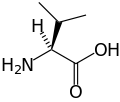
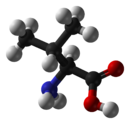
Valine
| Valine | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
|
Valine
|
|
|
Other names
2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 516-06-3 72-18-4 (L-isomer) 640-68-6 (D-isomer) |
| PubChem | 1182 |
| EC-number | 208-220-0 |
|
SMILES
CC(C)C(N)C(=O)O
|
|
| Properties[1] | |
| Molecular formula | C5H11NO2 |
| Molar mass | 117.15 g mol−1 |
| Density | 1.316 g/cm3 |
| Melting point |
298 ºC decomp. |
| Solubility in water | soluble |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) |
|
| Infobox references | |
Valine (abbreviated as Val or V)[2] is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH(CH3)2. L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. Human dietary sources include cottage cheese, fish, poultry, peanuts, sesame seeds, and lentils.
Along with leucine and isoleucine, valine is a branched-chain amino acid. It is named after the plant valerian. In sickle-cell disease, valine substitutes for the hydrophilic amino acid glutamic acid in hemoglobin. Because valine is hydrophobic, the hemoglobin does not fold correctly.
Contents |
Biosynthesis
Valine is an essential amino acid, hence it must be ingested, usually as a component of proteins. It is synthesized in plants via several steps starting from pyruvic acid. The initial part of the pathway also leads to leucine. The intermediate α-ketovalerate undergoes reductive amination with glutamate. Enzymes involved in this biosynthesis include:[3]
- Acetolactate synthase (also known as acetohydroxy acid synthase)
- Acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase
- Dihydroxyacid dehydratase
- Valine aminotransferase
Synthesis
Racemic valine can be synthesized by bromination of isovaleric acid followed by amination of the α-bromo derivative[4]
- HO2CCH2CH(CH3)2 + Br2 → HO2CCHBrCH(CH3)2 + HBr
- HO2CCHBrCH(CH3)2 + 2 NH3 → HO2CCH(NH2)CH(CH3)2 + NH4Br
References
- ↑ Weast, Robert C., ed. (1981), CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, p. C-569, ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ↑ "Nomenclature and symbolism for amino acids and peptides (IUPAC-IUB Recommendations 1983)", Pure Appl. Chem. 56 (5): 595–624, 1984, doi:10.1351/pac198456050595.
- ↑ Lehninger, Albert L.; Nelson, David L.; Cox, Michael M. (2000), Principles of Biochemistry (3rd ed.), New York: W. H. Freeman, ISBN 1-57259-153-6.
- ↑ Marvel, C. S. (1940), "dl-Valine", Org. Synth. 20: 106, http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV3P0848; Coll. Vol. 3: 848.
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |