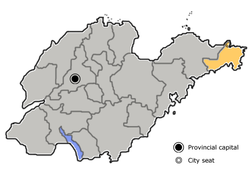
| City seat | Huancui District () |
| Government | |
| - CPC Secretary | Cui Yuechen (崔曰臣) |
| - Mayor | Wang Peiyan (王培廷) |
| Area | |
| - Total | 5,436 km2 (2,098.9 sq mi) |
| Population (2004) | |
| - Total | 2,596,753 |
| - Density | 477.7/km2 (1,237.2/sq mi) |
| Time zone | China Standard (UTC+8) |
| Area code(s) | 631 |
| GDP | RMB 178 billion (2008) |
| GDP per capita | RMB 63,519 (2008) |
| License Plate Prefix | 鲁K |
| Website | http://www.weihai.gov.cn/ |
| City Flower: Sweet Osmanthus, Osmanthus fragrans City Tree: Silk Tree, Albizia julibrissin |
|
Weihai (Chinese: 威海; pinyin: Wēihǎi) is a prefecture-level city in eastern Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It is the easternmost prefecture-level city in the province and a major seaport. Between 1898-1930, the town was a British colony. Weihai was not developed in the way that Hong Kong, the other British colony in China, was developed, because Weihai fell into Germany's sphere of influence. It was largely used as a naval station and a sanatorium. During the colonial period it was known as Weihaiwai or the Weihai Garrison (simplified Chinese: 威海卫; traditional Chinese: 威海衛; pinyin: Wēihǎi Wèi), and sometimes as Port Edward. Weihai borders Yantai to the west and the Yellow Sea to the east.
Contents |
Administrative divisions
The prefecture-level city of Weihai administers four county-level divisions, including one district and three county-level cities.
- Huancui District (环翠区)
- Wendeng City (文登市)
- Rongcheng City (荣成市)
- Rushan City (乳山市)
These are further divided into 66 township-level divisions, including 52 towns and 14 subdistricts.
History
The port was once the base for the Beiyang Fleet of China during the Qing Dynasty. During 1895, the Japanese captured it from the landward side. It was evacuated during 1898.
After Russia leased Port Arthur (on the opposite coast) from China for 25 years during March, 1898, the United Kingdom obtained a lease for Wei Hai Wei which was to exist for as long as the Russians leased Port Arthur. During 1905, when the Japanese assumed ownership of the lease for Port Arthur, the British lease was made to exist as long as the Japanese occupied Port Arthur. Thus the city was part of a territory (c.285 sq mi/740 km²) called "Weihaiwei", which was leased by the United Kingdom from 1898 until October 1, 1930. It was a summer station for the British naval China Station and it was also used as a sanatorium. It became one of two major ports for ships of the Royal Navy in the Far East (the other being Hong Kong in the south).
At the beginning of the lease the territory was administered by a Senior Naval Officer of the Royal Navy. During 1899, administration was transferred to a military and civil commissioner appointed by the War Office in London. The territorial garrison consisted of 200 British troops and a specially constituted Chinese Regiment with British officers. During 1901, it was decided that this base should not be fortified, and administration was transferred to the U.K.'s Colonial Office. A Civil Commissioner was appointed during 1902 to manage the territory, and the Chinese Regiment was disbanded during 1903.
The last British commissioner of Weihaiwei was Reginald Johnston. It was briefly a special administrative region after it was returned to the Republic of China, the successor of the Qing Dynasty. During 1949, Weihaiwei City was established, and was renamed Weihai City after it was occupied by the People's Republic of China.
During recent years, a proposal regarding the territoriality of Weihai during the 1800s was discovered in the British Archives. The proposal, made apparently by Hong Kong governor Sir Frederick Lugard, stipulated that the British would revert Weihai to Chinese rule, and receive perpetual rule of the 1898 leased territories of Hong Kong in return. This proposal was never adopted.
The nickname British sailors gave to this port was "Way High"; it was also sometimes referred to as Port Edward in English.
Geography and climate
| Weihai | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart () | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Weihai is surrounded by sea on three sides and the harbor is protected by Liugong Island. It is located on the north-eastern seashore of Shandong Province in China at .
