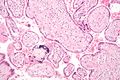
Placenta
| Placenta | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Placenta | |
| Precursor | decidua basalis, chorion frondosum |
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. Placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and lizards with varying levels of development up to mammalian levels.[1] The word placenta comes from the Latin for cake, from Greek plakóenta/plakoúnta, accusative of plakóeis/plakoús – πλακόεις, πλακούς, "flat, slab-like",[2] in reference to its round, flat appearance in humans. Protherial (egg-laying) and metatherial (marsupial) mammals produce a choriovitelline placenta that, while connected to the uterine wall, provides nutrients mainly derived from the egg sac. The placenta develops from the same sperm and egg cells that form the fetus, and functions as a fetomaternal organ with two components, the fetal part (Chorion frondosum), and the maternal part (Decidua basalis).
Contents |
Structure
In humans, the placenta averages 22 cm (9 inch) in length and 2–2.5 cm (0.8–1 inch) in thickness (greatest thickness at the center and become thinner peripherally). It typically weighs approximately 500 grams (1 lb). It has a dark reddish-blue or maroon color. It connects to the fetus by an umbilical cord of approximately 55–60 cm (22–24 inch) in length that contains two arteries and one vein.[3] The umbilical cord inserts into the chorionic plate (has an eccentric attachment). Vessels branch out over the surface of the placenta and further divide to form a network covered by a thin layer of cells. This results in the formation of villous tree structures. On the maternal side, these villous tree structures are grouped into lobules called cotyledons. In humans the placenta usually has a disc shape but different mammalian species have widely varying shapes.[4]
Development
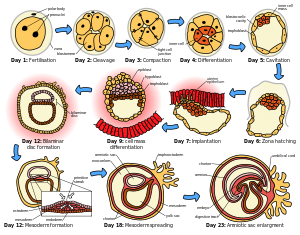
The placenta begins to develop upon implantation of the blastocyst into the maternal endometrium. The outer layer of the blastocyst becomes the trophoblast which forms the outer layer of the placenta. This outer layer is divided into two further layers: the underlying cytotrophoblast layer and the overlying syncytiotrophoblast layer. The syncytiotrophoblast is a multinucleate continuous cell layer which covers the surface of the placenta. It forms as a result of differentiation and fusion of the underlying cytotrophoblast cells, a process which continues throughout placental development. The syncytiotrophoblast (otherwise known as syncytium), thereby contributes to the barrier function of the placenta.
The placenta grows throughout pregnancy. Development of the maternal blood supply to the placenta is suggested to be complete by the end of the first trimester of pregnancy (approximately 12–13 weeks).
Placental circulation
Maternal placental circulation
In preparation for implantation, the uterine endometrium undergoes 'decidualisation'. Spiral arteries in the decidua are remodelled so that they become less convoluted and their diameter is increased. This increases maternal blood flow to the placenta and also decreases resistance so that blood flow is increased. The relatively high pressure as the maternal blood enters the intervillous space through these spiral arteries bathes the villi in blood. An exchange of gases takes place. As the pressure decreases, the deoxygenated blood flows back through the endometrial veins.
Maternal blood flow is approx 600–700 ml/min at term.
Fetoplacental circulation
Deoxygenated fetal blood passes through umbilical arteries to the placenta. At the junction of umbilical cord and placenta, the umbilical arteries branch radially to form chorionic arteries. Chorionic arteries also branch before they enter into the villi. In the villi, they form an extensive arteriocapillary venous system, bringing the fetal blood extremely close to the maternal blood; but no intermingling of fetal and maternal blood occurs ("placental barrier"[5]).
Functions
Nutrition and immunity
The perfusion of the intervillous spaces of the placenta with maternal blood allows the transfer of nutrients and oxygen from the mother to the fetus and the transfer of waste products and carbon dioxide back from the fetus to the mother. Nutrient transfer to the fetus is both actively and passively mediated by proteins called nutrient transporters that are expressed within placental cells.
Adverse pregnancy situations, such as those involving maternal diabetes or obesity, can increase or decrease levels of nutrient transporters in the placenta resulting in overgrowth or restricted growth of the fetus.
IgG antibodies can pass through the human placenta, thereby providing protection to the fetus in utero[6].
Endocrine function
In humans, aside from serving as the conduit for oxygen and nutrients for fetus, placenta secretes hormone (secreted by syncytial layer/syncytiotrophoblast of chorionic villi)that is important during pregnancy.
Hormones:
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG). The first placental hormone produced is hCG, which can be found in maternal blood and urine as early as the first missed menstrual period (shortly after implantation has occurred) through about the 100th day of pregnancy. This is the hormone analyzed by pregnancy test; a false-negative result from a pregnancy test may be obtained before or after this period. Women's blood serum will be completely negative for hCG by one to two weeks after birth. hCG testing is proof that all placental tissue is delivered. hCG is only present during pregnancy because it is secreted by the placenta, which of course is present only[7] during pregnancy. hCG also ensures that the corpus luteum continue to secrete progesterone and estrogen. Progesterone is very important during pregnancy because when its secretion decreases, endometrial lining will slough off and pregnancy will be lost. hCG suppresses the maternal immunologic response so that placenta is not rejected.
