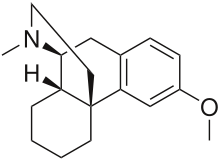
Dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan (DXM or DM) is an antitussive (cough suppressant) drug. It is one of the active ingredients in many over-the-counter cold and cough medicines, such as Robitussin, NyQuil, Dimetapp, Vicks, Coricidin, Delsym, and others, including generic labels. Dextromethorphan has also found other uses in medicine, ranging from pain relief to psychological applications. It is sold in syrup, tablet, spray, and lozenge forms. In its pure form, dextromethorphan occurs as a white powder.
DXM is also used recreationally. When exceeding label-specified maximum dosages, dextromethorphan acts as a dissociative hallucinogen. Its mechanism of action is as an NMDA receptor antagonist, producing effects similar to those of the controlled substances ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP).[2]
History
Dextromethorphan was identified as one of three compounds tested as part of US Navy and CIA-funded research that sought a "nonaddictive substitute for codeine"; it is implied that the compound was first found to have clinical potential in this study[3]. It was first patented under U.S. Patent 2,676,177. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved dextromethorphan for over-the-counter sale as a cough suppressant in 1958. This filled the need for a cough suppressant lacking the sedative side-effects, stronger potential for abuse, and physically addictive properties of codeine phosphate, the most widely used cough medication at the time.[4] In the United States, codeine phosphate syrup is still available in small quantities without a prescription in some states, but requires a signature and ID to purchase, similar to modern rules for sale of pseudoephedrine.
During the 1960s and 1970s, dextromethorphan became available in an over-the-counter tablet form by the brand name Romilar. In 1973, Romilar was taken off the shelves after a burst in sales because of frequent abuse, and was replaced by cough syrup in an attempt to cut down on abuse.[4]
More recently (the early 1990s), gel capsule forms began reappearing in the form of Drixoral Cough Liquid Caps and later Robitussin CoughGels as well as several generic forms of that preparation.
Uses
The primary use of dextromethorphan is as a cough suppressant, for the temporary relief of cough caused by minor throat and bronchial irritation (such as commonly accompanies the flu and common cold), as well as those resulting from inhaled irritants.
As with most cough suppressants, studies show that dextromethorphan's effectiveness is unproven,[5] especially in children.[6] Studies conducted by the American Academy of Pediatrics show that dextromethorphan is not superior to a placebo in providing nocturnal symptom relief for children with cough and sleep difficulty due to upper respiratory infections.[7]
In addition, a combination of dextromethorphan and quinidine has been shown to alleviate symptoms of easy laughing and crying (pseudobulbar affect) in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis.[8] Dextromethorphan is also being investigated as a possible treatment for neuropathic pain and pain associated with fibromyalgia.[9]
Recreational use

Dextromethorphan gel capsules
Since their introduction, over-the-counter preparations containing dextromethorphan have been used in manners inconsistent with their labeling, often as a recreational drug.[4] At doses higher than medically recommended, dextromethorphan is classified as a dissociative psychedelic drug, with visible effects that are similar to those of ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP). It can produce distortions of the visual field, feelings of dissociation, distortions of bodily perception, excitement, as well as a loss of comprehension of time.[10][11]
Chemistry
Dextromethorphan is the dextrorotatory enantiomer of the methyl ether of levorphanol, an opioid analgesic. It is also a stereoisomer of levomethorphan, an opioid analgesic. It is named according to IUPAC rules as (+)-3-methoxy-17-methyl-9α,13α,14α-morphinan. As the pure free base, dextromethorphan occurs as an odorless, white to slightly yellow crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in chloroform and insoluble in water. Dextromethorphan is commonly available as the monohydrated hydrobromide salt, however some newer extended-release formulations contain dextromethorphan bound to an ion exchange resin based on polystyrene sulfonic acid. Dextromethorphan's specific rotation in water is +27.6° (20°C, Sodium D-line).
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Dextromethorphan has been shown to possess the following properties, mainly in binding assays to various receptors of animal tissues. Low Ki values mean strong binding or high affinity; high Ki values mean weak binding to the target or low affinity:
- Uncompetitive NMDA receptor (PCP site) antagonist (Ki = 7,253 nM).[12][13][14][15]
- σ1 and σ2 sigma receptor agonist (Ki = 205 nM and 11,060 nM, respectively). In a comparative investigation of dimemorfan, dextromethorphan and dextrorphan in mouse cells, dextromethorpan binds with relatively high affinity to Sigma-1 receptors and with very low affinity to Sigma-2 receptors.[12]
- α3β4-, α4β2-, and α7-nACh receptor (Ki = in the μM range) antagonist. Dextromethorphan binds to nicotinic receptors in frog eggs (Xenopus oocytes), human embryonic kidney cells and mouse tissue. It inhibits the antinociceptive (pain killing) action of nicotine in the tail-flick test in mice, where mouse tails are exposed to heat, which makes the mouse flick its tail if it feels pain.[16][17][18]
- μ-, δ-, and κ-opioid receptor agonist (Ki = 1,280 nM, 11,500 nM, and 7,000 nM, respectively).[19]
- SERT and NET blocker (Ki = 23 nM and 240 nM, respectively).[19][20][21][22]
- NADPH oxidase inhibitor.[23]
Its affinities for some of the sites listed are relatively very low and are probably insignificant, such as binding to NMDA receptors and opioid receptors, even at high recreational doses. Instead of acting as a direct antagonist of the NMDA receptor itself, it is likely that dextromethorphan functions as a prodrug to its nearly 10-fold more potent metabolite dextrorphan, and this is the true mediator of its dissociative effects.[12] It is not entirely clear what role, if any, (+)-3-methoxymorphinan, dextromethorphan's other major metabolite, plays in its effects.[24]
Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration, dextromethorphan is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, where it enters the bloodstream and crosses the blood-brain barrier.
At therapeutic doses, dextromethorphan acts centrally (meaning that it acts on the brain) as opposed to locally (on the respiratory tract). It elevates the threshold for coughing, without inhibiting ciliary activity. Dextromethorphan is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and converted into the active metabolite dextrorphan in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2D6. The average dosage necessary for effective antitussive therapy is between 10 mg and 45 mg, depending on the individual. The International Society for the Study of Cough recommend "an adequate first dose of medication ie 60 mg in the adult and repeat dosing should be infrequent rather than the qds recommended."[25]
The duration of action after oral administration is approximately three to eight hours for dextromethorphan-hydrobromide, and ten to twelve hours for dextromethorphan-polistirex. Approximately 1 in 10 of the caucasian population has little or no CYP2D6 enzyme activity leading to long lived high drug levels.[26]
Because administration of dextromethorphan can trigger a histamine release (an allergic reaction), its use in atopic children is very limited.
Metabolism
The first-pass through the hepatic portal vein results in some of the drug's being metabolized by O-demethylation into an active metabolite of dextromethorphan called dextrorphan (DXO). DXO is the 3-hydroxy derivative of dextromethorphan. The therapeutic activity of dextromethorphan is believed to be caused by both the drug and this metabolite. Dextromethorphan also undergoes N-demethylation (to 3-methoxymorphinan or MEM),[27] and partial conjugation with glucuronic acid and sulfate ions. Hours after dextromethorphan therapy, (in humans) the metabolites (+)-3-hydroxy-N-methylmorphinan, (+)-3-morphinan, and traces of the unchanged drug are detectable in the urine.[28]
A major metabolic catalyst involved is the cytochrome P450 enzyme known as 2D6, or CYP2D6. A significant portion of the population has a functional deficiency in this enzyme and are known as poor CYP2D6 metabolizers. O-demethylation of DXM to DXO contributes to 100% of the DXO formed during DXM metabolism.[27] As CYP2D6 is a major metabolic pathway in the inactivation of dextromethorphan, the duration of action and effects of dextromethorphan can be increased by as much as three times in such poor metabolizers.[29] In one study on 252 Americans, 84.3% were found to be "fast" (extensive) metabolizers, 6.8% to be "intermediate" metabolizers, and 8.8% were "slow" metabolizers of DXM.[30] There are a number of known alleles for CYP2D6, including several completely inactive variants. The distribution of alleles is uneven amongst ethnic groups; see also CYP2D6 - Ethnic factors in variability.
A large number of medications are potent inhibitors of CYP2D6. Some types of medications known to inhibit CYP2D6 include certain SSRI and tricyclic antidepressants, some antipsychotics, and the commonly-available antihistamine diphenhydramine -- also known as Benadryl. There exists, therefore, the potential of interactions between dextromethorphan and medications that inhibit this enzyme, particularly in slow metabolizers. See also CYP2D6 - Ligands.
DXM is also metabolized by CYP3A4. N-demethylation is primarily accomplished by CYP3A4, contributing to at least 90% of the MEM formed as a primary metabolite of DXM.[27]
A number of other CYP enzymes are implicated as minor pathways of DXM metabolism. CYP2B6 is actually more effective than CYP3A4 at N-demethylation of DXM, but, since the average individual has a much lower CYP2B6 content in his/her liver relative to CYP3A4, most N-demethylation of DXM is catalyzed by CYP3A4.[27]
Side effects
Side-effects of dextromethorphan use can include:[28]
- Note: In the article cited, those marked with asterisks are listed not as side effects per se, but , rather as overdose symptoms, occurring at dosages 12.5 to 75 times the recommended therapeutic dose.
Dextromethorphan can also cause other gastrointestinal disturbances. Dextromethorphan had been thought to cause Olney's Lesions when administered intravenously; however, this was later proven inconclusive, due to lack of research on humans. Tests were performed on rats, giving them 50mg and up every day up to a month. Small lesions were believed to be found during the autopsy on the brain. However the only side effect the rats showed was a change in personality.[32][33] In some rare documented cases, dextromethorphan has produced psychological dependence in some people who used it recreationally. However, it does not produce physical addiction, according to the WHO Committee on Drug Dependence.[34]
Contraindications
Because dextromethorphan can trigger a histamine release (allergic reaction), atopic children, who are especially susceptible to allergic reactions, should be administered dextromethorphan only if absolutely necessary, and only under the strict supervision of a health care professional.[28]
Drug interactions
Dextromethorphan should not be taken with any of the following:
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)[28]
- Serotonin reuptake inhibitors (like SSRIs, SNRis, TCAs, etc.)[28]
- Opiates
- CNS depressant drugs and substances, including some psychotropics such as alcohol, will have a cumulative CNS depressant effect if taken with dextromethorphan.[28]
See also
- Antitussive
- Cough syrup
- Hallucinogen
- Dissociatives
- Morphinans
- Dextrorphan
- Dimemorfan
- Levomethorphan
- Methorphan
References
- ↑ "Plasma profile and pharmacokinetics of dextromethorphan after intravenous and oral administration". Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2885.2004.00608.x?cookieSet=1&journalCode=jvp.