Weihai lies in the transition zone between a humid subtropical and Humid continental climate (Koppen climate classification Cwa/Dwa), but as it is at the eastern tip of the Shandong Peninsula, its climate is strongly moderated by the surrounding Yellow Sea: springtime warming and autumn cooling are delayed by one month, and the average diurnal temperature throughout the year is very small - at only 5.0 °C (9.0 °F). Winters are cold and dry, with a January mean of −0.3 °C (31.5 °F), but warmer than places further inland. Spring begins in mid-March, lasting until late June. Summers are very warm, but the August high only averages 25.9 °C (78.6 °F). Precipitation is sparse in winter and is heavily concentrated in the summer months, totaling 665 millimetres (26.2 in).
| Climate data for Weihai (Chengshantou Cape, Rongcheng, 1971-2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration [1] | |||||||||||||
Economy
At present, Weihai is a commercial port and major fishing center with some light industries. Due to its close proximity to South Korea, Weihai also has a large Korean business community and receives many Korean tourists. Weihai is also a key production area for peanuts and fruit.
Industrial Zone
- Weihai Economic & Technological Development Zone
Weihai Economic and Technological Development Zone is a state-level development zone approved by the State Council on Oct 21, 1992. The administrative area has an area of 194km2, including the programmed area of 36km2 and an initial area of 11.88km2. Its nearest port is Weihai Port, and the airport closest to the zone is Wuhai Airport.[2]
- Weihai Export Processing Zone
Weihai Export & Processing Zone (EPZ) was set up by the approval of the State Council on April 27, 2000. Weihai EPZ is located in Weihai Economic & Technological Development Zone with programmed area of 2.6 km2. Weihai EPZ belongs to comprehensive export & processing zone. The EPZ is located 30 km to Weihai Airport, 3 km to Weihai Railway Station and 4 km to Weihai Harbor.[3]
- Weihai Torch Hi-Tech Science Park
Weihai Torch Hi-Tech Science Park is a state-level development zone approved by the State Council on March 1991. Located in Weihai's northwest zone of culture, education and science, the Park has the total area of 111.9 square kilometers, the coastal line of 30.5 kilometers and 150,000 residents. It is 3 kilometers away from the city center, 4 kilometers away from Weihai Port, 10 kilometers away from Weihai Railway Station, 30 kilometers away from Weihai Airport and 80 kilometers away from Yantai Airport.[4]
Education
Campuses of Shandong University and Harbin Institute of Technology are located in Weihai.
Transportation
Weihai Airport serves the city with regular service to Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Harbin domestically and the Korean cities of Seoul and Pusan. The K8262 and K8264 trains depart everyday at 7:17AM and 9:52PM respectively for Jinan, the provincial capital, the K412 goes directly to Beijing at 7:49PM, and the No. 1064 train leaves at 8:27AM for Hankou, one of the two railway stations of Wuhan, Hubei. Internally, the city is served by about 50 bus routes.
Sister cities
 Cheltenham, United Kingdom (since May 21, 1987)
Cheltenham, United Kingdom (since May 21, 1987) Ube, Yamaguchi, Japan (May 18, 1992)
Ube, Yamaguchi, Japan (May 18, 1992) Santa Barbara, California, United States (December 8, 1994)
Santa Barbara, California, United States (December 8, 1994) Yeosu, South Korea, (February 17, 1994)
Yeosu, South Korea, (February 17, 1994) Sochi, Russia (October 18, 1996)
Sochi, Russia (October 18, 1996) Biella, Italy (October 22, 1996)
Biella, Italy (October 22, 1996) Timaru, New Zealand (July 30, 1998)
Timaru, New Zealand (July 30, 1998) Brazzaville, Republic of the Congo (May 24, 2004)
Brazzaville, Republic of the Congo (May 24, 2004) Novopolotsk, Republic of Belarus (April 25, 2006)
Novopolotsk, Republic of Belarus (April 25, 2006)
See also
- Liugong Island
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年)" (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. http://cdc.cma.gov.cn/shuju/search1.jsp?dsid=SURF_CLI_CHN_MUL_MMON_19712000_CES&tpcat=SURF&type=table&pageid=3. Retrieved 2010年5月27日.
- ↑ RightSite.asia | Weihai Economic & Technological Development Zone
- ↑ RightSite.asia | Weihai Export Processing Zone
- ↑ RightSite.asia | Weihai Torch Hi-Tech Science Park
External links
- Government website of Weihai (available in Chinese, English, Japanese and Korean)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||