Cagayan de Oro City
- This article is about the City of Cagayan de Oro. For other meanings of the word, see Cagayan (disambiguation).
| City of Cagayan de Oro Dakbayan sa Cagayan de Oro Cagayan de Oro |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| — City — | |||
 |
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s): City of Golden Friendship | |||
 |
|||
 City of Cagayan de Oro
|
|||
| Coordinates: | |||
| Country | |||
| Island | Mindanao | ||
| Region | Northern Mindanao (Region X) | ||
| Class | 1st Class City; Highly urbanized | ||
| Province | Misamis Oriental (Capital) | ||
| Districts | 1st and 2nd Districts of Cagayan de Oro City | ||
| Barangays | 80 | ||
| Incorporated (Town) | 1871 | ||
| Incorporated (City) | June 15, 1950 | ||
| Government | |||
| - Type | Mayor-council | ||
| - Mayor | Vicente Y. Emano (Padayon Pilipino) | ||
| - Vice Mayor | Caesar Ian E. Acenas (Padayon Pilipino) | ||
| - Headquarters | Executive Building (Old City Hall) | ||
| - Representatives |
City Representatives
|
||
| - City Council |
Councilors
|
||
| Area | |||
| - Total | 488.86 km2 (188.7 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 10.0 m (33 ft) | ||
| Population (2007) | |||
| - Total | 553,966 | ||
| - Density | 945/km2 (2,447.5/sq mi) | ||
| - Demonym | Cagayanons, Kagay-anons | ||
| - Languages | Cebuano, Filipino (Tagalog), English | ||
| Time zone | PST (UTC+8) | ||
| ZIP Code | 9000 | ||
| Area code(s) | 88, 8822 | ||
| Abbreviations | CDO, CDOC, CdeO, Cag. de Oro | ||
| Website | www.cagayandeoro.gov.ph | ||
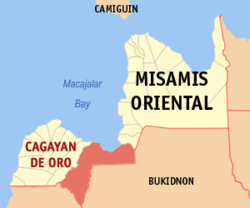
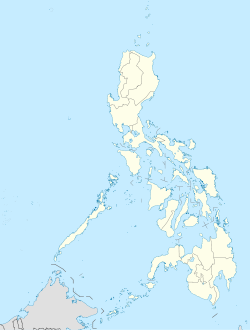
The City of Cagayan de Oro; (Cebuano: Dakbayan sa Cagayan de Oro; Filipino (Tagalog): Lungsod ng Cagayan de Oro), is the provincial capital city of the Province of Misamis Oriental and classified as first class city. Abbreviated CDO, CDOC, CdeO or Cag. de Oro, lies along the northern coastline on the Mindanao island, southern part of the Philippines.
It is considered as the melting pot of Mindanao in the Philippines because of its accessibility, business growth, attractions and most of its entire warm and hospitable people. The city serves as the regional center being the most populous highly urbanized city in Northern Mindanao (Region X). According to the 2007 Census, the city has an estimated population of about 553,996 inhabitants.
Cagayan de Oro is known by many nicknames such as "Gateway to Northern Mindanao" because of its location and good transportation facilities, "Rafting Capital of the Philippines", it is a primary whitewater rafting destination in the Philippines that has a whole year round of maneuverable rafting courses and is located within the city limit, "ICT Goldmine of the Philippines" due to its number of ICT infrastructures and businesses mushrooming the city providing job opportunities for ICT personnel and "A City in Bloom, in Blossom and in BOOM!" because of the great strides it has made by way of progress, notably in the last few years. Officially, Cagayan de Oro is dubbed locally as the "City of Golden Friendship" (Dakbayan sa Bulawanong Panaghigalaay) for its warm people. The official city seal bears this phrase.
There are also other places in the Philippines with a Cagayan name. One must distinguish Cagayan de Oro from Cagayan Province in Northern Luzon and the Cagayan Islands in the Sulu Sea.
Contents |
Etymology
The name Cagayan can be traced back during the arrival of the Spanish Augustinian Recollect friars in 1622, the area around Himologan (now Huluga), was already known as Cagayan. In fact, early Spanish documents in the 1500s already referred to the place as Cagayan. The area of Northern Mindanao, which included Cagayan, was granted as Encomienda to a certain Juan Griego on January 25, 1571. Former Congressman and Vice President of the Philippines Emmanuel Pelaez appended de Oro to Cagayan in recognition of the gold mining activities in the area known to Spaniards explorer, which is a combination of the ancient Malayo-Polynesian and Spanish languages that translates to "City of the River of Gold".
History
The area was first inhabited around 377 A.D. (the late Neolithic period), island natives lived in a settlement then known as Himologan[1] (now known as Huluga), eight kilometers from present day Cagayan de Oro. The natives were polytheistic animist and paid tributes to Sultan Muhammad Dipatuan Kudarat, the Sultan of Maguindanao.