- ↑ DEXTROMETHORPHAN (Street Names: DXM, CCC, Triple C, Skittles, Robo, Poor Man’s PCP)
- ↑ Memorandum for the Secretary of Defense"
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Dextromethorphan (DXM) | CESAR
- ↑ Cough medicines "have no benefit" BBC News: Health, Tuesday, July 6, 2004. Accessed July 28, 2007.
- ↑ "Kids' cough medicine no better than placebo" San Francisco Chronicle, July 8, 2004
- ↑ Paul IM, Yoder KE, Crowell KR (July 2004). "Effect of Dextromethorphan, Diphenhydramine, and Placebo on Nocturnal Cough and Sleep Quality for Coughing Children and Their Parents." Pediatrics 114 (1):85-90
- ↑ Brooks B, Thisted R, Appel S, Bradley W, Olney R, Berg J, Pope L, Smith R (2004). "Treatment of pseudobulbar affect in ALS with dextromethorphan/quinidine: a randomized trial". Neurology 63 (8): 1364–70. PMID 15505150.
- ↑ "Cough Drug May Help Fibromyalgia Pain". WebMD. http://www.webmd.com/content/article/106/108142.
- ↑ AJ Giannini. Drugs of Abuse--Second Edition. Los Angeles, Practice Management Information Corp, 1997.
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Chou YC, Liao JF, Chang WY, Lin MF, Chen CF (March 1999). "Binding of dimemorfan to sigma-1 receptor and its anticonvulsant and locomotor effects in mice, compared with dextromethorphan and dextrorphan". Brain Research 821 (2): 516–9. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(99)01125-7. PMID 10064839. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0006-8993(99)01125-7.
- ↑ Wong BY, Coulter DA, Choi DW, Prince DA (February 1988). "Dextrorphan and dextromethorphan, common antitussives, are antiepileptic and antagonize N-methyl-D-aspartate in brain slices". Neuroscience Letters 85 (2): 261–6. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(88)90362-X. PMID 2897648.
- ↑ Church J, Jones MG, Davies SN, Lodge D (June 1989). "Antitussive agents as N-methylaspartate antagonists: further studies". Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 67 (6): 561–7. PMID 2673498.
- ↑ Kamel IR, Wendling WW, Chen D, Wendling KS, Harakal C, Carlsson C (October 2008). "N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists--S(+)-ketamine, dextrorphan, and dextromethorphan--act as calcium antagonists on bovine cerebral arteries". Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology 20 (4): 241–8. doi:10.1097/ANA.0b013e31817f523f. PMID 18812887. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0898-4921&volume=20&issue=4&spage=241.
- ↑ Damaj MI, Flood P, Ho KK, May EL, Martin BR (February 2005). "Effect of dextrometorphan and dextrorphan on nicotine and neuronal nicotinic receptors: in vitro and in vivo selectivity". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 312 (2): 780–5. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.075093. PMID 15356218. http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15356218.
- ↑ Lee JH, Shin EJ, Jeong SM, et al. (April 2006). "Effects of dextrorotatory morphinans on alpha3beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes". European Journal of Pharmacology 536 (1-2): 85–92. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.02.034. PMID 16563374. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0014-2999(06)00215-9.
- ↑ Hernandez SC, Bertolino M, Xiao Y, Pringle KE, Caruso FS, Kellar KJ (2000). "Dextromethorphan and its metabolite dextrorphan block alpha3beta4 neuronal nicotinic receptors". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 293 (3): 962–7. PMID 10869398.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Codd EE, Shank RP, Schupsky JJ, Raffa RB (September 1995). "Serotonin and norepinephrine uptake inhibiting activity of centrally acting analgesics: structural determinants and role in antinociception". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 274 (3): 1263–70. PMID 7562497. http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=7562497.
- ↑ Henderson MG, Fuller RW (October 1992). "Dextromethorphan antagonizes the acute depletion of brain serotonin by p-chloroamphetamine and H75/12 in rats". Brain Research 594 (2): 323–6. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(92)91144-4. PMID 1280529. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0006-8993(92)91144-4.
- ↑ Gillman PK (October 2005). "Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, opioid analgesics and serotonin toxicity". British Journal of Anaesthesia 95 (4): 434–41. doi:10.1093/bja/aei210. PMID 16051647. http://bja.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16051647.
- ↑ Schwartz AR, Pizon AF, Brooks DE (September 2008). "Dextromethorphan-induced serotonin syndrome". Clinical Toxicology (Philadelphia, Pa.) 46 (8): 771–3. PMID 19238739.
- ↑ Zhang W, Wang T, Qin L, Gao HM, Wilson B, Ali SF, Zhang W, Hong JS, Liu B (20 January 2004). "Neuroprotective effect of dextromethorphan in the MPTP Parkinson's disease model: role of NADPH oxidase". The FASEB Journal 18 (3): 589–91. doi:10.1096/fj.03-0983fje. PMID 14734632.
- ↑ Schmider J, Greenblatt DJ, Fogelman SM, von Moltke LL, Shader RI (April 1997). "Metabolism of dextromethorphan in vitro: involvement of cytochromes P450 2D6 and 3A3/4, with a possible role of 2E1". Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition 18 (3): 227–40. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-081X(199704)18:3<227::AID-BDD18>3.0.CO;2-L. PMID 9113345.
- ↑ Professor Alyn H Morice paper titled 'Cough' par. 'Dextromethorphan' http://www.issc.info/cough.html
- ↑ Professor Alyn H Morice paper titled 'Cough' http://www.issc.info/cough.html
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 27.3 "Comparative Contribution to Dextromethorphan Metabolism by Cytochrome P450 Isoforms in Vitro: Can Dextromethorphan Be Used as a Dual Probe for Both CYP2D6 and CYP3A Activities?". http://dmd.aspetjournals.org/cgi/content/full/29/11/1514. Retrieved 2008-08-10.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 28.3 28.4 28.5 "Dextromethorphan". NHTSA. http://www.nhtsa.dot.gov/PEOPLE/injury/research/job185drugs/dextromethorphan.htm.
- ↑ "Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics — Abstract of article: The influence of CYP2D6 polymorphism and quinidine on the disposition and antitussive effect of dextromethorphan in humans[ast"]. http://www.nature.com/clpt/journal/v60/n3/abs/clpt1996482a.html. Retrieved 2007-07-16.
- ↑ "The polymorphic metabolism of dextromethorphan (abstract)". http://jcp.sagepub.com/cgi/content/abstract/27/2/139. Retrieved 2008-08-10.
- ↑ "Child deaths lead to FDA hearing on cough, cold meds - CNN.com". CNN. 2007-10-17. http://edition.cnn.com/2007/HEALTH/10/17/cough.syrup.deaths/index.html.
- ↑ Olney J, Labruyere J, Price M (1989). "Pathological changes induced in cerebrocortical neurons by phencyclidine and related drugs". Science 244 (4910): 1360–2. doi:10.1126/science.2660263. PMID 2660263.
- ↑ Hargreaves R, Hill R, Iversen L (1994). "Neuroprotective NMDA antagonists: the controversy over their potential for adverse effects on cortical neuronal morphology". Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 60: 15–9. PMID 7976530.
- ↑ WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence (1970) (PDF). Seventeenth Report. World Health Organization. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/trs/WHO_TRS_437.pdf. Retrieved 2008-12-29.
External links
|
Recreational drug use |
|
| Major Recreational Drugs |
|
|
|
|
|
Depressants
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Entactogens
|
|
|
|
Hallucinogens
|
|
Psychedelics
|
|
|
|
Dissociatives
|
|
|
|
Deliriants
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
| Culture and Related Topics |
|
|
420 · Stoner Film · Spiritual Use of Cannabis · Medical Cannabis · Cannabis Cultivation · Cannabis smoking
|
|
|
Psychedelic
|
Art · Drug · Experience · Literature · Music
|
|
|
Other
|
Counterculture of the 1960s · Club Drug · Dance Party · Drug Tourism · Drug Paraphernalia · Hippie · Party and Play · Poly Drug Use · Rave · Self-medication · Sex and Drugs · Spiritual use of drugs |
|
|
| Problems with Drug Use |
Abuse · Addiction (Prevention · Opioid Replacement Therapy · Rehabilitation · Responsible Use) · Drug-related crime · Illegal Trade · Overdose |
|
| Legality of Drug Use |
|
International
|
1961 Narcotic Drugs · 1971 Psychotropic Substances · 1988 Drug Trafficking
|
|
|
State Level
|
Drug Policy (Prohibition · Supply reduction · Decriminalization) · Policy Reform (Liberalization · Harm Reduction · Demand Reduction)
|
|
|
Other
|
Designer Drug · Drug Possession · Drug Test · Hard and Soft Drugs · Narc · War on Drugs · Mexican Drug War |
|
|
| Lists of Countries by... |
Alcohol Consumption · Cannabis Legality (Annual Use · Lifetime Use) · Cocaine Use · Opiate Use · Cigarette Consumption
|
|
|
Cough and cold preparations (R05) |
|
| Expectorants |
Althea root • Antimony pentasulfide • Creosote • Guaiacolsulfonate • Guaifenesin • Ipecacuanha (Syrup of ipecac) • Levoverbenone • Potassium iodide • Senega • Tyloxapol |
|
| Mucolytics |
Acetylcysteine • Ambroxol • Bromhexine • Carbocisteine • Domiodol • Dornase alfa • Eprazinone • Erdosteine • Letosteine • Mesna • Neltenexine • Sobrerol • Stepronin • Tiopronin
|
|
| Cough suppressants |
|
|
Acetyldihydrocodeine • Benzylmorphine • Codeine • Dextromethorphan • Diacetylmorphine • Dihydrocodeine • Dimemorfan • Droxypropine • Ethylmorphine • Hydrocodone • Hydromorphone • Isoaminile • Laudanum • Levomethadone • Levopropoxyphene • Methadone • Nicocodeine • Nicodicodeine • Normethadone • Noscapine • Pholcodine • Thebacon • Tipepidine • Zipeprol |
|
|
Other
|
Benzonatate • Benproperine • Bibenzonium bromide • Butamirate • Clobutinol • Clofedanol • Cloperastine • Diphenhydramine • Dibunate • Dimethoxanate • Dropropizine • Fedrilate • Glaucine • Levodropropizine • Meprotixol • Morclofone • Nepinalone • Oxolamine • Oxeladin • Pentoxyverine • Pipazetate • Prenoxdiazine • Piperidione |
|
|
|
|
anat(n, x, l, c)/phys/devp
|
noco(c)/cong/tumr, sysi/, injr
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depressants |
|
Antihistamines
H1R inverse agonists |
|
|
Antipsychotics
Mixed MOA |
|
|
| Channel Blockers |
Carbamazepine • Ethosuximide • Gabapentin • Lamotrigine • Oxcarbazepine • Phenytoin • Pregabalin • Topiramate • Zonisamide |
|
Dissociatives
NMDAR Antagonists |
|
Arylcyclohexylamines
|
3-MeO-PCP • Esketamine • Dieticyclidine • Eticyclidine • Gacyclidine • Ketamine • Phencyclidine • PCPr • Rolicyclidine • Tenocyclidine • Tiletamine |
|
|
Morphinans
|
Dextromethorphan / Methorphan • Dextrorphan / Morphanol
|
|
|
Others
|
|
|
|
| GABAergics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Carbamates
|
Carisoprodol • Felbamate • Meprobamate ...
|
|
|
|
1,4-BD • Aceburic Acid • Gabaculine • GBL • GABA • GABOB • GHB • GHV • GVL • Isovaleramide • Isovaleric Acid • Phenibut • Picamilon • Tiagabine • Valeric Acid • Valerenic Acid • Valnoctamide • Valproic Acid (Sodium Valproate / Valproate Semisodium) • Valpromide • Vigabatrin
|
|
|
Neuroactive Steroids
|
Alfaxalone • Allopregnanolone • Ganaxolone • Tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone ...
|
|
|
Nonbenzodiazepines
|
|
|
|
Piperidinediones
|
Glutethimide ...
