Cortisol
 |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (11β)-11,17,21-trihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 50-23-7 |
| ATC code | H02AB09 (and others) |
| PubChem | CID 5754 |
| ChemSpider | 5551 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C21H30O5 |
| Mol. mass | 362.460 |
| SMILES | eMolecules & PubChem |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. | C |
| Legal status | Rx Only (U.S.) (excluding 1-2% strength topical) |
| Routes | Oral tablets, intravenously, topical |
| |
|
Cortisol, also known as hydrocortisone, is a steroid hormone or glucocorticoid produced by the adrenal gland.[1] It is released in response to stress, and to a low level of blood glucocorticoids. Its primary functions are to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis, suppress the immune system, and aid in fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism.[2] It also decreases bone formation. Various synthetic forms of cortisol are used to treat a variety of different illnesses.
Contents |
Physiology
Production & release
Cortisol is produced by the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex, which is one of two parts of the adrenal gland.[1]
It is released in response to stress, or to a low level of blood glucocorticoids, and this release is controlled by the hypothalamus, a part of the brain.The secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) by the hypothalamus triggers pituitary secretion of adrenal corticotrophic hormone (ACTH); ACTH is carried by the blood to the adrenal cortex where it triggers glucocorticoid secretion.
Patterns and rhythms of release
The amount of cortisol hormone present in the blood undergoes diurnal variation, with the highest levels present in the early morning (approximately 8am), and the lowest levels present around 12-4am, or 3–5 hours after the onset of sleep. Information about the light/dark cycle is transmitted from the retina to the paired suprachiasmatic nuclei in the hypothalamus. The pattern is not present at birth (estimates of when it starts vary from two weeks to 9 months).[3]
Changed patterns of serum cortisol levels have been observed in connection with abnormal ACTH levels, clinical depression, psychological stress, and such physiological stressors such as hypoglycemia, illness, fever, trauma, surgery, fear, pain, physical exertion or extremes of temperature. Cortisol levels may also be different for people with autism or Asperger's syndrome.[4]
There is also significant individual variation, although a given person tends to have consistent rhythms.
Effects
Following stressful events, cortisol, like other glucocorticoid agents, has widespread actions which help restore homeostasis. Although cortisol secretion in response to stress is a natural function, prolonged cortisol secretion due to chronic stress could result in significant physiological changes.[5]
- Insulin
Cortisol counteracts insulin, contributing to hyperglycemia via stimulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis[6] and inhibition of the peripheral utilization of glucose[6] by decreasing the translocation of glucose transporters to the cell membrane,[7] specially GLUT4.[8] However cortisol increases glycogen synthesis (glycogenesis) in the liver.[9] Permissive effect of cortisol on insulin action on liver glycogenesis is observed in hepatocyte culture in laboratory, although the mechanism is unknown.
- Collagen
In laboratory rats, cortisol-induced collagen loss in the skin is ten times greater than any other tissue.[10][11] Cortisol (as opticortinol) may inversely inhibit IgA precursor cells in the intestines of calves.[12] Cortisol also inhibits IgA in serum, as it does IgM, but is not shown to inhibit IgE.[13]
- Gastric and renal secretion
Cortisol stimulates gastric acid secretion.[14] Cortisol's only direct effect on the hydrogen ion excretion of the kidneys is to stimulate excretion of ammonium ion by inactivation of renal glutaminase enzyme.[15] Net chloride secretion in the intestines is inversely decreased by cortisol in vitro (methylprednisolone).[16]
- Sodium
Cortisol inhibits sodium loss through the small intestine of mammals.[17] Sodium depletion, however, does not affect cortisol,[18] so cortisol cannot be used to regulate serum sodium. Cortisol's purpose may originally have been to transport sodium; this hypothesis is supported by the fact that freshwater fish utilize cortisol to stimulate sodium inward, while saltwater fish have a cortisol-based system for expelling excess sodium.[19]
- Potassium
Sodium load augments the intense potassium excretion by cortisol, and corticosterone is comparable to cortisol in this case.[20] In order for potassium to move out of the cell, cortisol moves in an equal number of sodium ions.[21] It can be seen that this should make pH regulation much easier, unlike the normal potassium deficiency situation in which about 2 sodium ions move in for each 3 potassium ions that move out, which is closer to the deoxycorticosterone effect. Nevertheless, cortisol consistently causes alkalosis of the serum, while in a deficiency pH does not change. Perhaps this may be for the purpose of bringing serum pH to a value most optimum for some of the immune enzymes during infection in those times when cortisol declines. Potassium is also blocked from loss in the kidneys directly somewhat by decline of cortisol (9 alpha fluorohydrocortisone).[22]
- Water
Cortisol also acts as an anti-diuretic hormone. Half the intestinal diuresis is so controlled.[17] Kidney diuresis is also controlled by cortisol in dogs. The decline in water excretion upon decline of cortisol (dexamethasone) in dogs is probably due to inverse stimulation of antidiuretic hormone (ADH or arginine vasopressin), the inverse stimulation of which is not overridden by water loading.[23] Humans also use this mechanism[24] and other different animal mechanisms operate in the same direction.