In 1622, two Spanish Augustinian Recollect Missionaries came in contact with the natives of Himologan and in 1626, Fray Agustin de San Pedro persuaded the chief of Himologan, Datu Salangsang, to transfer his settlement down river, to the present-day Gaston Park. Fray Agustin later fortified the new settlement against warriors who were sent by Sultan Kudarat.
In 1738, Spanish dominance was felt in Cagayan de Oro. When Misamis gained status of province in 1818, one of its four districts was the Partidos de Cagayan. In 1871, the "Partidos" became a town and was made a permanent capital of Misamis.
On February 27, 1872, the Spanish Governor-General Carlos Maria de La Torre issued a decree declaring Cagayan the permanent capital of Segundo Distrito de Misamis. During this era, the name of the town was known as Cagayan de Misamis.
In 1883, the town became a seat of the Spanish government in Mindanao for the Provinces of Misamis Oriental, Misamis Occidental, Bukidnon and Lanao del Norte.
On January 10, 1899, Cagayan de Misamis joined the Philippine government of Emilio Aguinaldo and celebrated its independence from Spain. It was the second time the Aguinaldo government was declared and the new Philippine flag raised on the Mindanao island.
By virtue of the 1898 Treaty of Paris, Spain ceded the Philippines to the United States of America; this caused friction and resulted in the Philippine-American War. In March 31, 1900, the Americans occupied Cagayan de Misamis and on April 7, 1900, battle erupted in the town center led by General Nicolas Capistrano[2] and Filipino resistance fighters. This would later be known as the Battle of Cagayan de Misamis. The Americans won the war, and about forty years later, gave the Philippines its Independence July 4, 1946.[3]
The war years in Cagayan de Oro were prompted by the presence of the Americans in 1898. The Americans were initially and successfully repulsed by the Kagay-anons forces lead by Mayor Don Apolinar Velez at the historic Battle of Makahambus on June 4, 1900.
After the troubled years, peace finally brought back the economic activities to normal under the guidance of Americans. Consequently, from a purely farming-fishing area, Cagayan de Oro emerged into a booming commerce and trade center.
On June 15, 1950 former President Elpidio Quirino signed Republic Act No. 521 in the Malacañang Palace, which granted the status of a chartered city to the Municipality of Cagayan de Misamis. This was made possible through the efforts of then Congressman Emmanuel Pelaez, who eventually became the Vice President of the Philippines.
Cagayan de Oro was declared a highly urbanized city by the Ministry of Local Government on November 22, 1983.
Geography
Location
Cagayan de Oro is located along the central coast of Northern Mindanao. It is situated in Mindanao, the second giant of the archipelago of all the landmass of the Philippines. The southern portion of the city is bordered by the Provinces of Bukidnon and Lanao del Norte. The Municipality of Opol borders the city on the west and Tagoloan, Misamis Oriental to the east. To the north lies Macajalar Bay facing Bohol Sea. Its total land area is 488.86 km² representing 13.9% of the entire Misamis Oriental Province. It includes 25 kilometers of coastline and a fine deep-water harbor, Macajalar Bay. 44.7% of the surface of Cagayan de Oro is classified as agricultural land and 38.4% is classified as open spaces.[4]
Districts
Cagayan de Oro is politically subdivided into 80 barangays. These are grouped into two congressional districts: 24 barangays in the 1st District (West) and 56 barangays in the 2nd District (East), with Cagayan de Oro River as the natural boundary. The city has a 57 urban barangays and 23 rural barangays all in all.
1st District (West)
|
2nd District (East)
|
|
|
Climate
Cagayan de Oro has a tropical climate. The average temperature whole year round is 28 °C (82 °F). The highest recorded temperature in the city was 39 °C (102 °F) on June 1998. Cagayan de Oro receives an even amount of rain through out the year. The driest month is April, while July is the wettest. Wet season in the city starts in June and ends in November. Drier season starts in December and ends in May. The city is outside the typhoon belt, but it is affected by the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone.
| Climate data for Cagayan de Oro, Philippines | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 37 (99) |
38 (100) |
38 (100) |
38 (100) |
38 (100) |
39 (102) |
37 (99) |
37 (99) |
36 (97) |
37 (99) |
38 (100) |
37 (99) |
39 (102) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30 (86) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
32 (90) |
32 (90) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 17 (63) |
17 (63) |
18 (64) |
20 (68) |
22 (72) |
18 (64) |
17 (63) |
21 (70) |
22 (72) |
18 (64) |
20 (68) |
18 (64) |
17 (63) |
| Source: Weatherbase[5] | |||||||||||||
Language
Cebuano is the city's main conversational language. English is mainly used for business, written text and is also widely used by the academic community. Most of the local populations are also fluent in Filipino (Tagalog) the country's national language. Other dialects are Higaonon, Chinese, Spanish, Ilongo, Maranao, Waray among others.