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quinazolinones
|
|
|
|
Others
|
|
|
|
| Glycinergics |
Alanine • Cycloserine • Dimethylglycine • Glycine • Hypotaurine • Methylglycine / Sarcosine • Serine • Taurine • Trimethylglycine / Betaine
|
|
Narcotics
MOR Agonists |
|
|
Sympatholytics
α/β-AR Modulators |
|
Alpha Blockers
|
Doxazosin • Phentolamine • Prazosin • Tamsulosin • Urapidil ...
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others
|
|
|
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
|
|
Hallucinogens |
|
Psychedelics
5-HT2AR agonists |
Lysergamides: AL-LAD • ALD-52 • BU-LAD • CYP-LAD • DAM-57 • Diallyllysergamide • Ergometrine (Ergonovine, Ergobasine) • ETH-LAD • LAE-32 • LSA (Ergine, Lysergamide) • LSD • LSH • LPD-824 • LSM-775 • Lysergic Acid 2-Butyl Amide • Lysergic Acid 2,4-Dimethylazetidide • Methylergometrine • Methylisopropyllysergamide • Methysergide • MLD-41 • PARGY-LAD • PRO-LAD;
Phenethylamines: Aleph • 2C-B • 2C-B-FLY • 2CBFly-NBOMe • 2C-C • 2C-D • 2CD-5EtO • 2C-E • 2C-F • 2C-G • 2C-I • 2C-N • 2C-O • 2C-O-4 • 2C-P • 2C-T • 2C-T-2 • 2C-T-4 • 2C-T-7 • 2C-T-8 • 2C-T-9 • 2C-T-13 • 2C-T-15 • 2C-T-17 • 2C-T-21 • 2C-TFM • 2C-YN • 2CBCB-NBOMe • 25B-NBOMe • 25I-NBMD • 25I-NBOH • 25I-NBOMe • 3C-E • 3C-P • Br-DFLY • DESOXY • DMMDA • DMMDA-2 • DOB • DOC • DOEF • DOET • DOF • DOI • DOM • DON • DOPR • DOTFM • Escaline • Ganesha • HOT-2 • HOT-7 • HOT-17 • IAP • Isoproscaline • Jimscaline • Lophophine • MDA • MDEA • MDMA • MMA • MMDA • MMDA-2 • MMDA-3a • MMDMA • Macromerine • Mescaline • Methallylescaline • Proscaline • TCB-2 • TFMFly • TMA;
Piperazines: pFPP • TMFPP;
Tryptamines: 1-Methyl-5-methoxy-diisopropyltryptamine • 2,N,N-TMT • 4,N,N-TMT • 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT • 4-Acetoxy-DET • 4-Acetoxy-DIPT • 4-Acetoxy-DMT • 4-Acetoxy-DPT • 4-Acetoxy-MiPT • 4-HO-DPT • 4-HO-MET • 4-Propionyloxy-DMT • 4-Hydroxy-N-Methyl-(α,N-trimethylene)tryptamine • 5-Me-MIPT • 5-N,N-TMT • 5-AcO-DMT • 5-MeO-2,N,N-TMT • 5-MeO-4,N,N-TMT • 5-MeO-α,N,N-TMT • 5-MeO-α-ET • 5-MeO-α-MT • 5-MeO-DALT • 5-MeO-DET • 5-MeO-DIPT • 5-MeO-DMT • 5-MeO-DPT • 5-MeO-EiPT • 5-MeO-MET • 5-MeO-MIPT • 5-Methoxy-N-methyl-(α,N-trimethylene)tryptamine • 7,N,N-TMT • α,N,N-TMT • α-ET • α-MT • AL-37350A • Baeocystin • Bufotenin • DALT • DBT • DET • DIPT • DMT • DPT • EiPT • Ethocin • Ethocybin • Iprocin • MET • Miprocin • MIPT • Norbaeocystin • PiPT • Psilocin • Psilocybin;
Others: AL-38022A • Ibogaine • Noribogaine • Voacangine
|
|
Dissociatives
NMDAR antagonists |
Adamantanes: Amantadine • Memantine • Rimantadine;
Arylcyclohexylamines: 3-MeO-PCP • 4-MeO-PCP • Dieticyclidine • Esketamine • Eticyclidine • Gacyclidine • Ketamine • Methoxetamine • Neramexane • Phencyclidine • PCPr • Rolicyclidine • Tenocyclidine • Tiletamine;
Morphinans: Dextrallorphan • Dextromethorphan • Dextrorphan • Methorphan (Racemethorphan) • Morphan (Racemorphan);
Others: 2-MDP • 8A-PDHQ • Aptiganel • Dexoxadrol • Dizocilpine (MK-801) • Etoxadrol • Ibogaine • Midafotel • NEFA • Nitrous Oxide • Noribogaine • Perzinfotel • Remacemide • Selfotel • Xenon
|
|
Deliriants
mAChR antagonists |
3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate • Atropine • Benactyzine • Benzatropine • Benzydamine • Biperiden • Brompheniramine • CAR-226,086 • CAR-301,060 • CAR-302,196 • CAR-302,282 • CAR-302,368 • CAR-302,537 • CAR-302,668 • Chlorpheniramine • Chloropyramine • Clemastine • CS-27349 • Cyclizine • Cyproheptadine • Dicyclomine (Dicycloverine) • Dimenhydrinate • Diphenhydramine • Ditran • Doxylamine • EA-3167 • EA-3443 • EA-3580 • EA-3834 • Elemicin • Flavoxate • Hydroxyzine • Hyoscyamine • Meclizine • Myristicin • N-Ethyl-3-piperidyl benzilate • N-Methyl-3-piperidyl benzilate • Pyrilamine • Orphenadrine • Oxybutynin • Pheniramine • Phenyltoloxamine • Procyclidine • Promethazine • Scopolamine (Hyoscine) • Tolterodine • Trihexyphenidyl • Tripelennamine • Triprolidine • WIN-2299
|
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
|
Cannabinol • CP-47,497 • CP-55,244 • CP-55,940 • DMHP • HU-210 • JWH-018 • JWH-030 • JWH-073 • JWH-081 • JWH-200 • JWH-250 • Nabilone • Nabitan • Nantradol • Parahexyl • THC (Dronabinol) • WIN-55,212-2
|
|
|
D2R agonists
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2-EMSB • 2-MMSB • Alazocine • Bremazocine • Butorphanol • Cyclazocine • Cyprenorphine • Dextrallorphan • Dezocine • Enadoline • Herkinorin • HZ-2 • Ibogaine • Ketazocine • Metazocine • Nalbuphine • Nalorphine • Noribogaine • Pentazocine • Phenazocine • Salvinorin A • Spiradoline • Tifluadom • U-50,488 • U-69,593
|
|
|
|
Dextrallorphan • Dextromethorphan • Dextrorphan • Noscapine (Narcotine)
|
|
|
Others
|
Efavirenz • Glaucine • Isoaminile
|
|
|
|
Adrenergics |
|
|
Receptor ligands |
|
|
α1
|
Agonists: 5-FNE • 6-FNE • Amidephrine • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Cirazoline • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Indanidine • Levonordefrin • Metaraminol • Methoxamine • Methyldopa • Midodrine • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Octopamine • Oxymetazoline • Phenylephrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pseudoephedrine • Synephrine • Tetrahydrozoline
Antagonists: Abanoquil • Adimolol • Ajmalicine • Alfuzosin • Amosulalol • Arotinolol • Atiprosin • Benoxathian • Buflomedil • Bunazosin • Carvedilol • CI-926 • Corynanthine • Dapiprazole • DL-017 • Domesticine • Doxazosin • Eugenodilol • Fenspiride • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Indoramin • Ketanserin • L-765,314 • Labetalol • Mephendioxan • Metazosin • Monatepil • Moxisylyte (Thymoxamine) • Naftopidil • Nantenine • Neldazosin • Nicergoline • Niguldipine • Pelanserin • Phendioxan • Phenoxybenzamine • Phentolamine • Piperoxan • Prazosin • Quinazosin • Ritanserin • RS-97,078 • SGB-1,534 • Silodosin • SL-89.0591 • Spiperone • Talipexole • Tamsulosin • Terazosin • Tibalosin • Tiodazosin • Tipentosin • Tolazoline • Trimazosin • Upidosin • Urapidil • Zolertine
* Note that many TCAs, TeCAs, antipsychotics, ergolines, and some piperazines like buspirone, trazodone, nefazodone, etoperidone, and mepiprazole all antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors as well, which contributes to their side effects such as orthostatic hypotension.
|
|
|
α2
|
Agonists: (R)-3-Nitrobiphenyline • 4-NEMD • 6-FNE • Amitraz • Apraclonidine • Brimonidine • Clonidine • Detomidine • Dexmedetomidine • Dihydroergotamine • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Ergotamine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Esproquin • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Guanabenz • Guanfacine • Guanoxabenz • Levonordefrin • Lofexidine • Medetomidine • Methyldopa • Mivazerol • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Phenylpropanolamine • Piperoxan • Pseudoephedrine • Rilmenidine • Romifidine • Talipexole • Tetrahydrozoline • Tizanidine • Tolonidine • Urapidil • Xylazine • Xylometazoline
Antagonists: 1-PP • Adimolol • Aptazapine • Atipamezole • BRL-44408 • Buflomedil • Cirazoline • Efaroxan • Esmirtazapine • Fenmetozole • Fluparoxan • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Idazoxan • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • MK-912 • NAN-190 • Olanzapine • Phentolamine • Phenoxybenzamine • Piperoxan • Piribedil • Rauwolscine • Rotigotine • SB-269,970 • Setiptiline • Spiroxatrine • Sunepitron • Tolazoline • Yohimbine
* Note that many atypical antipsychotics and azapirones like buspirone and gepirone (via metabolite 1-PP) antagonize α2-adrenergic receptors as well.