- Copper
It is probable that increasing copper availability for immune purposes is the reason many copper enzymes are stimulated to an extent which is often 50% of their total potential by cortisol.[25] This includes lysyl oxidase, an enzyme which is used to cross link collagen and elastin.[26] Particularly valuable for immunity is the stimulation of superoxide dismutase by cortisol[27] since this copper enzyme is almost certainly used by the body to permit superoxide to poison bacteria. Cortisol causes an inverse four- or fivefold decrease of metallothionein, a copper storage protein, in mice[28] (however rodents do not synthesize cortisol themselves). This may be to furnish more copper for ceruloplasmin synthesis or release of free copper. Cortisol has an opposite effect on alpha aminoisobuteric acid than on the other amino acids.[29] If alpha aminoisobuteric acid is used to transport copper through the cell wall, this anomaly would possibly be explained.
- Immune system
Cortisol can weaken the activity of the immune system. Cortisol prevents proliferation of T-cells by rendering the interleukin-2 producer T-cells unresponsive to interleukin-1 (IL-1), and unable to produce the T-cell growth factor.[30] Cortisol also has a negative feedback effect on interleukin-1.[31] IL-1 must be especially useful in combating some diseases; however, endotoxin bacteria have gained an advantage by forcing the hypothalamus to increase cortisol levels via forcing secretion of CRH hormone, thus antagonizing IL-1 in this case. The suppressor cells are not affected by GRMF,[32] so that the effective set point for the immune cells may be even higher than the set point for physiological processes. It reflects leukocyte redistribution to lymph nodes, bone marrow, and skin. Acute administration of corticosterone (the endogenous Type I and Type II receptor agonist), or RU28362 (a specific Type II receptor agonist), to adrenalectomized animals induced changes in leukocyte distribution. Natural killer cells are not affected by cortisol.[33]
- Bone metabolism
It lowers bone formation thus favoring development of osteoporosis in the long term. Cortisol moves potassium out of cells in exchange for an equal number of sodium ions as mentioned above.[34] This can cause a major problem with the hyperkalemia of metabolic shock from surgery. Cortisol reduces calcium absorption in the intestine.[35]
- Memory
It cooperates with epinephrine (adrenaline) to create memories of short-term emotional events; this is the proposed mechanism for storage of flash bulb memories, and may originate as a means to remember what to avoid in the future. However, long-term exposure to cortisol results in damage to cells in the hippocampus.[36] This damage results in impaired learning.
- Additional effects
- It increases blood pressure by increasing the sensitivity of the vasculature to epinephrine and norepinephrine. In the absence of cortisol, widespread vasodilation occurs.
- It inhibits the secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), resulting in feedback inhibition of ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone or corticotropin) secretion. Some researchers believe that this normal feedback system may become dysregulated when animals are exposed to chronic stress.
- It allows for the kidneys to produce hypotonic urine.
- It shuts down the reproductive system, resulting in an increase for the chance of miscarriage and, in some cases, temporary infertility. Fertility returns after cortisol levels are reduced back to normal levels.[37]
- It has anti-inflammatory effects by reducing histamine secretion and stabilizing lysosomal membranes. The stabilization of lysosomal membranes prevents their rupture, thereby preventing damage to healthy tissues.
- It stimulates hepatic detoxification by inducing tryptophan oxygenase (to reduce serotonin levels in the brain), glutamine synthase (reduce glutamate and ammonia levels in the brain), cytochrome P-450 hemoprotein (mobilizes arachidonic acid), and metallothionein (reduces heavy metals in the body).
