Cadmium
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
silvery gray metallic |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name, symbol, number | cadmium, Cd, 48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pronunciation | /ˈkædmiəm/ KAD-mee-əm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Element category | transition metal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Category notes | Alternatively considered a post-transition metal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group, period, block | 12, 5, d | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight | 112.411g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 5s2 4d10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 18, 2 (Image) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 8.65 g·cm−3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Liquid density at m.p. | 7.996 g·cm−3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 594.22 K, 321.07 °C, 609.93 °F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 1040 K, 767 °C, 1413 °F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 6.21 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 99.87 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specific heat capacity | (25 °C) 26.020 J·mol−1·K−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | 2, 1 (mildly basic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | 1.69 (Pauling scale) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies | 1st: 867.8 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2nd: 1631.4 kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd: 3616 kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | 151 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 144±9 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 158 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellanea | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | hexagonal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | (22 °C) 72.7 nΩ·m | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | (300 K) 96.6 W·m−1·K−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | (25 °C) 30.8 µm·m−1·K−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound (thin rod) | (20 °C) 2310 m/s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 50 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 19 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 42 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 203 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS registry number | 7440-43-9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most stable isotopes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main article: Isotopes of cadmium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cadmium (pronounced /ˈkædmiəm/, KAD-mee-əm) is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. The soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low melting point compared to transition metals. Cadmium and its congeners are not considered transition metals, in that they do not have partly filled d or f electron shells in the elemental or common oxidation states.[2] Average concentration in the earth’s crust is between 0.1 and 0.5 parts per million (ppm). It was discovered simultaneously by Stromeyer and Hermann, both in Germany, as an impurity in zinc carbonate[3].
Cadmium occurs as a minor component in most zinc ores and therefore is a byproduct of zinc production. Cadmium was used for a long time as a pigment and for corrosion resistant plating on steel. Cadmium compounds were used to stabilize plastic. With the exception of its use in nickel-cadmium batteries and cadmium telluride solar panels, the use of cadmium is generally decreasing in its other applications. These declines have been due to competing technologies, cadmium’s toxicity in certain forms and concentration and resulting regulations [4]. Although cadmium is toxic, one enzyme, a carbonic anhydrase with cadmium as reactive center has been discovered.
Contents |
Characteristics
Physical properties
Cadmium is a soft, malleable, ductile, bluish-white bivalent metal. It is similar in many respects to zinc but forms complex compounds. [5]
Chemical properties
See also Category: Cadmium compounds The most common oxidation state of cadmium is +2, though rare examples of +1 can be found. Cadmium burns in air to form brown amorphous cadmium oxide (CdO). The crystalline form of the same compound is dark red and changes color when heated, similar to zinc oxide. Hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid and nitric acid dissolve cadmium by forming cadmium chloride (CdCl2) cadmium sulfate (CdSO4) or cadmium nitrate (Cd(NO3)2). The oxidation state +1 can be reached by dissolving cadmium in a mixture of cadmium chloride and aluminium chloride, forming the Cd22+ cation, which is similar to the Hg22+ cation in mercury(I) chloride.[5]
- Cd + CdCl2 + 2 AlCl3 → Cd2[AlCl4]2
Isotopes

Naturally occurring cadmium is composed of 8 isotopes. For two of them, natural radioactivity was observed, and three others are predicted to be radioactive but their decay is not observed, due to extremely long half-life times. The two natural radioactive isotopes are 113Cd (beta decay, half-life is 7.7 × 1015 years) and 116Cd (two-neutrino double beta decay, half-life is 2.9 × 1019 years). The other three are 106Cd, 108Cd (double electron capture), and 114Cd (double beta decay); only lower limits on their half-life times have been set. At least three isotopes - 110Cd, 111Cd, and 112Cd - are stable. Among the isotopes absent in natural cadmium, the most long-lived are 109Cd with a half-life of 462.6 days, and 115Cd with a half-life of 53.46 hours. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 2.5 hours, and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 5 minutes. This element also has 8 known meta states, with the most stable being 113mCd (t½ = 14.1 years), 115mCd (t½ = 44.6 days), and 117mCd (t½ = 3.36 hours).
The known isotopes of cadmium range in atomic mass from 94.950 u (95Cd) to 131.946 u (132Cd). For isotopes lighter than 112 u, the primary decay mode is electron capture and the dominant decay product is element 47 (silver). Heavier isotopes decay mostly through beta emission producing element 49 (indium).
One isotope of cadmium, 113Cd, absorbs neutrons with very high probability if they have an energy below the cadmium cut-off and transmits them readily otherwise. The cadmium cut-off is about 0.5 eV.[6] Neutrons with energy below the cutoff are deemed slow neutrons, distinguishing them from intermediate and fast neutrons.
Cadmium is created via the long S-process in low-medium mass stars (.6 -> 10 solar masses), lasting thousands of years to do. It requires a silver atom to capture a neutron and then undergo beta decay.
History