People
The residents of Cagayan de Oro are a mixture of Spanish-American, Maranao, Bukidnon-Higaonon and Chinese blood. There are about 44% of the household population in Cagayan de Oro classified themselves as Visayan (Binisaya or bisaya), 22.15% as Cebuano, 4.38% as Boholano, while 28.07% as other ethnic groups (2000 Census).[6]
Religion

Roman Catholic is the city's dominant religion, represented by almost 85% of the population. Other religious affiliations includes Seventh Day Adventist, Iglesia ni Cristo, Philippine Independent Church, United Church of Christ, CCF, Islam among others. Archdiocese of Cagayan de Oro is an Archdiocese of the Roman Catholic Church in the Philippines. The archdiocese comprises three civil Provinces of Misamis Oriental, Bukidnon and Camiguin. It is a metropolitan see in the island of Mindanao. The current Archbishop is Most Reverend Antonio J. Ledesma, S.J., D.D., who was installed on March 4, 2006 and its seat is located at St. Augustine Metropolitan Cathedral. Recently, the Basilica of the Black Nazarene in Quiapo Church has also decided to move the replica statue of the Black Nazarene to Jesus Nazareno Parish Church in Cagayan de Oro, so that Black Nazarene devotees from Mindanao may not have to travel to Quiapo in Manila for their annual pilgrimage.
Infrastructures
Education
Aside from being the commercial capital of Northern Mindanao, Cagayan de Oro is also considered as the school capital of the region and home to several universities, colleges and tertiary schools. It has three major private universities: Capitol University, Liceo de Cagayan University and the first university in Mindanao is Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan. These institutions specialize in various disciplines such as medicine, nursing, commerce, engineering, and law, as well as graduate and post-graduate courses. The Mindanao University of Science and Technology (formerly Mindanao Polytechnic State College) is the only state university in the city.[7] AMA Computer University, Philippine Women's University and San Beda College has campus branches in the city offering limited courses. There are also a number of foreign schools in the city with study programs.
Health care

Cagayan de Oro has a hospital bed to population ratio of 1:474 as of 2003. There are twelve major well-equipped private and government-run hospitals including 50 Barangay Health Centers and 20 Family Planning Centers. There are also modern diagnostic centers and laboratories operating in the city.[4] J.R. Borja Memorial Medical Hospital (formerly City Hospital) and Northern Mindanao Medical Center (formerly Provincial Hospital) are the two main government-run hospitals. Polymedic Medical Plaza and Capitol University Medical City are the newer developments of the health services in city. In the recent years, private hospitals in the city have embarked on an aggressive expansion program. There has been a strong demand for medical facilities not only within the city but also from nearby Mindanao provinces.
Utilities
- There are five major land based phone companies: MisOrTel, PLDT-PhilCom, Smart Broadband (formerly CruzTelCo), BayanTel and ItalTel serving the city.
- Mobile phone services are provided by Globe, Smart and Sun Cellular.
- There are several Internet companies operating in the city offering dial up, broadband, Wi-Fi and cable services. Pueblo de Oro Business IT Park located in Upper Carmen is the first PEZA-registered IT park in Mindanao. The IT Park currently houses one of Cagayan de Oro's call centers.
- Water services are provided by the Cagayan de Oro Water District (COWD), it was the first water district established in the entire Philippines.
- Electricity is provided by the Cagayan Electric Power and Light Company (CEPALCO). CEPALCO, which began operations in 1952, covers the City of Cagayan de Oro and the Municipalities of Tagoloan, Villanueva and Jasaan, all in the Province of Misamis Oriental, including the 3,000-hectare PHIVIDEC Industrial Estate and caters to more than 100,000 consumers. The company's distribution system network now includes 138KV, 69KV, 34.5KV and 13.8KV systems. CEPALCO is also operating the developing world's first and largest (at the time of its inauguration in 2004) on-grid Solar Photovoltaic power plant. The 1-megawatt polycrystalline silicon-based Photovoltaic (PV) plant in Barangay Indahag of this city is connected with the distribution network of CEPALCO. It is the biggest solar power plant connected to the power grid in Southeast Asia.[8]
Economy

Cagayan de Oro is the business hub of Northern Mindanao region and the melting pot of Mindanao, considered as one of the most progressive and competitive cities in the Philippines. It was recorded to have reached the annual income of 1.345 billion pesos as of the fiscal year 2006. The city's economy is largely based on industry, commerce, trade, services and tourism. These are the major financial sources of the city and it has been sufficient for the city's economic growth development. Concentrix and Arriba Telecontact are among the few call centers that have recently opened their doors to the city. With the ongoing construction of the Laguindingan International Airport located in the Municipality of Laguindingan with international standard, business analysts predict the entry of more foreign and local investments and an increase in tourism activity in the region will make Cagayan de Oro as one of the chief cities in the southern part of the Philippines.[4] Cagayan de Oro is base to a multinational companies such as Del Monte Philippines. Pineapples in nearby Bukidnon Province are transported to their processing plant in Barangay Bugo and shipped to the entire Philippines and Asia-Pacific regions.
