Nevus
Nevus (or naevus, plural nevi or naevi, from nævus, Latin for "birthmark") is the medical term for sharply-circumscribed[1] and chronic lesions of the skin. These lesions are commonly named birthmarks and moles. Nevi are benign by definition. Using the term nevus and nevi loosely, most physicians and dermatologists are actually referring to a variant of nevus called the "melanocytic nevus", which are composed of melanocytes. Histologically, melanocytic nevi are differentiated from lentigines (also a type of benign pigmented macule) by the presence of nests of melanocytes, which lentigines (plural form of lentigo) lack.
Classification
Classification is based on cell line of origin. Melanocytic nevi are derived from melanocytes. Epidermal nevi are derived from keratinocytes or derivatives of keratinocytes. Connective tissue nevi are derived from connective tissue cells like adipocyte and fibroblasts. Vascular nevi are derived from structures of the blood vessels. See birthmark for a more complete discussion
Melanocytic nevus
- Congenital nevus implying a melanocytic nevus present at birth or near birth.
- Acquired melanocytic nevus. Implies a melanocytic nevus acquired later in life, and not at or near birth. Most melanocytic nevi are of the acquired variety.
- Melanocytic nevus (nevomelanocytic nevus, nevocellular nevus): benign proliferation of melanocytes, the skin cells that make the brown pigment melanin. Hence, most nevi are brown to black. They are very common; almost all adults have at least one, usually more. They may be congenital or acquired (usually at puberty).
- Dysplastic nevus usually an acquired melanocytic nevus with abnormal features making it difficult to distinguish from a melanoma. It can be a marker for an individual at risk for developing melanomas.
Epidermal nevus
- Epidermal nevus: congenital, flesh-colored, raised or warty, often linear lesion, usually on the upper half of the body.
- Nevus sebaceus: variant of epidermal nevus on the scalp presenting as a hairless, fleshy or yellowish area.
Connective tissue nevus
- Connective tissue nevus: fleshy, deep nodules. Rare.
Vascular nevus
- Hemangioma (strawberry mark or nevus).
- Nevus flammeus (port-wine stain).
- Spider angioma (nevus araneus).
- Blue Rubber Bleb Nevus Syndrome: dilatation of veins anywhere in the body (both skin and internal organs), usually lethal from internal hemorrhage. It is a very rare genetic disorder.
The term "venous nevus" has recently been proposed.[2]
Diagnosis of nevi

A dermatoscope.
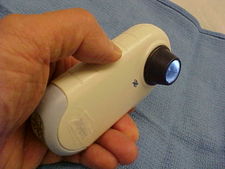
A modern polarized dermatoscope.
Clinical diagnosis of a melanocytic nevus from other nevi can be made with the naked eye using the ABCD guideline, or using dermatoscopy. The main concern is distinguishing between a benign nevus, a dysplastic nevus, and a melanoma. Other skin tumors can resemble a melanocytic nevus clinically, such as a seborrheic keratosis, pigmented basal cell cancer, hemangiomas, and sebaceous hyperplasia. A skin biopsy is required when clinical diagnosis is inadequate or when malignancy is suspected.
Normal Evolution or Maturation of Melanocytic Nevus
All melanocytic nevi will change with time - both congenital and acquired nevi. The "normal" maturation is evident as elevation of the lesion from a flat macule to a raised papule. The color change occurs as the melanocytes clump and migrate from the surface of the skin (epidermis) down deep into the dermis. The color will change from even brown, to speckled brown, and then losing the color and becomes flesh colored or pink. During the evolution, uneven migration can make the nevi look like melanomas, and dermatoscopy can help in differentiation between the benign and malignant lesions.[3]
See also
- Becker's nevus
- Dysplastic nevus - a melanocytic nevus with abnormal pigment features which can be difficult to distinguish from a melanoma.
- List of cutaneous conditions
References
External links
|
Diseases of the skin and appendages by morphology |
|
| Growths |
|
|
|
|
|
Pigmented
|
|
|
|
Dermal and
subcutaneous
|
epidermal inclusion cyst · hemangioma · dermatofibroma · keloid · lipoma · neurofibroma · xanthoma · Kaposi's sarcoma · infantile digital fibromatosis · granular cell tumor · leiomyoma · lymphangioma circumscriptum · myxoid cyst |
|
|
| Rashes |
|
With
epidermal
involvement
|
|
Eczematous
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Papular
|
scabies · insect bite reactions · lichen planus · miliaria · keratosis pilaris · lichen spinulosus · transient acantholytic dermatosis · lichen nitidus · pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hypopigmented
|
tinea versicolor · vitiligo · pityriasis alba · postinflammatory hyperpigmentation · tuberous sclerosis · idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis · leprosy · hypopigmented mycosis fungoides |
|
|
|
Without
epidermal
involvement
|
|
Red
|
|
Blanchable
Erythema
|
|
Generalized
|
|
|
|
Localized
|
cellulitis · abscess · boil · erythema nodosum · carcinoid syndrome · fixed drug eruption
|
|
|
Specialized
|
urticaria · erythema (multiforme · migrans · gyratum repens · annulare centrifugum · ab igne)
|
|
|
|
Nonblanchable
Purpura
|
|
Macular
|
thrombocytopenic purpura · actinic purpura
|
|
|
Papular