|
|
|
|
Agonists: 2-FNE • 5-FNE • Amibegron • Arbutamine • Arformoterol • Arotinolol • BAAM • Bambuterol • Befunolol • Bitolterol • Broxaterol • Buphenine • Carbuterol • Cimaterol • Clenbuterol • Denopamine • Deterenol • Dipivefrine • Dobutamine • Dopamine • Dopexamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etafedrine • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Fenoterol • Formoterol • Hexoprenaline • Higenamine • Indacaterol • Isoetarine • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • Isoxsuprine • Labetalol • Levonordefrin • Levosalbutamol • Mabuterol • Methoxyphenamine • Methyldopa • N-Isopropyloctopamine • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Orciprenaline • Oxyfedrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pirbuterol • Prenalterol • Ractopamine • Procaterol • Pseudoephedrine • Reproterol • Rimiterol • Ritodrine • Salbutamol (Albuterol) • Salmeterol • Solabegron • Terbutaline • Tretoquinol • Tulobuterol • Xamoterol • Zilpaterol • Zinterol
Antagonists: Acebutolol • Adaprolol • Adimolol • Afurolol • Alprenolol • Alprenoxime • Amosulalol • Ancarolol • Arnolol • Arotinolol • Atenolol • Befunolol • Betaxolol • Bevantolol • Bisoprolol • Bopindolol • Bormetolol • Bornaprolol • Brefonalol • Bucindolol • Bucumolol • Bufetolol • Buftiralol • Bufuralol • Bunitrolol • Bunolol • Bupranolol • Burocrolol • Butaxamine • Butidrine • Butofilolol • Capsinolol • Carazolol • Carpindolol • Carteolol • Carvedilol • Celiprolol • Cetamolol • Cicloprolol • Cinamolol • Cloranolol • Cyanopindolol • Dalbraminol • Dexpropranolol • Diacetolol • Dichloroisoprenaline • Dihydroalprenolol • Dilevalol • Diprafenone • Draquinolol • Dropranolol • Ecastolol • Epanolol • Ericolol • Ersentilide • Esatenolol • Esmolol • Esprolol • Eugenodilol • Exaprolol • Falintolol • Flestolol • Flusoxolol • Hydroxycarteolol • Hydroxytertatolol • ICI-118,551 • Idropranolol • Indenolol • Indopanolol • Iodocyanopindolol • Iprocrolol • Isoxaprolol • Isamoltane • Labetalol • Landiolol • Levobetaxolol • Levobunolol • Levocicloprolol • Levomoprolol • Medroxalol • Mepindolol • Metalol • Metipranolol • Metoprolol • Moprolol • Nadolol • Nadoxolol • Nafetolol • Nebivolol • Neraminol • Nifenalol • Nipradilol • Oberadilol • Oxprenolol • Pacrinolol • Pafenolol • Pamatolol • Pargolol • Parodilol • Penbutolol • Penirolol • PhQA-33 • Pindolol • Pirepolol • Practolol • Primidolol • Procinolol • Pronethalol • Propafenone • Propranolol • Ridazolol • Ronactolol • Soquinolol • Sotalol • Spirendolol • SR 59230A • Sulfinalol • TA-2005 • Talinolol • Tazolol • Teoprolol • Tertatolol • Terthianolol • Tienoxolol • Tilisolol • Timolol • Tiprenolol • Tolamolol • Toliprolol • Tribendilol • Trigevolol • Xibenolol • Xipranolol
|
|
|
|
|
Reuptake inhibitors |
|
|
NET
|
Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Amedalin • Atomoxetine (Tomoxetine) • Ciclazindol • Daledalin • Esreboxetine • Lortalamine • Mazindol • Nisoxetine • Reboxetine • Talopram • Talsupram • Tandamine • Viloxazine; Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Amineptine • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Fencamine • Fencamfamine • Lefetamine • Levophacetoperane • LR-5182 • Manifaxine • Methylphenidate • Nomifensine • O-2172 • Radafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Bicifadine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Eclanamine • Levomilnacipran • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • Venlafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Brasofensine • Diclofensine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • JNJ-7925476 • JZ-IV-10 • Methylnaphthidate • Naphyrone • NS-2359 • PRC200-SS • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • Tesofensine; Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Desipramine • Dosulepin • Doxepin • Imipramine • Lofepramine • Nortriptyline • Protriptyline • Trimipramine; Tetracyclic antidepressants: Amoxapine • Maprotiline • Mianserin • Oxaprotiline • Setiptiline; Others: Cocaine • CP-39,332 • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • Nefazodone • Nefopam • Pridefrine • Tapentadol • Tramadol • Ziprasidone
|
|
|
VMAT
|
|
|
|
|
|
Releasing agents |
|
Morpholines: Fenbutrazate • Morazone • Phendimetrazine • Phenmetrazine; Oxazolines: 4-Methylaminorex • Aminorex • Clominorex • Cyclazodone • Fenozolone • Fluminorex • Pemoline • Thozalinone; Phenethylamines (also amphetamines, cathinones, phentermines, etc): 2-OH-PEA • 4-CAB • 4-FA • 4-FMA • 4-MA • 4-MMA • Alfetamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amfepramone • Amphetamine ( Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • β-Me-PEA • BDB • Benzphetamine • BOH • Buphedrone • Butylone • Cathine • Cathinone • Clobenzorex • Clortermine • D-Deprenyl • Dimethylamphetamine • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, metamfepramone) • DMA • DMMA • EBDB • Ephedrine • Ethcathinone • Ethylamphetamine • Ethylone • Famprofazone • Fenethylline • Fenproporex • Flephedrone • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Hordenine • IAP • IMP • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline) • Lisdexamfetamine • Lophophine • MBDB • MDA (Tenamfetamine) • MDEA • MDMA • MDMPEA • MDOH • MDPEA • Mefenorex • Mephedrone • Mephentermine • Methamphetamine ( Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methcathinone • Methedrone • Methylone • NAP • Ortetamine • Paredrine • pBA • pCA • Pentorex (Phenpentermine) • Phenethylamine • Pholedrine • Phenpromethamine • Phentermine • Phenylpropanolamine • pIA • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Pseudoephedrine • Tiflorex • Tyramine • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine; Piperazines: 2C-B-BZP • BZP • MBZP • mCPP • MDBZP • MeOPP • pFPP; Others: 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene • 2-Aminoindane • 2-Aminotetralin • 2-Benzylpiperidine • 4-Benzylpiperidine • 5-IAI • Clofenciclan • Cyclopentamine • Cypenamine • Cyprodenate • Feprosidnine • Gilutensin • Heptaminol • Hexacyclonate • Indanorex • Isometheptene • Methylhexanamine • Octodrine • Phthalimidopropiophenone • Propylhexedrine (Levopropylhexedrine) • Tuaminoheptane
|
|
|
|
Enzyme inhibitors |
|
|
|
|
PAH
|
3,4-Dihydroxystyrene
|
|
|
TH
|
3-Iodotyrosine • Aquayamycin • Bulbocapnine • Metirosine • Oudenone
|
|
|
AAAD
|
Benserazide • Carbidopa • Genistein • Methyldopa
|
|
|
DBH
|
Bupicomide • Disulfiram • Dopastin • Fusaric acid • Nepicastat • Phenopicolinic acid • Tropolone
|
|
|
PNMT
|
CGS-19281A • SKF-64139 • SKF-7698
|
|
|
|
|
|
MAO
|
Nonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima; MAO-B selective: D-Deprenyl • Selegiline (L-Deprenyl) • Ladostigil • Lazabemide • Milacemide • Mofegiline • Pargyline • Rasagiline
* Note that MAO-B inhibitors also influence norepinephrine/epinephrine levels since they inhibit the breakdown of their precursor dopamine.