- In addition to the effects caused by cortisol binding to the glucocorticoid receptor, because of its molecular similarity to aldosterone, it also binds to the mineralocorticoid receptor. Aldosterone and cortisol have similar affinity for the mineralocorticoid receptor however, glucocorticoids circulate at roughly 100 times the level of mineralocorticoids. An enzyme exists in mineralocorticoid target tissues to prevent overstimulation by glucocorticoids and allow selective mineralocorticoid action. This enzyme, 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II (Protein:HSD11B2), catalyzes the deactivation of glucocorticoids to 11-dehydro metabolites.
- There are potential links between cortisol, appetite and obesity[38].
Binding
Most serum cortisol, all but about 4%, is bound to proteins including corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG), and serum albumin. Only free cortisol is available to receptors.
Regulation
The primary control of cortisol is the pituitary gland peptide, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH probably controls cortisol by controlling movement of calcium into the cortisol secreting target cells.[39] ACTH is in turn controlled by the hypothalamic peptide, corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH), which is under nervous control. CRH acts synergistically with arginine vasopressin, angiotensin II, and epinephrine.[40] When activated macrophages start to secrete interleukin-1 (IL-1), which synergistically with CRH increases ACTH,[31] T-cells also secrete glucosteroid response modifying factor (GRMF or GAF) as well as IL-1, both of which increase the amount of cortisol required to inhibit almost all the immune cells.[32] Thus immune cells take over their own regulation, but at a higher cortisol set point. Even so, the rise of cortisol in diarrheic calves is minimal over healthy calves and drops below with time.[41] The cells do not lose all of the fight or flight override because of interleukin-1's synergism with CRH. Cortisol even has a negative feedback effect on interleukin-1 [42] which must be especially useful for those diseases which gain an advantage by forcing the hypothalamus to secrete too much CRH, such as the endotoxin bacteria..The suppressor immune cells are not affected by GRMF,[32] so that the effective set point for the immune cells may be even higher than the set point for physiological processes. GRMF (called GAF in this reference) primarily affects the liver rather than the kidneys for some physiological processes.[43]
A high potassium media, which stimulates aldosterone secretion in vitro, also stimulates cortisol secretion from the fasciculata zone of dog adrenals [44] unlike corticosterone, upon which potassium has no effect.[45] Potassium loading increases ACTH and cortisol in people also.[46] This is no doubt the reason why a potassium deficiency causes cortisol to decline (as just mentioned) and why a potassium deficiency causes a decrease in conversion of 11deoxycortisol to cortisol.[47] This probably contributes to the pain in rheumatoid arthritis since cell potassium is always low in that disease [48]
Factors generally reducing cortisol levels
- Magnesium supplementation decreases serum cortisol levels after aerobic exercise,[49][50] but not in resistance training.[51]
- Omega 3 fatty acids, in a dose dependent manner (but not significantly),[52] can lower cortisol release influenced by mental stress[53] by suppressing the synthesis of interleukin-1 and 6 and enhance the synthesis of interleukin-2, where the former promote higher CRH release. Omega 6 fatty acids, on the other hand, acts inversely on interleukin synthesis.
- Music therapy can reduce cortisol levels in certain situations.[54]
- Massage therapy can reduce cortisol.[55]
- Sexual intercourse can reduce cortisol levels.
- Laughing and the experience of humour can lower cortisol levels.[56]
- Soy derived Phosphatidylserine interacts with cortisol but the right dosage is still unclear.[57][58]
- Vitamin C may slightly blunt cortisol release in response to a mental stressor.[59]
- Black tea may speed up recovery from a high cortisol condition.[60][61]
Factors generally increasing cortisol levels
- Caffeine may increase cortisol levels.[62]
- Sleep deprivation increases cortisol levels.[63]
- Intense (high VO2 max) or prolonged physical exercise stimulate cortisol release in order to increase gluconeogenesis and maintain blood glucose.[64] Proper nutrition[65] and high-level conditioning[66] can help stabilize cortisol release.