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indurated
|
scleroderma/morphea · granuloma annulare · lichen sclerosis et atrophicus · necrobiosis lipoidica
|
|
|
|
Miscellaneous
disorders |
|
Ulcers
|
|
|
|
|
telogen effluvium · androgenic alopecia · trichotillomania · alopecia areata · systemic lupus erythematosus · tinea capitis · loose anagen syndrome · lichen planopilaris · folliculitis decalvans · acne keloidalis nuchae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
aphthous stomatitis · oral candidiasis · lichen planus · leukoplakia · pemphigus vulgaris · mucous membrane pemphigoid · cicatricial pemphigoid · herpesvirus · coxsackievirus · syphilis · systemic histoplasmosis · squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
|
Gonadal tumors, paraganglioma, glomus, nevi and melanomas (ICD-O 8590-8799) |
|
Gonadal/
sex cord-gonadal stromal (8590-8679) |
sex cord (Granulosa cell tumour, Sertoli cell tumor)
stroma (Thecoma, Leydig cell tumor)
both (Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour, Luteoma)
|
|
Paragangliomas And
Glomus tumors (8680-8719) |
Neuroendocrine tumor: Paraganglioma (Pheochromocytoma)
Vascular tissue neoplasm: Glomus tumor (Glomangiosarcoma)
|
|
| Nevi and melanomas (8720-8799) |
|
Nevi
|
Melanocytic/pigmented nevus (Mongolian spot, Blue nevus, Nevus of Ota, Spitz nevus)
location (Junctional nevus, Compound nevus)
Halo nevus · Dysplastic nevus
|
|
|
|
Superficial spreading melanoma · Nodular melanoma · lentigo (Lentigo maligna/Lentigo maligna melanoma, Acral lentiginous melanoma)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tumors: Skin neoplasm, Nevi and melanomas (C43/D22, 172/216) |
|
| Melanoma |
Mucosal melanoma · Superficial spreading melanoma · Nodular melanoma · lentigo (Lentigo maligna/Lentigo maligna melanoma, Acral lentiginous melanoma)
Amelanotic melanoma · Desmoplastic melanoma · Melanoma with features of a Spitz nevus · Melanoma with small nevus-like cells · Polypoid melanoma · Soft-tissue melanoma
Melanocytic tumors of uncertain malignant potential
|
|
Nevus/
melanocytic nevus |
Nevus of Ito · Nevus of Ota · Compound nevus · Spitz nevus · Halo nevus · Pseudomelanoma · Blue nevus (Blue nevus of Jadassohn–Tièche, Cellular blue nevus, Epithelioid blue nevus, Deep penetrating nevus, Amelanotic blue nevus, Malignant blue nevus) · Giant pigmented nevus · Congenital melanocytic nevus (Medium-sized congenital nevocytic nevus, Small-sized congenital nevocytic nevus) · Balloon cell nevus · Dysplastic nevus/Dysplastic nevus syndrome
Acral nevus · Becker's nevus · Benign melanocytic nevus · Nevus spilus · Pigmented spindle cell nevus
|
|
| Pigmentation disorder |
lentigo/lentiginosis: Centrofacial lentiginosis · Generalized lentiginosis · Inherited patterned lentiginosis in black persons · Ink spot lentigo · Lentigo maligna · Lentigo simplex · Mucosal lentigines · Partial unilateral lentiginosis · PUVA lentigines · Solar lentigo
Ephelis · Melanoacanthoma
|
|
| Syndromes |
Carney complex · Moynahan syndrome · Peutz–Jeghers syndrome
|
|
|
|
|
noco(i,,d,q,u,,p,,,v)/cong/tumr(n,e,d), sysi/
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cardiovascular disease: vascular disease · Circulatory system pathology (I70–I99, 440–456) |
|
Arteries, arterioles
and capillaries |
|
|
Arteritis (Aortitis) · Buerger's disease
|
|
|
Arterial occlusive disease/
peripheral vascular disease
|
|
Arteriosclerosis
|
Atherosclerosis (Foam cell, Fatty streak, Atheroma, Intermittent claudication) · Monckeberg's arteriosclerosis · Arteriolosclerosis (Hyaline, Hyperplastic, oxycholesterol, cholesterol, LDL, trans fat)
|
|
|
Stenosis
|
Renal artery stenosis · Carotid artery stenosis
|
|
|
Other
|
|
|
|
|
|
torso: Aortic aneurysm (Thoracic aortic aneurysm, Abdominal aortic aneurysm) · Aortic dissection · Coronary artery aneurysm
head/neck: Cerebral aneurysm · Intracranial berry aneurysm · Carotid artery dissection · Vertebral artery dissection · Familial aortic dissection
|
|
|
Vascular malformation
|
Arteriovenous malformation · Arteriovenous fistula · Telangiectasia (Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia)
|
|
|
|
Spider angioma · Halo nevus · Cherry hemangioma
|
|
|
| Veins |
|
|
Phlebitis
|
|
|
Venous thrombosis/
Thrombophlebitis
|
primarily lower limb (Deep vein thrombosis)
abdomen (May-Thurner syndrome, Portal vein thrombosis, Budd–Chiari syndrome, Renal vein thrombosis)
upper limb/torso (Paget-Schroetter disease, Mondor's disease)
head (Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis)
Post-thrombotic syndrome
|
|
|
|
Varicocele · Gastric varices · Portacaval anastomosis ( Hemorrhoid, Esophageal varices, Caput medusae)
|
|
|
Other
|
Superior vena cava syndrome · Inferior vena cava syndrome · Venous ulcer · Chronic venous insufficiency · Chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency
|
|
|
| Arteries or veins |
|
|
| Blood pressure |
|
|
Hypertensive heart disease · Hypertensive nephropathy · Essential hypertension · Secondary hypertension (Renovascular hypertension) · Pulmonary hypertension · Malignant hypertension · Benign hypertension · Systolic hypertension · White coat hypertension |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
anat(a:h,u,t,a,l,v:h,u,t,a,l)/phys/devp/cell/
|
|
proc, drug(C2s/,C3,C4,C5,,C8,C9)
|
|
|
|

