Colitis
| Colitis | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
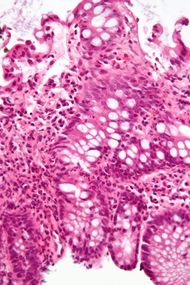 A micrograph demonstrating cryptitis, a microscopic correlate of colitis. H&E stain. |
|
| ICD-10 | K50. - K52 |
| ICD-9 | 558 |
| OMIM | 191390 |
| DiseasesDB | 31340 |
| MedlinePlus | 001125 |
| eMedicine | ped/435 |
| MeSH | C06.405.205.265 |
In medicine, colitis (pl. colitides) refers to an inflammation of the colon and is often used to describe an inflammation of the large intestine (colon, cecum and rectum).
Colitides may be acute and self-limited or chronic, i.e. persistent, and broadly fit into the category of digestive diseases.
In a medical context, the label colitis (without qualification) is used if:
- The etiology of the inflammation in the colon is undetermined; for example, colitis may be applied to Crohn's disease at a time when the diagnosis has not declared itself.
- The context is clear; for example, an individual with ulcerative colitis is talking about their disease with a physician that knows the diagnosis.
Contents |
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of colitides are quite variable and dependent on the etiology (or cause) of the given colitis and factors that modify its course and severity.
Symptoms of colitis may include: abdominal pain, loss of appetite, fatigue, diarrhea, cramping, urgency (tenesmus) and bloating.
Signs may include: abdominal tenderness, weight loss, changes in bowel habits (increased frequency), fever, bleeding (overt or occult)/bloody stools, diarrhea and distension.
Signs seen on colonoscopy include: colonic mucosal erythema (redness of the inner surface of the colon), ulcers, bleeding.
Diagnosis
Symptoms suggestive of colitis are worked-up by obtaining the medical history, a physical examination and laboratory tests (CBC, electrolytes, stool culture and sensitivity, stool ova and parasites et cetera). Additional tests may include medical imaging (e.g. abdominal computed tomography, abdominal X-rays) and an examination with a camera inserted into the rectum (sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy).
Types
There are many types of colitis. They are usually classified by the etiology.
Types of colitis include:
Autoimmune
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) - a group of chronic colitides.
- Ulcerative colitis - a chronic colitis that affects the large intestine.
Main article: Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease - a type of IBD often leads to a colitis.
Main article: Crohn's disease
- Ulcerative colitis - a chronic colitis that affects the large intestine.
Idiopathic
- Microscopic colitis - a colitis is diagnosed by microscopic examination of colonic tissue; macroscopically it is normal appearing.
- Lymphocytic colitis.
- Collagenous colitis.
Iatrogenic
- Diversion colitis.
- Chemical colitis.
Vascular disease
- Ischemic colitis.
Infectious
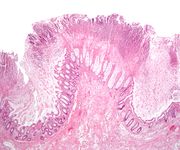
- Infectious colitis.
A well-known subtype of infectious colitis is pseudomembranous colitis, which results from infection by a toxigenic strain of Clostridium difficile (c-diff).[1]
Enterohemorrhagic colitis may be caused by Shiga toxin in Shigella dysenteriae or Shigatoxigenic group of Escherichia coli (STEC), which includes serotype O157:H7 and other enterohemorrhagic E. coli.[2]
Parasitic infections can also cause colitis.
Unclassifiable colitides
Indeterminate colitis is a term used for a colitis that has features of both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.[3] Indeterminate colitis' behaviour is usually closer to ulcerative colitis than Crohn's disease.[4]
Atypical colitis is a phrase that is occasionally used by physicians for a colitis that does not conform to criteria for accepted types of colitis. It is not an accepted diagnosis per se and, as such, a colitis that cannot be definitively classified.
Severity of colitides
Fulminant colitis is any colitis that becomes worse rapidly. In addition to the diarrhea, fever, and anemia seen in colitis, the patient has severe abdominal pain and presents a clinical picture similar to that of septicemia, where shock is present. About half of human patients require surgery. In horses, the fulminant colitis known as colitis X usually results in death within 24 hours.
Irritable bowel syndrome, a separate disease, has been called spastic colitis. This name may lead to confusion, since colitis is not always a feature of irritable bowel syndrome. Since the etiology of IBS is currently unknown and possibly multifactorial, there may be some overlap in symptoms between IBS and the various forms of colitis.
Treatment
How a given colitis is treated is dependent on its etiology, e.g. infectious colitis are usually treated with antimicrobial agents (e.g. antibiotics), autoimmune mediated colitis are treated with immune modulators/immune suppressants.
Severe colitis can be life-threatening and may require surgery.
See also
Notes
- ↑ "Clostridium Difficile Colitis - Overview". WebMD, LLC. http://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/tc/clostridium-difficile-colitis-overview. Retrieved 2006-09-15.
- ↑ Beutin L (2006). "Emerging enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli, causes and effects of the rise of a human pathogen". J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health 53 (7): 299–305. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0450.2006.00968.x. PMID 16930272.
- ↑ Romano, C.; Famiani, A.; Gallizzi, R.; Comito, D.; Ferrau', V.; Rossi, P. (Dec 2008). "Indeterminate colitis: a distinctive clinical pattern of inflammatory bowel disease in children.". Pediatrics 122 (6): e1278–81. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-2306. PMID 19047226.
- ↑ Melton, GB.; Kiran, RP.; Fazio, VW.; He, J.; Shen, B.; Goldblum, JR.; Achkar, JP.; Lavery, IC. et al. (Jul 2009). "Do preoperative factors predict subsequent diagnosis of Crohn's disease after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for ulcerative or indeterminate colitis?". Colorectal Dis. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1318.2009.02014.x. PMID 19624520.
External links
- Colitis at GPnotebook
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||