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL [Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin]). This hormone is lactogenic and growth-promoting properties. It promotes mammary gland growth in preparation for lactation in the mother. It also regulates maternal glucose, protein, fat levels so that this is always available to the fetus.
Estrogen. It is referred to as the "hormone of woman" because it influence the female appearance. It contributes to the woman's mammary gland development in preparation for lactation and stimulates uterine growth to accommodate growing fetus.
Progesterone. This is referred to as the "hormone of mothers" because it is necessary to maintain endometrial lining of the uterus during pregnancy. This hormone prevents preterm labor by reducing myometrial contraction. This hormone is high during pregnancy.
Cloaking from immune system of mother
The placenta and fetus may be regarded as a foreign allograft inside the mother, and thus must evade from attack by the mother's immune system.
For this purpose, the placenta uses several mechanisms:
- It secretes Neurokinin B containing phosphocholine molecules. This is the same mechanism used by parasitic nematodes to avoid detection by the immune system of their host.[8]
- Also, there is presence of small lymphocytic suppressor cells in the fetus that inhibit maternal cytotoxic T cells by inhibiting the response to interleukin 2.[9]
However, the placental barrier is not the sole means to evade the immune system, as foreign fetal cells also persist in the maternal circulation, on the other side of the placental barrier.[10]
Birth
When the fetus is born, its placenta begins a physiological separation for spontaneous expulsion afterwards (and for this reason is also called the afterbirth). In humans, the umbilical cord is routinely clamped and severed prior to the delivery of the placenta, often within seconds or minutes of birth, a medical protocol known as 'active management of third stage' which has been called into question by advocates of natural birth and 'passive management of third stage'.[11] The site of the former umbilical cord attachment in the center of the front of the abdomen is known as the navel, umbilicus, or belly-button.
Modern obstetric practice has decreased maternal death rates enormously. The addition of active management of the third stage of labor is a major contributor towards this. It involves giving oxytocin via intramuscular injection, followed by cord traction to assist in delivering the placenta. Premature cord traction can pull the placenta before it has naturally detached from the uterine wall, resulting in hemorrhage. The BMJ summarized the Cochrane group metanalysis (2000) of the benefits of active third stage as follows:
"One systematic review found that active management of the third stage of labour, consisting of controlled cord traction, early cord clamping plus drainage, and a prophylactic oxytocic agent, reduced postpartum haemorrhage of 500 or 1000 mL or greater and related morbidities including mean blood loss, postpartum haemoglobin less than 9 g/dL, blood transfusion, need for supplemental iron postpartum, and length of third stage of labour. Although active management increased adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, and headache, one RCT identified by the review found that women were less likely to be dissatisfied when their third stage of labour was actively managed."[1]
Risks of retained placenta include hemorrhage and infection. If the placenta fails to deliver in 30 minutes in a hospital environment, manual extraction may be required if heavy ongoing bleeding occurs, and very rarely a curettage is necessary to ensure that no remnants of the placenta remain (in rare conditions with very adherent placenta (placenta accreta)). However, in birth centers and attended home birth environments, it is common for licensed care providers to wait for the placenta's birth up to 2 hours in some instances.
Non-humans
In most mammalian species, the mother bites through the cord and consumes the placenta, primarily for the benefit of prostaglandin on the uterus after birth. This is known as placentophagy. However, it has been observed in zoology that chimpanzees, with which humans share 94%–99% of genetic material,[12][13] apply themselves to nurturing their offspring, and keep the fetus, cord, and placenta intact until the cord dries and detaches the next day. The placenta exists in most mammals and some reptiles. It is probably polyphyletic.
Pathology
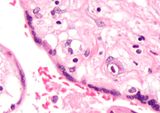
Numerous pathologies can affect the placenta.
When the placenta implants too deeply:
- Placenta accreta
- Placenta praevia
- Placental abruption/abruptio placentae
Infections involving the placenta:
- Placentitis, such as the TORCH infections.
- Chorioamnionitis.
Use in medicine
Human placenta is increasingly being used in western medicine with even a branch called "placenta pharmacology" being updated regularly.[14]
Cultural practices and beliefs
The placenta often plays an important role in various human cultures, with many societies conducting rituals regarding its disposal. In the Western world, the placenta is most often incinerated.[15]
Some cultures bury the placenta for various reasons. The Māori of New Zealand traditionally bury the placenta from a newborn child to emphasize the relationship between humans and the earth.[16] Similarly, the Navajo bury the placenta and umbilical cord at a specially chosen site,[17] particularly if the baby dies during birth.[18] In Cambodia and Costa Rica, burial of the placenta is believed to protect and ensure the health of the baby and the mother.[19] If a mother dies in childbirth, the Aymara of Bolivia bury the placenta in a secret place so that the mother's spirit will not return to claim her baby's life.[20]

The placenta is believed by some communities to have power over the lives of the baby or its parents. The Kwakiutl of British Columbia bury girls' placentas to give the girl skill in digging clams, and expose boys' placentas to ravens to encourage future prophetic visions. In Turkey, the proper disposal of the placenta and umbilical cord is believed to promote devoutness in the child later in life. In Ukraine, Transylvania, and Japan, interaction with a disposed placenta is thought to influence the parents' future fertility.