The city's business climate continues to rise with opening of new business establishments everywhere. Because of the influx of tourist's both local and foreign, the city's hotel demand is fast rising. In the past few years, new hotels had opened, current hotels are undergoing expansion and more hotels and in the pipeline to meet the demand. Also being a convention city, the city hosts numerous conventions and other large gatherings every year. More and more people keep coming back to the city. Despite the global recession, the city is currently having a construction boom, similar to what the city experienced in the mid-1990s. With its strategic location and the impending opening of the under construction Laguindingan International Airport, the city's progress is on a high note. Cagayan de Oro is a favorite destination among businessmen because of its stable peace and order, urban amenities, active private business sector, good banking system and credit facilities, strategic location of Cagayan de Oro via international and domestic markets, center for transportation and communication and many shopping centers and convenience stores.
Transportation
As the gateway to Northern Mindanao, Cagayan de Oro is very accessible by land, air and water transportations. It is also home of the busiest airport and seaport in the country, the place can assure safe and secure journey.
Airports
- Lumbia Airport is the second-busiest airport in Mindanao, often called as Cagayan de Oro Airport caters domestic flights to and from Manila and Cebu. From Manila, it is an hour and fifteen minutes away by plane and from Cebu is about forty-five minutes away. Lumbia Airport is set to be replaced by the larger Laguindingan International Airport, currently under construction in the Municipality of Laguindingan, some 46 kilometers southwest of Cagayan de Oro. When it finished, the international airport will serve Northern Mindanao including its major cities; Iligan and Cagayan de Oro.
- Laguindingan International Airport, currently ongoing construction located in the Municipality of Laguindingan that will serve Northern Mindanao including its major cities; Iligan and Cagayan de Oro, and soon caters international flights to South Korea and other parts of the world. It is a flagship project of the Cagayan de Oro-Iligan Corridor Special Development Project, which covers both cities of Iligan and Cagayan de Oro, as well as five coastal towns in Lanao del Norte, and in the twenty two towns especially Gingoog of Misamis Oriental first and second congressional districts. The airport sits on a 4.17 square kilometer site in Barangay Moog, Laguindingan, Misamis Oriental[9] and located 46 kilometers from the existing Lumbia Airport. It was inaugurated on January 11, 2006 with groundbreaking ceremonies presided by President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo, who advocated the idea of an international airport in the Cagayan de Oro-Iligan Corridor.[10] Upon its completion, it will be the fourth international airport in Mindanao, after Francisco Bangoy International Airport in Davao, Zamboanga International Airport in Zamboanga and General Santos International Airport in Gen. Santos, as well as the first international airport in Northern Mindanao (Region X). Construction of the international airport will be completed by 2011.
Seaport

Cagayan de Oro Port is a modern international seaport situated near the estuary of Cagayan de Oro River, it has an anchorage depth of 18 meters and is around 400 meters from the shoreline. It has two authorized cargo-handling operators. With the recent completion of the P250 million rehabilitation project, the port is now the largest international and domestic seaport in the country.[12] The international seaport serves regular trips to and from Manila, Cebu, Tagbilaran, Bacolod, Dumaguete, Iloilo and Jagna, Bohol. It is the busiest seaport in the Philippines. General Milling and Del Monte Philippines also operates their own port facilities within Cagayan de Oro. The $85 million Mindanao International Container Port is located in Tagoloan, Misamis Oriental 17 kilometers from Cagayan de Oro serves the PHIVIDEC Industrial Estate.
Public transport

Cagayan de Oro is quite sufficient when it comes to land transportation. It can easily roam around the city by any means of land transport. To go around, there is a number of private firms provide rent-a-car services; operate taxi cabs, public utility jeepneys and trucking or hauling services. Taxis in the city are all air-conditioned and most are new models. They are both colour yellow and white, and have yellow plates. Another land transportation in the city is the Rela, Cagayan de Oro's version of the Philippine tricycle. It is a common mode of transportation within the city proper, which can seat around six to eight people and could get cramped. This is not an advised mode of transportation for plus sized people.