|
|
|
COMT
|
Entacapone • Tolcapone
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others |
|
|
Precursors
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others
|
Activity enhancers: BPAP • PPAP; Release blockers: Bethanidine • Bretylium • Guanadrel • Guanazodine • Guanclofine • Guanethidine • Guanoxan; Toxins: Oxidopamine (6-Hydroxydopamine)
|
|
|
|
|
Cholinergics |
|
|
Receptor ligands |
|
|
mAChR
|
Agonists: 77-LH-28-1 · AC-42 · AC-260,584 · Aceclidine · Acetylcholine · AF30 · AF150(S) · AF267B · AFDX-384 · Alvameline · AQRA-741 · Arecoline · Bethanechol · Butyrylcholine · Carbachol · CDD-0034 · CDD-0078 · CDD-0097 · CDD-0098 · CDD-0102 · Cevimeline · cis-Dioxolane · Ethoxysebacylcholine · LY-593,039 · L-689,660 · LY-2,033,298 · McNA343 · Methacholine · Milameline · Muscarine · NGX-267 · Ocvimeline · Oxotremorine · PD-151,832 · Pilocarpine · RS86 · Sabcomeline · SDZ 210-086 · Sebacylcholine · Suberylcholine · Talsaclidine · Tazomeline · Thiopilocarpine · Vedaclidine · VU-0029767 · VU-0090157 · VU-0152099 · VU-0152100 · VU-0238429 · WAY-132,983 · Xanomeline · YM-796
Antagonists: 3-Quinuclidinyl Benzilate · 4-DAMP · Aclidinium Bromide · Anisodamine · Anisodine · Atropine · Atropine Methonitrate · Benactyzine · Benzatropine (Benztropine) · Benzydamine · BIBN 99 · Biperiden · Bornaprine · CAR-226,086 · CAR-301,060 · CAR-302,196 · CAR-302,282 · CAR-302,368 · CAR-302,537 · CAR-302,668 · CS-27349 · Cyclobenzaprine · Cyclopentolate · Darifenacin · DAU-5884 · Dimethindene · Dexetimide · DIBD · Dicyclomine (Dicycloverine) · Ditran · EA-3167 · EA-3443 · EA-3580 · EA-3834 · Elemicin · Etanautine · Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) · Flavoxate · Himbacine · HL-031,120 · Ipratropium · J-104,129 · Hyoscyamine · Mamba Toxin 3 · Mamba Toxin 7 · Mazaticol · Mebeverine · Methoctramine · Metixene · Myristicin · N-Ethyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate · N-Methyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate · Orphenadrine · Otenzepad · Oxybutynin · PBID · PD-102,807 · Phenglutarimide · Phenyltoloxamine · Pirenzepine · Piroheptine · Procyclidine · Profenamine · RU-47,213 · SCH-57,790 · SCH-72,788 · SCH-217,443 · Scopolamine (Hyoscine) · Solifenacin · Telenzepine · Tiotropium · Tolterodine · Trihexyphenidyl · Tripitamine · Tropatepine · Tropicamide · WIN-2299 · Xanomeline · Zamifenacin; Others: 1st Generation Antihistamines (Brompheniramine, chlorpheniramine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, mepyramine/pyrilamine, phenindamine, pheniramine, tripelennamine, triprolidine, etc) · Tricyclic Antidepressants ( Amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine, etc) · Tetracyclic Antidepressants (Amoxapine, maprotiline, etc) · Typical Antipsychotics ( Chlorpromazine, thioridazine, etc) · Atypical Antipsychotics ( Clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, etc)
|
|
|
nAChR
|
Agonists: 5-HIAA · A-84,543 · A-366,833 · A-582,941 · A-867,744 · ABT-202 · ABT-418 · ABT-560 · ABT-894 · Acetylcholine · Altinicline · Anabasine · AR-R17779 · Butyrylcholine · Carbachol · Cotinine · Cytisine · Decamethonium · Desformylflustrabromine · Dianicline · Dimethylphenylpiperazinium · Epibatidine · Epiboxidine · Ethanol · Ethoxysebacylcholine · EVP-4473 · EVP-6124 · Galantamine · GTS-21 · Ispronicline · Lobeline · MEM-63,908 (RG-3487) · Nicotine · NS-1738 · PHA-543,613 · PHA-709,829 · PNU-120,596 · PNU-282,987 · Pozanicline · Rivanicline · Sazetidine A · Sebacylcholine · SIB-1508Y · SIB-1553A · SSR-180,711 · Suberylcholine · TC-1698 · TC-1734 · TC-1827 · TC-2216 · TC-5214 · TC-5619 · TC-6683 · Tebanicline · Tropisetron · UB-165 · Varenicline · WAY-317,538 · XY-4083
Antagonists: 18-Methoxycoronaridine · α-Bungarotoxin · α-Conotoxin · Alcuronium · Amantadine · Anatruxonium · Atracurium · Bupropion (Amfebutamone) · Chandonium · Chlorisondamine · Cisatracurium · Coclaurine · Coronaridine · Dacuronium · Decamethonium · Dextromethorphan · Dextropropoxyphene · Dextrorphan · Diadonium · DHβE · Dimethyltubocurarine (Metocurine) · Dipyrandium · Dizocilpine (MK-801) · Doxacurium · Duador · Esketamine · Fazadinium · Gallamine · Hexafluronium · Hexamethonium (Benzohexonium) · Ibogaine · Isoflurane · Ketamine · Kynurenic acid · Laudexium (Laudolissin) · Levacetylmethadol · Malouetine · Mecamylamine · Memantine · Methadone · Methorphan (Racemethorphan) · Methyllycaconitine · Metocurine · Mivacurium · Morphanol (Racemorphanol) · Neramexane · Nitrous Oxide · Pancuronium · Pempidine · Pentamine · Pentolinium · Phencyclidine · Pipecuronium · Radafaxine · Rapacuronium · Rocuronium · Surugatoxin · Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine) · Thiocolchicoside · Toxiferine · Trimethaphan · Tropeinium · Tubocurarine · Vecuronium · Xenon
|
|
|
|
|
Reuptake inhibitors |
|
|
|
|
CHT Inhibitors
|
Hemicholinium-3 (Hemicholine; HC3) · Triethylcholine
|
|
|
|
Vesicular
|
|
VAChT Inhibitors
|
Vesamicol
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enzyme inhibitors |
|
|
|
|
ChAT inhibitors
|
1-(-Benzoylethyl)pyridinium · 2-(α-Naphthoyl)ethyltrimethylammonium · 3-Chloro-4-stillbazole · 4-(1-Naphthylvinyl)pyridine · Acetylseco hemicholinium-3 · Acryloylcholine · AF64A · B115 · BETA · CM-54,903 · N,N-Dimethylaminoethylacrylate · N,N-Dimethylaminoethylchloroacetate
|
|
|
|
|
|
AChE inhibitors
|
Reversible: Carbamates: Aldicarb · Bendiocarb · Bufencarb · Carbaryl · Carbendazim · Carbetamide · Carbofuran · Chlorbufam · Chloropropham · Ethienocarb · Ethiofencarb · Fenobucarb · Fenoxycarb · Formetanate · Furadan · Ladostigil · Methiocarb · Methomyl · Miotine · Oxamyl · Phenmedipham · Pinmicarb · Pirimicarb · Propamocarb · Propham · Propoxur; Stigmines: Ganstigmine · Neostigmine · Phenserine · Physostigmine · Pyridostigmine · Rivastigmine; Others: Acotiamide · Ambenonium · Donepezil · Edrophonium · Galantamine · Huperzine A · Minaprine · Tacrine · Zanapezil
Irreversible: Organophosphates: Acephate · Azinphos-methyl · Bensulide · Cadusafos · Chlorethoxyfos · Chlorfenvinphos · Chlorpyrifos · Chlorpyrifos-Methyl · Coumaphos · Cyclosarin (GF) · Demeton · Demeton-S-Methyl · Diazinon · Dichlorvos · Dicrotophos · Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (Guthion) · Diisopropylphosphate · Dimethoate · Dioxathion · Disulfoton · EA-3148 · Echothiophate · Ethion · Ethoprop · Fenamiphos · Fenitrothion · Fenthion · Fosthiazate · GV · Isofluorophate · Isoxathion · Malaoxon · Malathion · Methamidophos · Methidathion · Metrifonate · Mevinphos · Monocrotophos · Naled · Novichok agent · Omethoate · Oxydemeton-Methyl · Paraoxon · Parathion · Parathion-Methyl · Phorate · Phosalone · Phosmet · Phostebupirim · Phoxim · Pirimiphos-Methyl · Sarin (GB) · Soman (GD) · Tabun (GA) · Temefos · Terbufos · Tetrachlorvinphos · Tribufos · Trichlorfon · VE · VG · VM · VR · VX; Others: Demecarium · Onchidal ( Onchidella binneyi)
|
|
|
BChE inhibitors
|
* Many of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors listed above act as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others |
|
|
Precursors
|
Choline (Lecithin) · Citicoline · Cyprodenate · Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE, deanol) · Glycerophosphocholine · Meclofenoxate (Centrophenoxine) · Phosphatidylcholine · Phosphatidylethanolamine · Phosphorylcholine · Pirisudanol
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others
|
Acetylcholine releasing agents: α-Latrotoxin · β-Bungarotoxin; Acetylcholine release inhibitors: Botulinum toxin (Botox); Acetylcholinesterase reactivators: Asoxime · Obidoxime · Pralidoxime
|
|
|
|
|
Glutamatergics |
|
| Ionotropic |
|
AMPA
|
Agonists: 5-Fluorowillardiine • AMPA • Domoic acid • Quisqualic acid; Positive allosteric modulators: Aniracetam • Cyclothiazide • CX-516 • CX-546 • CX-614 • CX-691 • CX-717 • Diazoxide • HCTZ • IDRA-21 • LY-392,098 • LY-404,187 • LY-451,395 • LY-451,646 • LY-503,430 • Oxiracetam • PEPA • Piracetam • Pramiracetam • S-18986 • Sunifiram • Unifiram
Antagonists: ATPO • Barbiturates • Caroverine • CNQX • DNQX • GYKI-52466 • NBQX • Perampanel • Talampanel • Tezampanel • Topiramate; Negative allosteric modulators: GYKI-53,655
|
|
|
|
Agonists: Glutamate/acite site competitive agonists: Aspartate • Glutamate • Homoquinolinic acid • Ibotenic acid • NMDA • Quinolinic acid • Tetrazolylglycine; Glycine site agonists: ACBD • ACPC • ACPD • Alanine • CCG • Cycloserine • DHPG • Fluoroalanine • Glycine • HA-966 • L-687,414 • Milacemide • Sarcosine • Serine • Tetrazolylglycine; Polyamine site agonists: Acamprosate • Spermidine • Spermine