- Val/Val variation of the BDNF gene in men, and the Val/Met variation in women is associated with increased salivary cortisol in a stressful situation.[67]
- Hypoestrogenism and melatonin supplementation increases cortisol levels in postmenopausal women.[68]
- Burnout is associated with higher cortisol levels.[69]
- Severe trauma or stress events can elevate cortisol levels in the blood for prolonged periods.[70]
- Subcutaneous adipose tissue regenerates cortisol from cortisone.[71]
- Anorexia nervosa may be associated with increased cortisol levels.[72]
- The serotonin receptor gene 5HTR2C is associated with increased cortisol production in men.[73]
- Some formulations of combined oral contraceptive pills increase cortisol levels in young women who perform whole-body resistance exercise training.[74]
- Commuting increases cortisol levels, related to the length of the trip, the amount of effort involved and the predictability of the trip[75]
Clinical chemistry
- Hypercortisolism: Excessive levels of cortisol in the blood.
- Hypocortisolism (adrenal insufficiency): Insufficient levels of cortisol in the blood.
The relationship between cortisol and ACTH, and some consequent conditions, are as follows:
| Plasma ACTH | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ↓ | ↑ | ||
| Plasma Cortisol | ↑ | Primary hypercortisolism (Cushing's syndrome) | Secondary hypercortisolism (pituitary or ectopic tumor, Cushing's disease, pseudo-Cushing's syndrome) |
| ↓ | Secondary hypocortisolism (pituitary tumor, Sheehan's syndrome) | Primary hypocortisolism (Addison's disease, Nelson's syndrome) | |
A 2010 study has found that serum cortisol predicts increased cardiovascular mortality in patients with acute coronary syndrome.[76][77]
Pharmacology
Hydrocortisone is the pharmaceutical term for cortisol used for oral administration, intravenous injection, or topical application. It is used as an immunosuppressive drug, given by injection in the treatment of severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis and angioedema, in place of prednisolone in patients who need steroid treatment but cannot take oral medication, and peri-operatively in patients on long-term steroid treatment to prevent an Addisonian crisis. It may be used topically for allergic rashes, eczema, psoriasis and certain other inflammatory skin conditions. It may also be injected into inflamed joints resulting from diseases such as gout.
Compared to prednisolone, hydrocortisone is about 1/4 the strength for the anti-inflammatory effect, while dexamethasone is about 40 times as strong as hydrocortisone . For side effects, see corticosteroid and prednisolone.
Hydrocortisone creams and ointments are available without prescription in strengths ranging from 0.05% to 2.5%, depending on local regulations, with stronger forms available with prescriptions only. Covering the skin after application increases the absorption and effect. Such enhancement is sometimes prescribed, but otherwise should be avoided to prevent over-dosing and systemic impacts.
Advertising for the dietary supplement CortiSlim originally (and falsely) claimed that it contributed to weight loss by blocking cortisol. The manufacturer was fined $12 million by the Federal Trade Commission in 2007 for false advertising, and no longer claims in their marketing that CortiSlim is a cortisol antagonist.[78]
Biochemistry
Biosynthesis
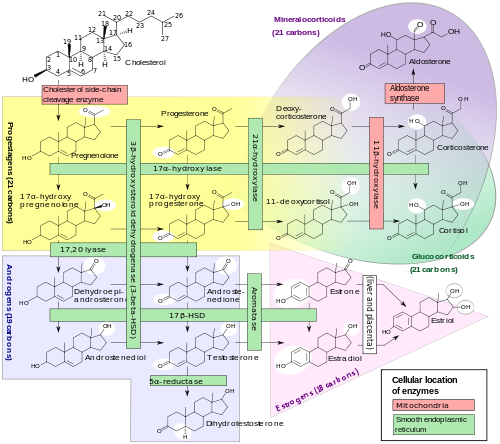
Cortisol is synthesized from cholesterol. The synthesis takes place in the zona fasciculata of the cortex of the adrenal glands. (The name cortisol comes from cortex.) While the adrenal cortex also produces aldosterone (in the zona glomerulosa) and some sex hormones (in the zona reticularis), cortisol is its main secretion. The medulla of the adrenal gland lies under the cortex and mainly secretes the catecholamines, adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) under sympathetic stimulation.
The synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal gland is stimulated by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH); production of ACTH is in turn stimulated by corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), released by the hypothalamus. ACTH increases the concentration of cholesterol in the inner mitochondrial membrane (via regulation of STAR (steroidogenic acute regulatory) protein). ACTH also stimulates the main rate-limiting step in cortisol synthesis where cholesterol is converted to pregnenolone, catalyzed by Cytochrome P450SCC (side chain cleavage enzyme).[79]
Metabolism
Cortisol is metabolized by the 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase system (11-beta HSD), which consists of two enzymes: 11-beta HSD1 and 11-beta HSD2.
- 11-beta HSD1 utilizes the cofactor NADPH to convert biologically inert cortisone to biologically active cortisol.
- 11-beta HSD2 utilizes the cofactor NAD+ to convert cortisol to cortisone.
Overall the net effect is that 11-beta HSD1 serves to increase the local concentrations of biologically active cortisol in a given tissue, while 11-beta HSD2 serves to decrease the local concentrations of biologically active cortisol.
Cortisol is also metabolized into 5-alpha tetrahydrocortisol (5-alpha THF) and 5-beta tetrahydrocortisol (5-beta THF), reactions for which 5-alpha reductase and 5-beta reductase are the rate-limiting factors, respectively. 5-beta reductase is also the rate-limiting factor in the conversion of cortisone to tetrahydrocortisone (THE).
An alteration in 11-beta HSD1 has been suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis of obesity, hypertension, and insulin resistance, sometimes referred to as the metabolic syndrome.[80]
An alteration in 11-beta HSD2 has been implicated in essential hypertension and is known to lead to the syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess (SAME).
Media
 11-Deoxycortisol |
See also
- Adrenaline
- ACTH stimulation test
- Dexamethasone suppression test
- Corticotropin-releasing hormone
- Cushing's syndrome
- HPA axis
- Hypopituitarism
- Posttraumatic stress disorder
- Central serous retinopathy
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://themedicalbiochemistrypage.org/images/adrenalsteroidsynthesis.jpg
- ↑ First Aid USMLE Step 1 2009, Tao Le et al.
- ↑ de Weerth C, Zijl R, Buitelaar J (2003). "Development of cortisol circadian rhythm in infancy". Early Hum Dev 73 (1-2): 39–52. doi:10.1016/S0378-3782(03)00074-4. PMID 12932892.
- ↑ "Asperger's stress hormone 'link'". BBC News. 2009-04-02. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/7976489.stm. Retrieved 2010-04-30.
- ↑ "Cortisol and Stress: How Cortisol Affects Your Body, and How To Stay Healthy in the Face of Stress". Stress.about.com. http://stress.about.com/od/stresshealth/a/cortisol.htm. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 USMLE Step 1 Secrets. 2003. p. 63.
- ↑ King, Michael W. (2005). Lange Q&A USMLE Step 1 (Sixth ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division. p. 82. ISBN 0071445781.
- ↑ PMID 17426391 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Baynes, J., Dominiczak, M., Medical Biochemistry. Elsevier Limited; Third Edition (2009). ISBN 978-0-323-05371-6.
- ↑ Houck JC, Sharma VK, Patel YM, Gladner JA. Induction of collagenolytic and proteolytic activities by anti-inflammatoes this by inhibiting collagen formation, decreasing amino acid uptake by muscle, and inhibiting protein synthesis..
- ↑ Manchester, K.L., “Sites of Hormonal Regulation of Protein Metabolism. p. 229”, Mammalian Protein [Munro, H.N., Ed.]. Academic Press, New York. On p273.
- ↑ Husband AJ, Brandon MR, Lascelles AK (October 1973). "The effect of corticosteroid on absorption and endogenous production of immunoglobulins in calves". Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 51 (5): 707–10. doi:10.1038/icb.1973.67. PMID 4207041.
- ↑ Posey WC, Nelson HS, Branch B, Pearlman DS (December 1978). "The effects of acute corticosteroid therapy for asthma on serum immunoglobulin levels". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 62 (6): 340–8. doi:10.1016/0091-6749(78)90134-3. PMID 712020.
- ↑ Soffer, L.J.; Dorfman, R.I.; Gabrilove, J.L,. “The Human Adrenal Gland”. Febiger, Phil.
- ↑ Kokshchuk, G.I.; Pakhmurnyi, B.A. (1979) “Role of Glucocorticoids in Regulation of the Acid-Excreting Function of the Kidneys”. Fiziol. Z H SSR I.M.I.M. Sechenova 65: 751,.