There are three major integrated bus and jeepney terminals, which offer regular land trips:
- Agora Integrated Bus Terminal offers regular land trips to and from Gingoog, Bukidnon, Kabacan, North Cotabato, Butuan, Surigao in the Caraga region, Davao, Tacurong and Balingoan (ferry going for Camiguin). Recently, the terminal is on a huge renovation.
- Eastbound-Gusa Jeepney Terminal offers regular land trips to and from Gingoog, the cities of Malaybalay and Valencia in Bukidnon, eastern towns of Misamis Oriental, Camp Philips, Libona and Manolo Fortich in Bukidnon.
- Westbound Integrated Bus and Jeepney Terminal offers regular land trips to and from western towns of Misamis Oriental including Laguindingan and El Salvador, Iligan, Marawi, Oroquieta, Ozamiz, Dipolog, Pagadian, Zamboanga and some parts of western Mindanao.
Government

Cagayan de Oro has been administered by elected and appointed officials since June 15, 1950, with a strong Mayor-council government. The city political government is composed of the Mayor, Vice Mayor, two Congressional districts Representatives, sixteen City Councilors, one Sangguniang Kabataan (SK) Federation Representative and an Association of Barangay Captains (ABC) Representative. Each official is elected publicly to a three-year terms. The current Mayor of Cagayan de Oro is Vicente Emano with his Vice Mayor Ian Acenas.
Most respected Mayor of Cagayan de Oro
Many residents of Cagayan de Oro consider Justiniano R. Borja the most admired and respected mayor of Cagayan de Oro. A graduate of Silliman University, Borja started his government service in 1954. He was responsible for the phenomenal growth of the city since 1959, when he opened the Cogon Public Market. A statue built in his honor stands at the Plaza Divisoria, made by national artist for sculpture Napoleon V. Abueva. Borja was called the "Arsenio Lacson of Cagayan de Oro" because he was above all and no non-sense. He ruled without fear or favor. He had political will. Most importantly, he remained simple and would walk to and from his office without any bodyguards. Borja is the only city mayor who has been given multiple honors, proof of how much he was loved by the city that he served so well. There are J.R. Borja Street, J.R. Borja Memorial Medical Hospital (formerly City Hospital) and a statue located at Plaza Divisoria (Golden Friendship Park). He was the only city mayor of Cagayan de Oro given a doctorate degree "Honoris causa" in public administration by Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan.
Law enforcement
Cagayan de Oro, being the regional center is the base to major military and police camps in Northern Mindanao region.
- Camp Vicente Alagar is the headquarters of the Philippine National Police (PNP). It is located in Barangay Lapasan on top of a hilly area overlooking the city. Camp Alagar has jurisdiction over the entire Northern Mindanao, namely the Provinces of Bukidnon, Camiguin, Lanao del Norte, Misamis Occidental and Misamis Oriental including its major cities; Cagayan de Oro and Iligan.[13] Recently, the national government provided new vehicles and equipments to improve police response time and increase police visibility in the city.
- Camp Edilberto Evangelista, located in Barangay Patag is the largest military camp in Mindanao with an area of 129 hectares. It is home to the 4rth Infantry Division of the Philippine Army. Camp Evangelista's external jurisdiction covers the Northern Mindanao and Caraga regions. Minor military camps are also located in Barangay Lumbia and Upper Puerto.
Tourism
Cagayan de Oro is considered as one of the Tourist' spots in the Philippines. The city is also a favorite among nature lovers and adventurers because of its famous whitewater rafting. Whitewater rafting[14] has been one of the tourism activities being promoted in the Cagayan de Oro River. The city administration and the Department of Tourism made it as the banner tourism activity in Cagayan de Oro.[15] Due to the national government's aggressive tourism campaign, local and foreign tourist arrivals in the city is on the rise. In 2004, the city registered a tourist arrival of 307,820; an increase from a previous of 232,257 in 2003.[4] Other tourist destinations in the city include Gardens of Malasag Eco-Tourism Village, Mapawa Nature Park, Macahambus Cave and Gorge, and Guadalupe Shrine. Cagayan de Oro is also the jump-off point for the island paradise of Camiguin and other interesting places such as Divine Mercy Shrine in El Salvador City and the Canopy Walk in Claveria, Misamis Oriental.
Parks and resorts



- Gaston Park and St. Augustine Cathedral, the park is located across the St. Augustine Metropolitan Cathedral, the city's main Roman Catholic Church and Seat of the Archdiocese of Cagayan de Oro. The park, noted for its water-dancing fountain, is a favourite place to unwind for many Kagay-anons, especially during Sundays.
- Whitewater Rafting and River Trekking along the Cagayan de Oro River has gained popularity through the years after former President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo herself went whitewater rafting in 2002.[16]
- Catanico Falls is concealed by huge boulders, the rapids, cascading falls and natural pool of Barangay F.S. Catanico.
- Mapawa Nature Park for horseback riding, biking, zipline and nature trekking adventures.