Antagonists: Competitive antagonists: AP5 (APV) • AP7 • CGP-37849 • CGP-39551 • CGP-39653 • CGP-40116 • CGS-19755 • CPP • LY-233,053 • LY-235,959 • LY-274,614 • MDL-100,453 • Midafotel (d-CPPene) • NPC-12,626 • NPC-17,742 • PBPD • PEAQX • Perzinfotel • PPDA • SDZ-220581 • Selfotel; Noncompetitive antagonists: ARR-15,896 • Caroverine • Dexanabinol • FPL-12495 • FR-115,427 • Hodgkinsine • Magnesium • MDL-27,266 • NPS-1506 • Psychotridine • Zinc; Uncompetitive pore blockers: 2-MDP • 3-MeO-PCP • 8A-PDHQ • Amantadine • Aptiganel • ARL-12,495 • ARL-15,896-AR • ARL-16,247 • Budipine • Delucemine • Dexoxadrol • Dextrallorphan • Dieticyclidine • Dizocilpine • Endopsychosin • Esketamine • Etoxadrol • Eticyclidine • Gacyclidine • Ibogaine • Indantadol • Ketamine • Ketobemidone • Loperamide • Memantine • Meperidine (Pethidine) • Methadone • Methorphan (Dextromethorphan, Levomethorphan) • Methoxetamine • Milnacipran • Morphanol (Dextrorphan, Levorphanol) • NEFA • Neramexane • Nitrous oxide • Noribogaine • Orphenadrine • PCPr • Phencyclamine • Phencyclidine • Propoxyphene • Remacemide • Rhynchophylline • Riluzole • Rimantadine • Rolicyclidine • Sabeluzole • Tenocyclidine • Tiletamine • Tramadol • Xenon; Glycine site antagonists: ACEA-1021 • ACEA-1328 • ACPC • Carisoprodol • CGP-39653 • CKA • DCKA • Felbamate • Gavestinel • GV-196,771 • Kynurenic acid • L-689,560 • L-701,324 • Lacosamide • Licostinel • LU-73,068 • MDL-105,519 • Meprobamate • MRZ 2/576 • PNQX • ZD-9379; NR2B subunit antagonists: Besonprodil • CO-101,244 (PD-174,494) • CP-101,606 • Eliprodil • Haloperidol • Ifenprodil • Isoxsuprine • Nylidrin • Ro8-4304 • Ro25-6981 • Traxoprodil; Polyamine site antagonists: Arcaine • Co 101676 • Diaminopropane • Diethylenetriamine • Huperzine A • Putrescine • Ro 25-6981; Unclassified/unsorted antagonists: Chloroform • Diethyl ether • Enflurane • Ethanol (Alcohol) • Halothane • Isoflurane • Methoxyflurane • Toluene • Trichloroethane • Trichloroethanol • Trichloroethylene • Xylene
|
|
|
Kainate
|
Agonists: 5-Iodowillardiine • ATPA • Domoic acid • Kainic acid • LY-339,434 • SYM-2081
Antagonists: CNQX • DNQX • LY-382,884 • NBQX • NS102 • Tezampanel • Topiramate • UBP-302; Negative allosteric modulators: NS-3763
|
|
|
| Metabotropic |
|
Group I
|
Agonists: Unselective: ACPD • DHPG • Quisqualic acid; mGlu1-selective: Ro01-6128 • Ro67-4853 • Ro67-7476 • VU-71; mGlu5-selective: ADX-47273 • CDPPB • CHPG • DFB • VU-1545
Antagonists: Unselective: MCPG • NPS-2390; mGlu1-selective: BAY 36-7620 • CPCCOEt • LY-367,385 • LY-456,236; mGlu5-selective: DMeOB • Fenobam • LY-344,545 • MPEP • MTEP • SIB-1757 • SIB-1893
|
|
|
Group II
|
Agonists: Unselective: CBiPES • DCG-IV • Eglumegad • LY-379,268 • LY-404,039 • LY-487,379 • MGS-0028; mGlu2-selective: BINA • LY-566,332
Antagonists: Unselective: APICA • EGLU • HYDIA • LY-307,452 • LY-341,495 • MCPG: mGlu2-selective: PCCG-4; mGlu3-selective: CECXG
|
|
|
Group III
|
Agonists: Unselective: L-AP4; mGlu4-selective: PHCCC • VU-001,171 • VU-0155,041; mGlu7-selective: AMN082; mGlu8-selective: DCPG
Antagonists: Unselective: CPPG • MAP4 • MSOP • MPPG • MTPG • UBP-1112; mGlu7-selective: MMPIP
|
|
|
Transporter
inhibitors |
|
EAATs
|
DHKA • PDC • WAY-213,613
|
|
|
vGluTs
|
7-CKA • Evans blue
|
|
|
|
Opioids |
|
Opium and
Poppy straw
derivatives |
Crude opiate extracts/
whole opium products |
Compote/Kompot/Polish heroin · Diascordium · B & O Supprettes · Dover's powder · Laudanum · Mithridate · Opium · Paregoric · Poppy straw concentrate · Poppy tea · Smoking opium · Theriac
|
|
| Natural Opiates |
Opium Alkaloids
see also: |
|
|
| Alkaloid Salts Mixtures |
Pantopon · Papaveretum (Omnopon) · Tetrapon
|
|
|
| Semisynthetics |
| Morphine Family |
2-(p-Nitrophenyl)-4-isopropylmorphine · 14-Hydroxymorphine · 14β-Hydroxymorphine · 14β-Hydroxymorphone · 2,4-Dinitrophenylmorphine · 6-Methyldihydromorphine · 6-Methylenedihydrodesoxymorphine · 6-Acetyldihydromorphine/6-Monoacetyldihydromorphine · Acetyldihydromorphine · Azidomorphine · Chlornaltrexamine · Dihydrodesoxymorphine (Desomorphine) · Dihydromorphine · Ethyldihydromorphine · Hydromorphinol · Methyldesorphine · N-Phenethylnormorphine · Pseudomorphine · RAM-378
|
|
| 3,6 Diesters of Morphine |
6-acetyl-1-iodocodeine · 6-nicotinoyldihydromorphine · Acetylpropionylmorphine · Acetylbutyrylmorphine · Diacetyldihydromorphine (Dihydroheroin) · Diacetyldibenzoylmorphine · Dibutyrylcodeine · Dibutyrylmorphine · Dibenzoylmorphine · Diformylmorphine · Dipropanoylmorphine · Heroin (Diacetylmorphine) · Nicomorphine · Tetrabenzoylmorphine · Tetrabutyrylmorphine
|
|
| Codeine-Dionine Family |
14-Hydroxydihydrocodeine · Acetylcodeine · Benzylmorphine · Codeine methylbromide · Desocodeine · Dimethylmorphine (Methocodeine) · Dihydroethylmorphine · Methyldihydromorphine (Dihydroheterocodeine) · Ethylmorphine (Dionine) · Heterocodeine · Isocodeine · Isopropylmorphine · Morpholinylethylmorphine (Pholcodine) · Myrophine · Nalodeine · Transisocodeine
|
|
| Morphinones & Morphols |
1-Bromohydrocodone · 1-Bromooxycodone · 1-Chlorohydrocodone · 1-Chlorooxycodone · 1-Iodohydrocodone · 1-Iodooxycodone · 14-Cinnamoyloxycodeinone · 14-Ethoxymetopon · 14-Methoxymetopon · 14β-Hydroxymorphone · 14-O-Methyloxymorphone · 14-Phenylpropoxymetopon · 7-Spiroindanyloxymorphone · 8,14-Dihydroxydihydromorphinone · Acetylcodone · Acetylmorphinol · Acetylmorphone · α-hydrocodol · Bromoisopropropyldihydromorphinone · Codeinone · Codorphone · Codol · Codoxime · Thebacon (Acetyldihydrocodeinone / Dihydrocodeinone enol acetate) · Ethyldihydromorphinone · Hydrocodol · Hydrocodone · Hydromorphinone · Hydromorphol · Hydromorphone · Hydroxycodeine · Isopropropyldihydrocodeinone · Isopropropyldihydromorphinone · Methyldihydromorphinone · Metopon · Morphenol · Morphinol · Morphinone · Morphol · N-Phenethyl-14-ethoxymetopon · Oxycodone · Oxymorphol · Oxymorphinol · Oxymorphone · Pentamorphone · Semorphone
|
|
| Morphides |
α-chlorocodide (Alphachlorocodide/Chlorocodide) · α-chloromorphide · 3-Bromomorphide · Bromocodide · Bromomorphide (8-Bromomorphide) · Chlorocodide · Chloromorphide · · Codide · Fluorocodide (8-Fluorocodide) · Fluormorphide · Iodocodide · Iodomorphide (8-Iodomorphide) · Morphide
|
|
| Dihydrocodeine Series |
14-hydroxydihydrocodeine · Acetyldihydrocodeine · Dihydrocodeine · Dihydrodesoxycodeine/Desocodeine · Dihydroisocodeine · Nicocodeine · Nicodicodeine
|
|
| Nitrogen Morphine Derivatives |
1-Nitrocodeine · 2-Nitrocodeine · 1-Nitromorphine · 2-Nitromorphine · Codeine-N-Oxide · Heroin-N-Oxide · Hydromorphone-N-Oxide · Morphine-N-Oxide
|
|
| Hydrazones |
Acetylmorphazone · Hydromorphazone · Morphazone · Oxymorphazone
|
|
| Halogenated Morphine Derivatives |
1-Bromocodeine · 2-Bromocodeine · 1-Bromodiacetylmorphine · 2-Bromodiacetylmorphine · 1-Bromodihydrocodeine · 2-Bromodihydrocodeine · 1-Bromodihydromorphine · 2-Bromodihydromorphine · 1-Bromomorphine · 2-Bromomorphine · 1-Chlorocodeine · 2-Chlorocodeine · 1-Chlorodiacetylmorphine · 2-Chlorodiacetylmorphine · 1-Chlorodihydrocodeine · 2-Chlorodihydrocodeine · 1-Chlorodihydromorphine · 2-Chlorodihydromorphine · 1-Chloromorphine · 2-Chloromorphine · 1-Fluorocodeine · 2-Fluorocodeine · 1-Fluorodiacetylmorphine · 2-Fluorodiacetylmorphine · 1-Fluorodihydrocodeine · 2-Fluorodihydrocodeine · 1-Fluorodihydromorphine · 2-Fluorodihydromorphine · 1-Fluoromorphine · 2-Fluoromorphine · 3-Fluoromorphine · 1-Iodocodeine · 2-Iodocodeine · 1-Iododiacetylmorphine · 2-Iododiacetylmorphine · 1-Iododihydrocodeine · 2-Iododihydrocodeine · 1-Iododihydromorphine · 2-Iododihydromorphine · 1-Iodomorphine · 2-Iodomorphine · Chlorethylmorphine
|
|
| Others |
|
|
|
Active Opiate
Metabolites |
Codeine-N-Oxide (Genocodeine) · Dihydromorphine-6-glucuronide · Hydromorphone-N-Oxide · Heroin-7,8-Oxide · Morphine-6-glucuronide · 6-Acetylmorphine · Morphine-N-Oxide (Genomorphine) · Naltrexol · Norcodeine · Normorphine
|
|
|
| Morphinans |
| Morphinan Series |
4-chlorophenylpyridomorphinan · Cyclorphan · Dextrallorphan · Dimemorfan · Levargorphan · Levallorphan · Levorphanol · Levorphan · Levophenacylmorphan · Levomethorphan · Norlevorphanol · N-Methylmorphinan · Oxilorphan · Phenomorphan · Methorphan / Racemethorphan · Morphanol / Racemorphanol · Ro4-1539 · Stephodeline · Xorphanol
|
|
| Others |
1-Nitroaknadinine · 14-episinomenine · 5,6-Dihydronorsalutaridine · 6-Ketonalbuphine · Aknadinine · Butorphanol · Cephakicine · Cephasamine · Cyprodime · Drotebanol · Fenfangjine G · Nalbuphine · Sinococuline · Sinomenine (Cocculine) · Tannagine
|
|
|
| Benzomorphans |
5,9-DEHB · Alazocine · Anazocine · Bremazocine · Cogazocine · Cyclazocine · Dezocine · Eptazocine · Etazocine · Ethylketocyclazocine · Fluorophen · Ketazocine · Metazocine · Pentazocine · Phenazocine · Quadazocine · Thiazocine · Tonazocine · Volazocine · Zenazocine
|
|
| 4-Phenylpiperidines |
Pethidines
(Meperidines) |