Several cultures believe the placenta to be or have been alive, often a relative of the baby. Nepalese think of the placenta as a friend of the baby's; Malaysian Orang Asli regard it as the baby's older sibling. The Ibo of Nigeria consider the placenta the deceased twin of the baby, and conduct full funeral rites for it.[19] Native Hawaiians believe that the placenta is a part of the baby, and traditionally plant it with a tree which can then grow alongside the child.[15]
In some cultures, the placenta is eaten, a practice known as placentophagy. In some eastern cultures, such as China and Hong Kong, the placenta is thought to be healthful and is used in medicine and various health products.[21]
Additional images
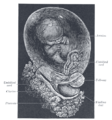 Fetus of about 8 weeks, enclosed in the amnion. Magnified a little over two diameters. |
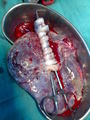 Picture of freshly delivered placenta and umbilical cord wrapped around Kelly clamps |
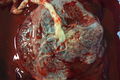 Fresh human placenta |
|
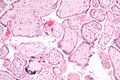 Micrograph of CMV placentitis. |
See also
References
- ↑ Pough et al. 1992. Herpetology: Third Edition. Pearson Prentice Hall:Pearson Education, Inc., 2002.
- ↑ Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, "A Greek-English Lexicon", at Perseus
- ↑ Examination of the placenta
- ↑ http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/reprod/placenta/structure.html Placental Structure and Classification
- ↑ Placental blood circulation
- ↑ Simister, N.E., and Story, C.M. 1997. "Human placental Fc receptors and the transmission of antibodies from mother to fetus." Journal of Reproductive Immunology 37: 1-23.
- ↑ Pillitteri, Adele(2010). Maternal and Child Health Nursing(6th Edition[Philippine Edition]): Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
- ↑ "Placenta 'fools body's defences'". BBC News. 10 November 2007. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/7081298.stm.
- ↑ Clark DA, Chaput A, Tutton D (March 1986). "Active suppression of host-vs-graft reaction in pregnant mice. VII. Spontaneous abortion of allogeneic CBA/J x DBA/2 fetuses in the uterus of CBA/J mice correlates with deficient non-T suppressor cell activity". J. Immunol. 136 (5): 1668–75. PMID 2936806. http://www.jimmunol.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=2936806.
- ↑ Williams Z, Zepf D, Longtine J, et al. (March 2008). "Foreign fetal cells persist in the maternal circulation". Fertil. Steril. 91 (6): 2593–5. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.02.008. PMID 18384774.
- ↑ http://www.sarahjbuckley.com/articles/leaving-well-alone.htm
- ↑ Mary-Claire King, Protein polymorphisms in chimpanzee and human evolution, Doctoral dissertation, University of California, Berkeley (1973).
- ↑ "Humans and Chimps: Close But Not That Close". Scientific American. 19 December 2006. http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?chanID=sa003&articleID=9D0DAC2B-E7F2-99DF-3AA795436FEF8039. Retrieved 20 December 2006.
- ↑ http://www.amazon.com/Placental-Pharmacology-Toxicology-Rama-Sastry/dp/0849378117
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Why eat a placenta?". BBC. 18 April 2006. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/magazine/4918290.stm. Retrieved 8 January 2008.
- ↑ Metge, Joan. 2005. "Working in/Playing with three languages: English, Te Reo Maori, and Maori Bod Language." In Sites N.S vol. 2, No 2:83-90.
- ↑ Francisco, Edna (3 December 2004). "Bridging the Cultural Divide in Medicine". Minority Scientists Network. http://sciencecareers.sciencemag.org/career_development/previous_issues/articles/3360/bridging_the_cultural_divide_in_medicine/. Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- ↑ Shepardson, Mary (1978). "Changes in Navajo Mortuary Practices and Beliefs". American Indian Quarterly. University of Nebraska Press. http://www.jstor.org/view/0095182x/ap040015/04a00080/0. Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Buckley, Sarah J.. "Placenta Rituals and Folklore from around the World". Mothering. http://www.mothering.com/articles/pregnancy_birth/birth_preparation/amazing_placenta_side.html. Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- ↑ Davenport, Ann (June 2005). "The Love Offer". Johns Hopkins Magazine. http://www.jhu.edu/~jhumag/0605web/ruminate.html. Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- ↑ Falcao, Ronnie. "Medicinal Uses of the Placenta". http://www.gentlebirth.org/archives/eatplcnt.html. Retrieved 25 November 2008.
External links
- Additional Human placenta photography [2]
- The Placenta, gynob.com, with quotes from Williams Obstetrics, 18th Edition, F. Gary Cunningham, M.D., Paul C. MacDonald, M.D., Norman F. Grant, M.D., Appleton & Lange, Publishers.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||