- ↑ Tai YH, Decker RA, Marnane WG, Charney AN, Donowitz M (May 1981). "Effects of methylprednisolone on electrolyte transport by in vitro rat ileum". Am. J. Physiol. 240 (5): G365–70. PMID 6112881.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Sandle GI, Keir MJ, Record CO (1981). "The effect of hydrocortisone on the transport of water, sodium, and glucose in the jejunum. Perfusion studies in normal subjects and patients with coeliac disease". Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 16 (5): 667–71. doi:10.3109/00365528109182028. PMID 7323700.
- ↑ Mason PA, Fraser R, Morton JJ, Semple PF, Wilson A (August 1977). "The effect of sodium deprivation and of angiotensin II infusion on the peripheral plasma concentrations of 18-hydroxycorticosterone, aldosterone and other corticosteroids in man". J. Steroid Biochem. 8 (8): 799–804. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(77)90086-3. PMID 592808.
- ↑ Gorbman, A.; Dickhoff, W.W.; Vigna, S.R.; Clark, N.B.; Muller, A.F,. “Comparative Endocrinology”. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
- ↑ Muller AF Oconnor CM, ed. (1958) “An International Symposium on Aldosterone”, page 58. Little Brown & Co.
- ↑ KNIGHT RP, KORNFELD DS, GLASER GH, BONDY PK (February 1955). "Effects of intravenous hydrocortisone on electrolytes of serum and urine in man". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 15 (2): 176–81. doi:10.1210/jcem-15-2-176. PMID 13233328.
- ↑ BARGER AC, BERLIN RD, TULENKO JF (June 1958). "Infusion of aldosterone, 9-alpha-fluorohydrocortisone and antidiuretic hormone into the renal artery of normal and adrenalectomized, unanesthetized dogs: effect on electrolyte and water excretion". Endocrinology 62 (6): 804–15. doi:10.1210/endo-62-6-804. PMID 13548099.
- ↑ Boykin J, DeTorrenté A, Erickson A, Robertson G, Schrier RW (October 1978). "Role of plasma vasopressin in impaired water excretion of glucocorticoid deficiency". J. Clin. Invest. 62 (4): 738–44. doi:10.1172/JCI109184. PMID 701472.
- ↑ Dingman, J.F.; Gonzalez-Auvert Ahmed, A.B.J.; Akinura, A. (1965) “Antidiuretic Hormone in Adrenal Insufficiency”. Journal of Clinical Investigation 44: 1041,.
- ↑ Weber, C.E (1984). “Copper Response to Rheumatoid Arthritis”. Medical Hypotheses 15: 333-348, on p337,.
- ↑ Weber, C.E. (1984) “Copper Response to Rheumatoid Arthritis”. Medical Hypotheses 15: 333,.on p334.
- ↑ Flohe, L.; Beckman, R.; Giertz, H.; Loschen, G. “Oxygen Centered Free Radicals as Mediators of Inflammation. p. 405”, Oxidative Stress (Sies H, ed) Academic Press, New York.
- ↑ Piletz JE, Herschman HR (June 1983). "Hepatic metallothionein synthesis in neonatal Mottled-Brindled mutant mice". Biochem. Genet. 21 (5-6): 465–75. doi:10.1007/BF00484439. PMID 6870774.
- ↑ Chambers, J.W.; Georg, R.H. and Bass, A.D. (1965) “Effect of Hydrocortisone and Insulin on Uptake of Alpha Aminoisobutyric Acid by Isolated Perfused Rat Liver”. Mol. Pharmacol. 1: 66,.
- ↑ Palacios R., Sugawara I. (1982). "Hydrocortisone abrogates proliferation of T cells in autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction by rendering the interleukin-2 Producer T cells unresponsive to interleukin-1 and unable to synthesize the T-cell growth factor". Scand J Immunol 15 (1): 25–31. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00618.x. PMID 6461917.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Besedovsky, H.O.; Del Rey, A.; Sorkin, E. (1984) "Integration of Activated Immune Cell Products in Immune Endocrine Feedback Circuits." p. 200 in Leukocytes and Host Defense Vol. 5 [Oppenheim, J.J.; Jacobs, D.M., eds]. Alan R. Liss, New York,.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 Fairchild SS, Shannon K, Kwan E, Mishell RI (February 1984). "T cell-derived glucosteroid response-modifying factor (GRMFT): a unique lymphokine made by normal T lymphocytes and a T cell hybridoma". J. Immunol. 132 (2): 821–7. PMID 6228602.