4-Fluoromeperidine · Allylnorpethidine · Anileridine · Benzethidine · Carperidine · Difenoxin · Diphenoxylate · Etoxeridine (Carbetidine) · Furethidine · Hydroxypethidine (Bemidone) · Hydroxymethoxypethidine · Morpheridine · Oxpheneridine (Carbamethidine) · Meperidine-N-Oxide · Pethidine (Meperidine) · Pethidine Intermediate A · Pethidine Intermediate B (Norpethidine) · Pethidine Intermediate C (Pethidinic Acid) · Pheneridine · Phenoperidine · Piminodine · Properidine (Ipropethidine) · Sameridine
|
|
| Prodines |
Allylprodine · Isopromedol · Meprodine (α-meprodine / β-meprodine) · MPPP (Desmethylprodine) · PEPAP · Prodine (α-prodine / β-prodine) · Prosidol · Trimeperidine (Promedol)
|
|
| Ketobemidones |
Acetoxyketobemidone · Droxypropine · Ketobemidone · Methylketobemidone · Propylketobemidone
|
|
| Others |
Alvimopan · Loperamide · Picenadol
|
|
|
Open Chain
Opioids |
| Amidones |
Dextromethadone · Dextroisomethadone · Dipipanone · Hexalgon (Norpipanone) · Isomethadone · Levoisomethadone · Levomethadone · Methadone · Methadone intermediate · Normethadone · Norpipanone · Phenadoxone (Heptazone) · Pipidone
|
|
| Methadols |
Dimepheptanol (Racemethadol) · Levacetylmethadol · Noracetylmethadol
|
|
| Moramides |
Dextromoramide · Levomoramide · Moramide intermediate · Racemoramide
|
|
| Thiambutenes |
Diethylthiambutene · Dimethylthiambutene · Ethylmethylthiambutene · Piperidylthiambutene · Pyrrolidinylthiambutene · Thiambutene · Tipepidine
|
|
| Phenalkoxams |
|
|
| Ampromides |
Diampromide · Phenampromide · Propiram
|
|
| Others |
IC-26 · Isoaminile · Lefetamine · R-4066
|
|
|
| Anilidopiperidines |
3-Allylfentanyl · 3-Methylfentanyl · 3-Methylthiofentanyl · 4-Phenylfentanyl · Alfentanil · α-methylacetylfentanyl · α-methylfentanyl · α-methylthiofentanyl · Benzylfentanyl · β-hydroxyfentanyl · β-hydroxythiofentanyl · β-methylfentanyl · Brifentanil · Carfentanil · Fentanyl · Lofentanil · Mirfentanil · Ocfentanil · Ohmefentanyl · Parafluorofentanyl · Phenaridine · Remifentanil · Sufentanil · Thenylfentanyl · Thiofentanyl · Trefentanil
|
|
Oripavine
derivatives |
6,14-Endoethenotetrahydrooripavine · 7-PET · Acetorphine · Alletorphine · BU-48 · Buprenorphine · Butorphine · Cyprenorphine · Dihydroetorphine · Diprenorphine (M5050) · Etorphine · 18,19-Dehydrobuprenorphine (HS-599) · N-cyclopropylmethyl-noretorphine · Nepenthone · Norbuprenorphine · Thevinone · Thienorphine
|
|
| Phenazepanes |
Ethoheptazine · Meptazinol · Metheptazine · Metethoheptazine · Proheptazine
|
|
| Pirinitramides |
Bezitramide · Piritramide
|
|
| Benzimidazoles |
Clonitazene · Etonitazene · Nitazene
|
|
| Indoles |
18-MC · 7-Acetoxymitragynine · 7-Hydroxymitragynine · Akuammidine · Akuammine · Eseroline · Hodgkinsine · Ibogaine · Mitragynine · Noribogaine · Pericine · ψ-Akuammigine
|
|
| Diphenylmethylpiperazines |
BW373U86 · DPI-221 · DPI-287 · DPI-3290 · SNC-80
|
|
Opioid peptides
see also: The Opioid Peptides |
Adrenorphin · Amidorphin · Casomorphin · DADLE · DALDA · DAMGO · Dermenkephalin · Dermorphin · Deltorphin · DPDPE · Dynorphin · Endomorphin · Endorphin · Enkephalin · Gliadorphin · Morphiceptin · Nociceptin · Octreotide · Opiorphin · Rubiscolin · TRIMU 5
|
|
| Others |
3-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyltropane · AH-7921 • Azaprocin · BDPC · Bisnortilidine · BRL-52537 · Bromadoline • C-8813 · Ciramadol · Doxpicomine • Enadoline · Esketamine · Faxeladol · GR-89696 · Herkinorin · ICI-199,441 · ICI-204,448 · J-113,397 · JTC-801 · Ketamine · LPK-26 · Methopholine · Methoxetamine · N-Desmethylclozapine · NNC 63-0532 · Nortilidine · O-Desmethyltramadol · Phenadone · Phencyclidine · Prodilidine · Profadol · Ro64-6198 · Salvinorin A · SB-612,111 · SC-17599 · RWJ-394,674 · TAN-67 · Tapentadol · Tecodine · Tifluadom · Tilidine · Tramadol · Trimebutine · U-50,488 · U-69,593 · Viminol · W-18 ·
|
|
Opioid Antagonists
&
Inverse-Agonists |
5'-Guanidinonaltrindole · β-Funaltrexamine · 6β-Naltrexol · Alvimopan · Amiphenazole · Binaltorphimine · Chlornaltrexamine · Clocinnamox · Cyclazocine · Cyprodime · Diprenorphine (M5050) · Fedotozine · JDTic · Levallorphan · Methocinnamox · Methylnaltrexone · Nalfurafine · Nalmefene · Nalmexone · Naloxazone · Naloxonazine · Naloxone · Naloxone benzoylhydrazone · Nalorphine · Naltrexone · Naltriben · Naltrindole · Norbinaltorphimine · Oxilorphan · S-allyl-3-hydroxy-17-thioniamorphinan (SAHTM)
|
|
|
Serotonergics |
|
|
5-HT1 receptor ligands |
|
|
5-HT1A
|
Agonists: Azapirones: Alnespirone • Binospirone • Buspirone • Enilospirone • Eptapirone • Gepirone • Ipsapirone • Perospirone • Revospirone • Tandospirone • Tiospirone • Umespirone • Zalospirone; Antidepressants: Etoperidone • Nefazodone • Trazodone; Antipsychotics: Aripiprazole • Asenapine • Clozapine • Quetiapine • Ziprasidone; Ergolines: Dihydroergotamine • Ergotamine • Lisuride • Methysergide • LSD; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MeO-DMT • 5-MT • Bufotenin • DMT • Psilocin • Psilocybin; Others: 8-OH-DPAT • Adatanserin • Befiradol • BMY-14802 • Cannabidiol • Dimemebfe • Ebalzotan • Eltoprazine • F-11,461 • F-12,826 • F-13,714 • F-14,679 • F-15,063 • F-15,599 • Flesinoxan • Flibanserin • Lesopitron • Lu AA21004 • LY-293,284 • LY-301,317 • MKC-242 • NBUMP • Osemozotan • Oxaflozane • Pardoprunox • Piclozotan • Rauwolscine • Repinotan • Roxindole • RU-24,969 • S 14,506 • S-14,671 • S-15,535 • Sarizotan • SSR-181,507 • Sunepitron • U-92016A • Urapidil • Vilazodone • Xaliproden • Yohimbine
Antagonists: Antipsychotics: Iloperidone • Risperidone • Sertindole; Beta blockers: Alprenolol • Cyanopindolol • Iodocyanopindolol • Oxprenolol • Pindobind • Pindolol • Propranolol • Tertatolol; Others: AV965 • BMY-7378 • CSP-2503 • Dotarizine • Flopropione • GR-46611 • Isamoltane • Lecozotan • Metitepine/Methiothepin • MPPF • NAN-190 • PRX-00023 • Robalzotan • S-15535 • SB-649915 • SDZ 216-525 • Spiperone • Spiramide • Spiroxatrine • UH-301 • WAY-100,135 • WAY-100,635 • Xylamidine
|
|
|
5-HT1B
|
Agonists: Lysergamides: Dihydroergotamine • Ergotamine • Methysergide; Piperazines: Eltoprazine • TFMPP; Triptans: Avitriptan • Eletriptan • Sumatriptan • Zolmitriptan; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MT; Others: CGS-12066A • CP-93,129 • CP-94,253 • CP-135,807 • RU-24969
Antagonists: Lysergamides: Metergoline; Others: AR-A000002 • Elzasonan • GR-127,935 • Isamoltane • Metitepine/Methiothepin • SB-216,641 • SB-224,289 • SB-236,057 • Yohimbine
|
|
|
5-HT1D
|
Agonists: Lysergamides: Dihydroergotamine • Methysergide; Triptans: Almotriptan • Avitriptan • Eletriptan • Frovatriptan • Naratriptan • Rizatriptan • Sumatriptan • Zolmitriptan; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MT; Others: CP-135,807 • CP-286,601 • GR-46611 • L-694,247 • L-772,405 • PNU-109,291 • PNU-142,633
Antagonists: Lysergamides: Metergoline; Others: Alniditan • BRL-15572 • Elzasonan • GR-127,935 • Ketanserin • LY-310,762 • LY-367,642 • LY-456,219 • LY-456,220 • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Ritanserin • Yohimbine • Ziprasidone
|
|
|
5-HT1E
|
Agonists: Lysergamides: Methysergide; Triptans: Eletriptan; Tryptamines: BRL-54443 • Tryptamine
Antagonists: Metitepine/Methiothepin
|
|
|
5-HT1F
|
Agonists: Triptans: Eletriptan • Naratriptan • Sumatriptan; Tryptamines: 5-MT; Others: BRL-54443 • Lasmiditan • LY-334,370
Antagonists: Metitepine/Methiothepin
|
|
|
|
|
5-HT2 receptor ligands |
|
|
|
5-HT2A
|
Agonists: Lysergamides: ALD-52 • Ergonovine • Lisuride • LA-SS-Az • LSD • LSD-Pip • Lysergic acid 2-butyl amide • Methysergide; Phenethylamines: 25I-NBMD • 25I-NBOH • 25I-NBOMe • 2C-B • 2C-B-FLY • 2CB-Ind • 2C-E • 2C-I • 2C-T-2 • 2C-T-7 • 2C-T-21 • 2CBCB-NBOMe • 2CBFly-NBOMe • Bromo-DragonFLY • DOB • DOC • DOI • DOM • MDA • MDMA • Mescaline • TCB-2 • TFMFly; Piperazines: BZP • Quipazine • TFMPP; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MeO-α-ET • 5-MeO-α-MT • 5-MeO-DET • 5-MeO-DiPT • 5-MeO-DMT • 5-MeO-DPT • 5-MT • α-ET • α-Methyl-5-HT • α-MT • Bufotenin • DET • DiPT • DMT • DPT • Psilocin • Psilocybin; Others: AL-34662 • AL-37350A • Dimemebfe • Medifoxamine • Oxaflozane • PNU-22394 • RH-34
Antagonists: Atypical antipsychotics: Amperozide • Aripiprazole • Carpipramine • Clocapramine • Clozapine • Gevotroline • Iloperidone • Melperone • Mosapramine • Olanzapine • Paliperidone • Pimozide • Quetiapine • Risperidone • Sertindole • Ziprasidone • Zotepine; Typical antipsychotics: Loxapine • Pipamperone; Antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Amoxapine • Aptazapine • Etoperidone • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Nefazodone • Trazodone; Others: 5-I-R91150 • AC-90179 • Adatanserin • Altanserin • AMDA • APD-215 • Blonanserin • Cinanserin • CSP-2503 • Cyproheptadine • Deramciclane • Dotarizine • Eplivanserin • Esmirtazapine • Fananserin • Flibanserin • Ketanserin • KML-010 • Lubazodone • Mepiprazole • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Nantenine • Pimavanserin • Pizotifen • Pruvanserin • Rauwolscine • Ritanserin • S-14,671 • Sarpogrelate • Setoperone • Spiperone • Spiramide • SR-46349B • Volinanserin • Xylamidine • Yohimbine