- The Gardens of Malasag Eco-Tourism Village is located in a reforested area in Malasag Hill. This seven-hectare village has replicas of tribal houses in the region and a panoramic view of Macajalar Bay. The tourism village is owned and managed by the Philippine Tourism Authority.[17]
- Gov. Vicente de Lara Park is situated in front of the Provincial Capitol of Misamis Oriental with age-old mahogany trees that provide a therapeutic canopy for the promenades. This is also the site of the Press Freedom Monument and a Signature Sculpture Tableau of Misamis Oriental. The park is a popular jogging area during the morning.
- Plaza Divisoria (Golden Friendship Park) is located in downtown area, it was built in the early 1900s as a town divider Divisoria or fire breaker after a great fire that almost burned down the entire town. It is now a park dedicated to local and national heroes like President Ramon Magsaysay, Andres Bonifacio, Dr. Jose Rizal, and former Cagayan de Oro Mayor Borja. The Kiosko Kagawasan, City Tourism Information Center and the Park Café are located in Plaza Divisoria..[18]
- Bonifacio Park is among several parks located in Plaza Divisoria. Most of the Kagay-anons soldiers who died during the Philippine-American War are buried beneath the monument.
- Rizal Park is a park dedicated to the country's national hero Dr. Jose Rizal, who was been executed by the Spanish authorities, located in Plaza Divisoria. The monument has survived the ravages of time including World War II.
- Kagay-an Resort (formerly Lawndale Spring) in the Taguanao area, is usually packed with families and groups on weekends lounging in the cold springs.
- Pueblo de Oro Township in upper Carmen is an expansive class business and residential area. This is where Hotel Koresco, SM City Cagayan de Oro, Pueblo de Oro Golf Course and Country Club designed by Robert Trent Jones II, and hosts of middle to high-end residential areas are located. It is also home to the Pueblo de Oro Business IT Park, the first PEZA-registered IT park in Mindanao. The IT Park currently houses one of Cagayan de Oro's call centers.

- High Ridge is located on a hilltop in Aluba area. High ridge has been open to the public for outdoor picnics and a scenic view of Cagayan de Oro.
- Monigue Cave is located in Barangay Mambuaya this city; the cave entrance is flowing water from underground stream. The cave has a small opening that seems too narrow to be passable, it has a six inches airspace between ceiling and water that you have submerge yourselves one by one, equipped with a helmet and a water-proof cap lamp. It contains a beautiful sparkling formation, which is called the Calcium Carbonates (CaCO3) or Calcites. These stalactites and stalagmites, white and brown, are sign of oxidized materials that take 50–60 years to form an inch the cave is definitely spellbinding. There were formations of flowstone, gurpool-resembling, rice terraces, transparent crystals and picturesque speleothems, such as cathedral drapes and icons.
- Macahambus Adventure Park is located in Barangay Lumbia, one can experience walking on a suspended steel bridge connected to a trees about hundred feet above ground level. Crossing back using a zip line or rappel down to the Macahambus Hill and Cave, and this is also the site of the historical battle between Kagay-anons and American soldiers during the Philippine-American War (Philippine Insurrection) circa 1900s.
Museums and Historical places
- City Museum formerly a water tower built in 1922 just near the Gaston Park and St. Augustine Metropolitan Cathedral. Recently, it was been upgraded into a museum.
- Museo de Oro is a museum located within the campus of Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan. The museum exhibits artefacts dug from Huluga Cave and repertoire of Bukidnon and Maranao cultures that have survived the ravages of time.[18]
- Museum of Three Cultures is a newly opened museum of Capitol University. It houses a gallery of Maranao antiquities from Tugaya, Lanao del Sur; a gallery of ethno history which shall display Cagayan de Oro history, Butuan archaeological artefacts, lumad arts and crafts from the Higaonon and Manobo cultures, and a treasure of Christian lowland artefacts of Northern Mindanao; and finally an art gallery and coffee shop that shall promote the local visual arts of Mindanao. It also has a research archives that will house Spanish era documents, photographs, memorabilia of well-known personalities in Mindanao, which is open to all researchers and students of culture.
- La Castilla is a museum of Philippine household heirlooms and antiques. This is the Rodolfo and Elsa Pelaez family memorabilia administered by the Liceo de Cagayan University.
- Huluga Caves is an archaeological site in Sitio Taguanao, Barangay Indahag. It is composed of an open site and two caves where skeletal remains of a child and woman were found. A fragment of the woman's skull was 377 A.D. by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in La Jolla, California, USA. The open site is the venue of prehistoric settlement.
- Plaza de Los Heroes is a memorial park dedicated to the heroes of the Three Battles of Cagayan de Oro during the Philippine-American War. It is located along Mastersons Avenue in Upper Carmen.
