Ivanovo
| Ivanovo (English) Иваново (Russian) |
|
|---|---|
| — Inhabited locality — | |
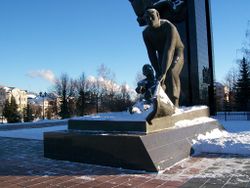 Revolution Square |
|
.svg.png) Location of Ivanovo Oblast in Russia |
|
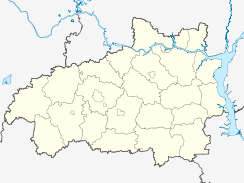 Ivanovo
|
|
| Coordinates: | |
.png) |
.png) |
| Administrative status | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal subject | Ivanovo Oblast |
| Administrative center of | Ivanovo Oblast |
| Municipal status | |
| Urban okrug | Ivanovo Urban Okrug |
| Head | Alexander Fomin[1] |
| Statistics | |
| Area | 104.8 km2 (40.5 sq mi) |
| Population (2002 Census) | 406,465 inhabitants[2] |
| - Rank | 40 |
| - Density | 3,878 /km2 (10,040 /sq mi)[3] |
| Time zone | MSK/MSD (UTC+3/+4) |
| Founded | 1561 |
| Postal code(s) | 24401 |
| Dialing code(s) | +7 4932 |
| Official website | |
Ivanovo (Russian: Ива́ново) is a city and the administrative center of Ivanovo Oblast, Russia. Population: 406,465 (2008); 431,721 (2002 Census);[2] 481,042 (1989 Census).[4]
Ivanovo has traditionally been called the textile capital of Russia. Since most textile workers are women, it has also been known as the "City of Brides". Probably the most famous of the city's female natives was the postmodern French writer Nathalie Sarraute.
It is home to Ivanovo Severny, which is one of the largest military airlift bases in Russia. Civilian air services are provided at Ivanovo Yuzhny Airport.
Ivanovo has several educational institutions: Ivanovo State University, Ivanovo State University of Chemistry and Technology, Ivanovo Medical Academy, Ivanovo Architectural Academy, Ivanovo State Power University(ISPU). University of Chemistry is one of the oldest Universities in the town. It prepares specialists in chemistry.
Contents |
History
Ivanovo was created by merging the old flax-processing village Ivanovo (first documented in 1561) with the industrial Voznesensky Posad in 1871. Until 1932, its official name was Ivanovo-Voznesensk. Because of its textile manufacturing industry, Ivanovo earned the sobriquet of the "Russian Manchester" during the 19th century.[5]
By the early 20th century, Ivanovo competed with Łódź (also a part of the Russian Empire at that time) for the title of the primary textile production centre in Europe. As the workers' living conditions were appalling, the strikes were frequent. One of these strikes led to the first Russian revolution. According to the Soviet historiography, e.g., Great Soviet Encyclopedia, article "Soviets of Workers' Deputies" (Russian: Советы депутатов трудящихся), the Ivanovo Soviet (created in May 1905) was one of the first Soviets in the history. However this statement is contested, see Saint Petersburg Soviet.
Notable people
- Andrei Bubnov - Bolshevik Politician
- Yelena Kruglova - sportsman-swimmer
- Pavel Kupriyanovsky - scientist-philologist, writer, holder of an Order
- Leonid Taganov - scientist-philologist, writer, holder of an Order
- Valery Memetov - scientist-historian, holder of an Order
- Sergei Nechaev- Revolutionary Nihilist
- Nathalie Sarraute - writer
- Alexandr Spryskov - scientist-chemist, holder of an Order
- Georgii Evgen'evich Shilov- mathematician
- Vladimir Tsybin - flautist and conductor
- Vyacheslav Mikhailovich Zaitsev - designer, painter, graphic artist and theatrical costume designer.
- Vitaly Tepikin - scientist-historian, writer
- Zoya Yakovleva - scientist-chemist, holder of an Order
Twin Towns - Sister Cities
Ivanovo is twinned with:
 Łódź in Poland (since 1992) [6]
Łódź in Poland (since 1992) [6] Plano in Texas, United States.
Plano in Texas, United States. Staffordshire in the United Kingdom.
Staffordshire in the United Kingdom. Hanover in Germany.
Hanover in Germany. Khmelnytskyi in Ukraine.
Khmelnytskyi in Ukraine. Dzerzhinsky in Russia.
Dzerzhinsky in Russia. Kazan in Republic of Tatarstan, Russia.
Kazan in Republic of Tatarstan, Russia. Plovdiv in Bulgaria.
Plovdiv in Bulgaria.
See also
- Interdom
- Ivanovo State University of Chemistry and Technology
 Ivanovo State University of Chemistry and Technology |
 Ivanovo's rapidly-changing industrial cityscape. |
 Tram service in Ivanovo was cancelled in June 2008 |
 M.Frunze's monument |
References
- Notes
- ↑ Official website of the Administration of Ivanovo. Alexander Germanovich Fomin, Head of the City (Russian)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек (Population of Russia, its federal districts, federal subjects, districts, urban localities, rural localities—administrative centers, and rural localities with population of over 3,000)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002). Federal State Statistics Service. http://perepis2002.ru/ct/html/TOM_01_04_1.htm. Retrieved 2009-08-19.
- ↑ The value of density was calculated automatically by dividing the 2002 Census population by the area specified in the infobox. Please note that this value may not be accurate as the area specified in the infobox does not necessarily correspond to the area of the entity proper or is reported for the same year as the Census (2002).
- ↑ "Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров. (All Union Population Census of 1989. Present population of union and autonomous republics, autonomous oblasts and okrugs, krais, oblasts, districts, urban settlements, and villages serving as district administrative centers.)" (in Russian). Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года (All-Union Population Census of 1989). Demoscope Weekly (website of the Institute of Demographics of the State University—Higher School of Economics. 1989. http://demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/rus89_reg.php. Retrieved 2007-12-13.
- ↑ Cookson, Roy (2002). A World of Manchesters. Casthermen Books. p. 111. ISBN 0-9542404-0-5.
- ↑ "Twin Cities". The City of Łódź Office.

 (in English and Polish) © 2007 UMŁ. http://en.www.uml.lodz.pl/index.php?str=2029. Retrieved 2008-10-23.
(in English and Polish) © 2007 UMŁ. http://en.www.uml.lodz.pl/index.php?str=2029. Retrieved 2008-10-23.
External links
- Ivanovo official website
- Ivanovo city portal
- Ivanovo Region Newspaper IVANOVSKAYA GAZETA - Internet version
- Ivanovo official business website
- Ivanovo business informational classified directory website
- Ivanovo Wiki (IvanovoWiki - wikipedia of Ivanovo)
- All textil company - city Ivanovo
- Ivanovo city streets views
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