- ↑ Onsrud M, Thorsby E (1981). "Influence of in vivo hydrocortisone on some human blood lymphocyte subpopulations. I. Effect on natural killer cell activity". Scand. J. Immunol. 13 (6): 573–9. PMID 7313552.
- ↑ Knight, R.P., Jr. Kornfield, D.S. Glaser, G.H. Bondy, P.K. (1955). "Effects of intravenous hydrocortisone on electrolytes of serum and urine in man". J Clin Endocrinol Metab 15 (2): 176–81. doi:10.1210/jcem-15-2-176. PMID 13233328.
- ↑ Shultz TD, Bollman S, Kumar R (June 1982). "Decreased intestinal calcium absorption in vivo and normal brush border membrane vesicle calcium uptake in cortisol-treated chickens: evidence for dissociation of calcium absorption from brush border vesicle uptake". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79 (11): 3542–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.79.11.3542. PMID 6954501.
- ↑ Mc Auley MM, Kenny RA, Kirkwood TT, Wilkinson DD, Jones JJ, Miller VM (March 2009). "A Mathematical Model of aging-related and cortisol induced hippocampal dysfunction". BMC Neurosci 10 (1): 26. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-10-26. PMID 19320982.
- ↑ An Introduction to Behavioral Endocrinology, Randy J Nelson, 3rd edition, Sinauer
- ↑ "Stress Cortisol Connection". Unm.edu. http://www.unm.edu/~lkravitz/Article%20folder/stresscortisol.html. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ Davies E. Keyon, C.J.; Fraser, R. (1985) "The role of calcium ions in the mechanism of ACTH stimulation of cortisol synthesis." Steroids 45: 557.
- ↑ Plotsky PM, Otto S, Sapolsky RM (September 1986). "Inhibition of immunoreactive corticotropin-releasing factor secretion into the hypophysial-portal circulation by delayed glucocorticoid feedback". Endocrinology 119 (3): 1126–30. doi:10.1210/endo-119-3-1126. PMID 3015567.
- ↑ Dvorak, M.; "Plasma 17-Hydroxycorticosteroid Levels in Healthy and Diarrheic Calves." British Veterinarian Journal 127: 372, 1971.
- ↑ Besedovsky, H.O.; Del Rey, A.; Sorkin, E. (1984) "Integration of Activated Immune Cell Products in Immune Endocrine Feedback Circuits." p. 200 in Leukocytes and Host Defense Vol. 5 [Oppenheim, J.J.; Jacobs, D.M., eds]. Alan R. Liss, New York,.
- ↑ Stith RD, McCallum RE (1986). "General effect of endotoxin on glucocorticoid receptors in mammalian tissues". Circ. Shock 18 (4): 301–9. PMID 3084123.
- ↑ Mikosha, A.S.; Pushkarov, I.S.; Chelnakova, I.S.; Remennikov, G.Y.A. (1991) “Potassium Aided Regulation of Hormone Biosynthesis in Adrenals of Guinea Pigs Under Action of Dihydropyridines: Possible Mechanisms of Changes in Steroidogenesis Induced by 1,4, Dihydropyridines in Dispersed Adrenocorticytes.” Fiziol. [Kiev] 37: 60,.
- ↑ Mendelsohn FA, Mackie C (July 1975). "Relation of intracellular K+ and steroidogenesis in isolated adrenal zona glomerulosa and fasciculata cells". Clin Sci Mol Med 49 (1): 13–26. PMID 168026.
- ↑ Ueda Y, Honda M, Tsuchiya M, et al. (April 1982). "Response of plasma ACTH and adrenocortical hormones to potassium loading in essential hypertension". Jpn. Circ. J. 46 (4): 317–22. PMID 6283190.
- ↑ Bauman K Muller J 1972 “Effect of potassium on the final status of aldosterone biosynthesis in the rat. I 18-hydroxylation and 18hydroxy dehydrogenation. II beta-hydroxylation.” Acta Endocrin. Copenh. 69; I 701-717, II 718-730.