- Executive Building (Old City Hall) is Seat of the Local Government. This is a former Spanish provincial Governors residence and was called before as Casa Real de Cagayan.
- Gen. MacArthur Memorial Marker is located at the edge of Cagayan de Oro Port, the monument commemorates two historical events.
- Macahambus Cave is an underground cave with a 130 foot (40 m) circular gorge. The ravine is thick with various species of plants and huge trees. It is the site of the historic Battle of Makahambus Hill between Kagay-anons and American soldiers during the Philippine-American War (1900).[19]
- MOGCHS Administration Building was part of the 1907 Gabaldon initiatives to established and build public schools all over the Philippines under the American regime.
- Gaston Park named after a former Mayor of Cagayan de Oro. It was the site of the first Spanish settlement established in 1622. Gaston Park is noted for its water-dancing fountain and a favourite place to unwind for many Kagay-anons, especially during Sundays.
- Balay na Bato (Casa del Chino Ygua ) was built in 1882 by Sia family, the first Chinese migrants in Cagayan de Oro. Most of the revolutionaries died and buried behind the house during the Philippine-American War.
Shopping


Cagayan de Oro is the shopping capital of the Northern Mindanao region. Residents from nearby provinces visit the city to shop and enjoy the mall facilities with numerous of department stores, supermarkets, retail stores and modern public markets. SM Prime Holdings and Robinsons Land Corporation is drawing plans to further expand their mall operations in the city proper. Ayala Land recently launched its residential estate in Barangay Indahag and would soon construct its own mall, the Ayala Center Cagayan de Oro. Plans are also underway for the construction of Pacific Island City Mall along Barangay Nazareth.
Major Shopping centers are as follows:
- Limketkai Center is the pride of Cagayan de Oro, which covers around 25 hectares making it one of the most expansive commercial complexes in the country. Located in the heart of the city in Lapasan near the National Highway. The Atrium (Entertainment Hall) can accommodate over 3,000 people that have already hosted several local and foreign concerts, conventions, exhibits, and other events.
- Makro
- SM City Cagayan de Oro at Masterson Avenue, Upper Carmen.
- Robinsons Cagayan de Oro is a two-level commercial establishment built to meet the shopping needs of Kagay-anons and people from the nearby provinces. Located at the corner of Rosario Crescent and Florentino Street in Limketkai Complex, and behind Limketkai Mall. It is also right beside the Grand Caprice Restaurant and Convention Center. Robinsons first mall development in Mindanao.
- Divisoria Night Café and Market is set up on Friday and Saturday nights. Kagay-anons and visitors gather in the streets of Plaza Divisoria to have barbecue and seafood among many choices and enjoy the live band music, beer, and also the great bargains from the nearby Night Market.[18]
- Ororama Chain of Stores in Lapasan, Cogon and Carmen.
- Gaisano City Mall at C.M. Recto Avenue cor. Corrales Extension. Gaisano City has also two branches in Cogon and Carmen.
- Georgetown Cybermall is a Wi-Fi free mall located along R.N. Pelaez Boulevard.
- Cogon Public Market and Commercial Complex is the main public market located in downtown area where many smaller shopping centers are located and where items are sold at bargain prices.
- Carmen Public Market and Commercial Complex
- Ayala Center Cagayan de Oro (Proposed)[20]
- Pacific Island City Mall (Proposed)
- Market City (Under construction)
- SM Savemore - Market City (Soon to open)
City events
- Kagay-an Festival is held every 26th to the 28th of August in celebration of Cagayan de Oro's patron, Señor San Agustin. The highlights of Kagay-an Festival are: Kagay-an Agro-Trade Fair that features the native products of the city and province particularly on agriculture products, Miss Kagay-an, Higaonon Street Dancing which features colourful attires and cultural dances of the Higaonon tribe, Golden Float Parade and Halad sa Lambagohan. There are also cultural shows, competitions and celebrity concerts.
- Charter Day is the city's celebration of its city hood established in June 15, 1950. It is a non-working holiday and a roster of special activities is lined up annually to mark this occasion. The original name of the city was Cagayan de Misamis until 1950 when it was changed to Cagayan de Oro in virtue of Republic Act No. 521, which was signed by then President Elpidio Quirino. The city's status was made possible due to the efforts of then Congressman and Vice President of the Philippines Emmanuel Pelaez.
- Kumbira is a culinary show and exhibit started in 1996 by Kagay-anons hoteliers and restaurants. It has been evolved over the years and it now hosts a culinary competition among students and professionals all over Mindanao. The competition is divided into students and professionals where Hotel and Restaurant Management schools and professional chefs compete against each other in their respective categories. This is usually held in mid of August as part of the Kagay-an Festival.