|
|
|
5-HT2B
|
Agonists: Oxazolines: 4-Methylaminorex • Aminorex; Phenethylamines: Chlorphentermine • Cloforex • DOB • DOC • DOI • DOM • Fenfluramine • MDA • MDMA • Norfenfluramine; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MT • α-Methyl-5-HT; Others: BW-723C86 • Cabergoline • mCPP • Pergolide • PNU-22394 • Ro60-0175
Antagonists: Agomelatine • Asenapine • EGIS-7625 • Ketanserin • Lisuride • LY-272,015 • Metitepine/Methiothepin • PRX-08066 • Rauwolscine • Ritanserin • RS-127,445 • Sarpogrelate • SB-200,646 • SB-204,741 • SB-206,553 • SB-215,505 • SB-221,284 • SB-228,357 • SDZ SER-082 • Tegaserod • Yohimbine
|
|
|
5-HT2C
|
Agonists: Phenethylamines: 2C-B • 2C-E • 2C-I • 2C-T-2 • 2C-T-7 • 2C-T-21 • DOB • DOC • DOI • DOM • MDA • MDMA • Mescaline; Piperazines: Aripiprazole • mCPP • TFMPP; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MeO-α-ET • 5-MeO-α-MT • 5-MeO-DET • 5-MeO-DiPT • 5-MeO-DMT • 5-MeO-DPT • 5-MT • α-ET • α-Methyl-5-HT • α-MT • Bufotenin • DET • DiPT • DMT • DPT • Psilocin • Psilocybin; Others: A-372,159 • AL-38022A • CP-809,101 • Dimemebfe • Lorcaserin• Medifoxamine • MK-212 • ORG-37,684 • Oxaflozane • PNU-22394 • Ro60-0175 • Vabicaserin • WAY-629 • WAY-161,503 • YM-348
Antagonists: Atypical antipsychotics: Clozapine • Iloperidone • Melperone • Olanzapine • Paliperidone • Pimozide • Quetiapine • Risperidone • Sertindole • Ziprasidone • Zotepine; Typical antipsychotics: Chlorpromazine • Loxapine • Pipamperone; Antidepressants: Agomelatine • Amitriptyline • Amoxapine • Aptazapine • Etoperidone • Fluoxetine • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Nefazodone • Nortriptyline • Trazodone; Others: Adatanserin • Cinanserin • Cyproheptadine • Deramciclane • Dotarizine • Eltoprazine • Esmirtazapine • FR-260,010 • Ketanserin • Ketotifen • Latrepirdine • Lu AA24530 • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Methysergide • Pizotifen • Ritanserin • RS-102,221 • S-14,671 • SB-200,646 • SB-206,553 • SB-221,284 • SB-228,357 • SB-242,084 • SB-243,213 • SDZ SER-082 • Xylamidine
|
|
|
|
|
5-HT3, 5-HT4, 5-HT5, 5-HT6, 5-HT7 ligands |
|
|
|
5-HT3
|
Agonists: Piperazines: BZP • Quipazine; Tryptamines: 2-Methyl-5-HT • 5-CT; Others: Chlorophenylbiguanide • Butanol • Ethanol • Halothane • Isoflurane • RS-56812 • SR-57,227 • SR-57,227-A • Toluene • Trichloroethane • Trichloroethanol • Trichloroethylene • YM-31636
Antagonists: Antiemetics: AS-8112 • Alosetron • Azasetron • Batanopride • Bemesetron • Cilansetron • Dazopride • Dolasetron • Granisetron • Lerisetron • Ondansetron • Palonosetron • Ramosetron • Renzapride • Tropisetron • Zacopride • Zatosetron; Atypical antipsychotics: Clozapine • Olanzapine • Quetiapine; Tetracyclic antidepressants: Amoxapine • Mianserin • Mirtazapine; Others: CSP-2503 • ICS-205,930 • Lu AA21004 • Lu AA24530 • MDL-72,222 • Memantine • Nitrous Oxide • Ricasetron • Sevoflurane • Thujone • Xenon
|
|
|
5-HT4
|
Agonists: Gastroprokinetic Agents: Cinitapride • Cisapride • Dazopride • Metoclopramide • Mosapride • Prucalopride • Renzapride • Tegaserod • Zacopride; Others: 5-MT • BIMU-8 • CJ-033,466 • PRX-03140 • RS-67333 • RS-67506 • SL65.0155 • TD-5108
Antagonists: GR-113,808 • GR-125,487 • L-Lysine • Piboserod • RS-39604 • RS-67532 • SB-203,186
|
|
|
5-HT5A
|
Agonists: Lysergamides: Ergotamine • LSD; Tryptamines: 5-CT; Others: Valerenic Acid
Antagonists: Asenapine • Latrepirdine • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Ritanserin • SB-699,551
* Note that the 5-HT5B receptor is not functional in humans.
|
|
|
5-HT6
|
Agonists: Lysergamides: Dihydroergotamine • Ergotamine • Lisuride • LSD • Mesulergine • Metergoline • Methysergide; Tryptamines: 2-Methyl-5-HT • 5-BT • 5-CT • 5-MT • Bufotenin • E-6801 • E-6837 • EMD-386,088 • EMDT • LY-586,713 • N-Methyl-5-HT • Tryptamine; Others: WAY-181,187 • WAY-208,466
Antagonists: Antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Amoxapine • Clomipramine • Doxepin • Mianserin • Nortriptyline; Atypical antipsychotics: Aripiprazole • Asenapine • Clozapine • Fluperlapine • Iloperidone • Olanzapine • Tiospirone; Typical antipsychotics: Chlorpromazine • Loxapine; Others: BGC20-760 • BVT-5182 • BVT-74316 • EGIS-12233 • GW-742,457 • Ketanserin • Latrepirdine • Lu AE58054 • Metitepine/Methiothepin • MS-245 • PRX-07034 • Ritanserin • Ro 04-6790 • Ro 63-0563 • SB-258,585 • SB-271,046 • SB-357,134 • SB-399,885 • SB-742,457
|
|
|
5-HT7
|
Agonists: Lysergamides: LSD; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MT • Bufotenin; Others: 8-OH-DPAT • AS-19 • Bifeprunox • LP-12 • LP-44 • RU-24,969 • Sarizotan
Antagonists: Lysergamides: 2-Bromo-LSD • Bromocriptine • Dihydroergotamine • Ergotamine • Mesulergine • Metergoline • Methysergide; Antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Amoxapine • Clomipramine • Imipramine • Maprotiline • Mianserin; Atypical antipsychotics: Amisulpride • Aripiprazole • Clozapine • Olanzapine • Risperidone • Sertindole • Tiospirone • Ziprasidone • Zotepine; Typical antipsychotics: Chlorpromazine • Loxapine; Others: Butaclamol • EGIS-12233 • Ketanserin • LY-215,840 • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Pimozide • Ritanserin • SB-258,719 • SB-258,741 • SB-269,970 • SB-656,104 • SB-656,104-A • SB-691,673 • SLV-313 • SLV-314 • Spiperone • SSR-181,507
|
|
|
|
|
Reuptake inhibitors |
|
|
SERT
|
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): Alaproclate • Citalopram • Dapoxetine • Desmethylcitalopram • Desmethylsertraline • Escitalopram • Femoxetine • Fluoxetine • Fluvoxamine • Indalpine • Ifoxetine • Litoxetine • Lu AA21004 • Lubazodone • Panuramine • Paroxetine • Pirandamine • RTI-353 • Seproxetine • Sertraline • Vilazodone • Zimelidine; Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs): Bicifadine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Eclanamine • Levomilnacipran • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • Venlafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (SNDRIs): Brasofensine • Diclofensine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • NS-2359 • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • Tesofensine; Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs): Amitriptyline • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Desipramine • Dosulepin • Doxepin • Imipramine • Lofepramine • Nortriptyline • Pipofezine • Protriptyline • Trimipramine; Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs): Amoxapine; Piperazines: Nefazodone • Trazodone; Antihistamines: Brompheniramine • Chlorpheniramine • Diphenhydramine • Mepyramine/Pyrilamine • Pheniramine • Tripelennamine; Opioids: Meperidine (Pethidine) • Methadone • Propoxyphene; Others: Cocaine • CP-39,332 • Cyclobenzaprine • Dextromethorphan • Dextrorphan • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • Mesembrine • Nefopam • PIM-35 • Pridefrine • Roxindole • SB-649,915 • Ziprasidone
|
|
|
VMAT
|
|
|
|
|
|
Releasing agents |
|
Aminoindanes: 5-IAI • ETAI • MDAI • MDMAI • MMAI • TAI; Aminotetralins: 6-CAT • 8-OH-DPAT • MDAT • MDMAT; Oxazolines: 4-Methylaminorex • Aminorex • Clominorex • Fluminorex; Phenethylamines (also Amphetamines, Cathinones, Phentermines, etc): 2-Methyl-MDA • 4-CAB • 4-FA • 4-FMA • 4-HA • 4-MTA • 5-APDB • 5-Methyl-MDA • 6-APDB • 6-Methyl-MDA • Amiflamine • BDB • BOH • Brephedrone • Butylone • Chlorphentermine • Cloforex • Diethylcathinone • Dimethylcathinone • DMA • DMMA • EBDB • EDMA • Ethylone • Etolorex • Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine) • Flephedrone • IAP • IMP • Lophophine • MBDB • MDA • MDEA • MDHMA • MDMA • MDMPEA • MDOH • MDPEA • Mephedrone • Methedrone • Methylone • MMA • MMDA • MMDMA • NAP • Norfenfluramine • pBA • pCA • pIA • PMA • PMEA • PMMA • TAP; Piperazines: 2C-B-BZP • BZP • MBZP • mCPP • MDBZP • MeOPP • Mepiprazole • pFPP • TFMPP; Tryptamines: 4-Methyl-αET • 4-Methyl-αMT • 5-CT • 5-MeO-αET • 5-MeO-αMT • 5-MT • αET • αMT • DMT • Tryptamine (itself); Others: Indeloxazine • Tramadol • Viqualine
|
|
|
|
Enzyme inhibitors |
|
|
|
|
TPH
|
AGN-2979 • Fenclonine
|
|
|
AAAD
|
Benserazide • Carbidopa • Genistein • Methyldopa
|
|
|
|
|
|
MAO
|
Nonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A Selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others |
|
|
Precursors
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others
|
Activity enhancers: BPAP • PPAP; Reuptake enhancers: Tianeptine
|
|
|
|