- ↑ LaCelle PL et al. (1964) “An investigation of total body potassium in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.” Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Rheumatism Association, Arthritis and Rheumatism 7; 321.
- ↑ PMID 6527092 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 9794094 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ doi:10.1186/1550-2783-1-2-12
This citation will be automatically completed in the next few minutes. You can jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 1832814 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 12909818 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 15086180 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 16162447 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ "Cortisol and Catecholamine stress hormone decrease is associated with the behavior of perceptual anticipation of mirthful laughter". The FASEB Journal. http://www.fasebj.org/cgi/content/meeting_abstract/22/1_MeetingAbstracts/946.11. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ PMID 15512856 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Starks MA, Starks SL, Kingsley M, Purpura M, Jäger R (2008). "The effects of phosphatidylserine on endocrine response to moderate intensity exercise". J Int Soc Sports Nutr 5: 11. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-11. PMID 18662395.
- ↑ Vitamin C: Stress Buster Psychology today
- ↑ "Black tea 'soothes away stress'". BBC News. 2006-10-04. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/5405686.stm. Retrieved 2010-04-30.
- ↑ "Journal Article". SpringerLink. http://www.springerlink.com/content/m226111566k24u65/. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ Lovallo WR, Farag NH, Vincent AS, Thomas TL, Wilson MF (March 2006). "Cortisol responses to mental stress, exercise, and meals following caffeine intake in men and women". Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 83 (3): 441–7. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2006.03.005. PMID 16631247.
- ↑ "Sleep loss results in an elevation of cortisol levels the next evening". Cat.inist.fr. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=2068517. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ Robson PJ, Blannin AK, Walsh NP, Castell LM, Gleeson M (February 1999). "Effects of exercise intensity, duration and recovery on in vitro neutrophil function in male athletes". Int J Sports Med 20 (2): 128–35. doi:10.1055/s-2007-971106. PMID 10190775.
- ↑ PMID 16572599 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Kraemer WJ, Spiering BA, Volek JS, et al. (January 2009). "Recovery from a national collegiate athletic association division I football game: muscle damage and hormonal status". J Strength Cond Res 23 (1): 2–10. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31819306f2 (inactive 2010-01-03). PMID 19077734.
- ↑ PMID 18990498 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 9181519 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.02.015
This citation will be automatically completed in the next few minutes. You can jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Advanced Nutrition and Human Metabolism. 2008. p. 247.
- ↑ "Cortisol Release From Adipose Tissue by 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 in Humans". Diabetes.diabetesjournals.org. 2008-10-13. http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/58/1/46. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ "Body composition changes in female adolescents with anorexia nervosa". American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2008.26958. http://www.ajcn.org/cgi/content/abstract/ajcn.2008.26958v1. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ "New Clues about Genetic Influence of Stress on Men’s Health". Dukehealth.org. http://www.dukehealth.org/HealthLibrary/News/new_clues_about_genetic_influence_of_stress_on_men_s_health. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ "Birth control pills can limit muscle-training gains". Sciencenews.org. http://sciencenews.org/view/generic/id/43210/title/Science_%2B_the_Public__Birth_control_pills_can_limit_muscle-training_gains. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ "The Impact of Mode and Mode Transfer on Commuter Stress, The Montclair Connection" (PDF). http://www.utrc2.org/research/assets/74/commuterstress2-report1.pdf. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ "Serum cortisol predicts increased cardiovascular mortality in patients with acute coronary syndrome". Endocrine-abstracts.org. http://www.endocrine-abstracts.org/ea/0022/ea0022OC4.6.htm. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ↑ doi:10.1530/eje.1.01959
This citation will be automatically completed in the next few minutes. You can jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Iwata, Edward (January 5, 2007). "Diet pill sellers fined $25M". USA Today. http://www.usatoday.com/news/washington/2007-01-04-weight-loss-pills_x.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- ↑ Mechanism of ACTH action on adrenal cortical cells Andrew N. Margioris, M.D., and Christos Tsatsanis, Ph.D. Updated: December 4, 2006
- ↑ [1] Tomlinson JW, Walker EA, Bujalska IJ, Draper N, Lavery GG, Cooper MS, Hewison M, Stewart PM. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1: a tissue-specific regulator of glucocorticoid response. Endocr Rev. 2004 Oct;25(5):831-66.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||