- Halad sa Lambagohan, organized way back in the mid 1980's, this fluvial parade, also called Lambagohan Festival is held along the Cagayan de Oro River.
- Miss Kagay-an is a beauty pageant presenting the native beauty of Cagayan de Oro lads. It is one of the most prestigious beauty pageants in the city.
- Golden Float Parade was started in 2007; it includes marching bands from different city schools. It is also participated by local government departments and commercial establishments.
- A Holy-Week Trek, March or April (Movable) on the eve of Good Friday (Thursday evening), where thousands of Kagay-anons trek Malasag Hill for the annual Via crucis or way of the cross. This event is the city's catholic devotees in observation of the holy week.
International relations
Sister cities
 Tainan City, Taiwan (2005)
Tainan City, Taiwan (2005) Harbin, China (2007)
Harbin, China (2007) Norfolk, USA (2008)
Norfolk, USA (2008) Butuan City, Philippines
Butuan City, Philippines Schelklingen, Germany
Schelklingen, Germany.svg.png) Dinant, Belgium
Dinant, Belgium
See also
- Misamis Oriental
- Macajalar Bay
- Battle of Makahambus Hill
- Northern Mindanao, designated as Region X of the Philippines.
- Mindanao
External links
 |
Macajalar Bay |  |
||
| Opol, Misamis Oriental, Laguindingan, Misamis Oriental, El Salvador City , Iligan City | Tagoloan, Misamis Oriental, Gingoog City | |||
| Bukidnon, Lanao del Norte |
- Official website of the City Government of Cagayan de Oro
- Online tourist guide of Cagayan de Oro
- Socio-Economic profile of Cagayan de Oro
References
- ↑ Antonio J. Montalvan II. "History of Cagyan de Oro, with Update on Destruction of Ancestral Home". Heritage Conservation Advocates, Philippines. http://heritage.elizaga.net/history/.
- ↑ "CENTRAL LUZON & NCR, Philippines Unsung Heroes". MSC Institute of Technology. http://www.msc.edu.ph/centennial/hero/ncr/page3.html.
- ↑ Philippine History Group of Los Angeles (1996-07-04). "The Independence Day That Wasn't". Press release. http://www.bibingka.com/phg/misc/july4not.htm.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Cagayan de Oro City Official Website
- ↑ "Weatherbase: Historical Weather for Cagayan de Oro, Philippines". Weatherbase. 2007. http://www.weatherbase.com/weather/weather.php3?s=84789&refer=. Retrieved 2007-02-04.
- ↑ Cagayan De Oro City: Population Growth Rate Declined to 1.63 Percent
- ↑ http://www.gov.ph/news/?i=23237
- ↑ http://www.irradiance.com/philippine.html
- ↑ Waiting for the flight from Laguindingan, Philippine Daily Inquirer, July 22, 2007
- ↑ Arroyo to inaugurate int'l airport project, Sun.Star Cagayan de Oro, January 11, 2006
- ↑ Infrastructure of Cagayan de Oro
- ↑ P250-M rehab for Mindanao’s biggest port completed - INQUIRER.net, Philippine News for Filipinos
- ↑ :: WWW.PNP.GOV.PH :: Philippine National Police
- ↑ Whitewater Kayaking with KayakDomain.com
- ↑ Cagayan de Oro Tourism Website
- ↑ GMA goes whitewater rafting in Cagayan de Oro - and looks forward to mountain climbing : Philippines : Gov.Ph : News
- ↑ Gardens of Malasag Eco-Tourism Village
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Cagayan De Oro Travel Guide
- ↑ http://www.cagayandeoro.cdo.ph/pages/gln_history.htm
- ↑ http://kagayandeoro.blogspot.com/2008/09/jaraula-confirms-p45-b-ayala-mall-to.html
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Leading population centers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | City | Population | Pop. Growth Rate | Region |  Metro Manila  Cebu City |
||
| 1 | Quezon City | 2,679,450 | 2.53% | National Capital Region | |||
| 2 | Manila | 1,660,714 | 0.03% | National Capital Region | |||
| 3 | Caloocan | 1,378,856 | 2.53% | National Capital Region | |||
| 4 | Davao City | 1,363,337 | 1.81% | Davao Region | |||
| 5 | Cebu City | 798,809 | 2.16% | Central Visayas | |||
| 6 | Zamboanga City | 774,407 | 3.54% | Zamboanga Peninsula | |||
| 7 | Antipolo | 633,971 | 5.22% | CALABARZON | |||
| 8 | Pasig | 617,301 | 2.29% | National Capital Region | |||
| 9 | Taguig | 613,343 | 4.07% | National Capital Region | |||
| 10 | Valenzuela | 568,928 | 2.23% | National Capital Region | |||
| based on the Philippines 2007 Census | |||||||