Cadmium (Latin cadmia, Greek καδμεία meaning "calamine", a cadmium-bearing mixture of minerals, which was named after the Greek mythological character, Κάδμος Cadmus, the founder of Thebes) was discovered simultaneously by Friedrich Stromeyer[7] and Karl Samuel Leberecht Hermann, both in Germany, as an impurity in zinc carbonate[4]. Stromeyer found the new element as an impurity in zinc carbonate (calamine), and, for 100 years, Germany remained the only important producer of the metal. The metal was named after the Latin word for calamine, since the metal was found in this zinc compound. Stromeyer noted that some impure samples of calamine changed color when heated but pure calamine did not. He was persistent in studying these results and eventually isolated cadmium metal by roasting and reduction of the sulfide. Even though cadmium and its compounds may be toxic in certain forms and concentrations, the British Pharmaceutical Codex from 1907 states that cadmium iodide was used as a medication to treat "enlarged joints, scrofulous glands,[8] and chilblains".
In 1927, the International Conference on Weights and Measures redefined the meter in terms of a red cadmium spectral line (1 m = 1,553,164.13 wavelengths).[9] This definition has since been changed (see krypton).
After the industrial scale production of cadmium started in the 1930s and 1940s the major application was the coating of iron and steel to prevent corrosion[4]. In 1944, 62% and in 1956 59% of the cadmium in the United States was used for this purpose.[10] The second application was red, orange and yellow pigments based on sulfides and selenides of cadmium. In 1956, 24% of the cadmium used within the United States was used for this purpose.[10] The stabilizing effect of cadmium-containing chemicals (carboxylates such as the laureate and the stearate) on PVC led to a increased use of those compounds in the 1970s and 1980s. The use of cadmium in applications such as pigments, coatings, stabilizers and alloys declined due to environmental and health regulations in the 1980s and 1990s. In 2006, only 7% of total cadmium consumption was used for plating and coating and only 10% was used for pigments[4]. The decrease in consumption in other applications was made up by a growing demand of cadmium in nickel-cadmium batteries, which accounted for 81% of the cadmium consumption in the United States in 2006.[11]
Occurrence

See also Category: Cadmium minerals Cadmium-containing ores are rare and are found to occur in small quantities. However, traces do naturally occur in phosphate, and have been shown to transmit in food through fertilizer application.[12] Greenockite (CdS), the only cadmium mineral of importance, is nearly always associated with sphalerite (ZnS). As a consequence, cadmium is produced mainly as a byproduct from mining, smelting, and refining sulfidic ores of zinc, and, to a lesser degree, lead and copper. Small amounts of cadmium, about 10% of consumption, are produced from secondary sources, mainly from dust generated by recycling iron and steel scrap. Production in the United States began in 1907, but it was not until after World War I that cadmium came into wide use.[13][14]
One place where metallic cadmium can be found is the Vilyuy River basin in Siberia.[15]
Extraction
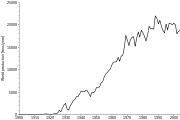
In 2001, China was the top producer of cadmium with almost one-sixth world share closely followed by South Korea and Japan, reports the British Geological Survey.[16]
Cadmium is a common impurity in zinc ores, and it is most often isolated during the production of zinc. Some zinc ores concentrates from sulfidic zinc ores contain up to 1.4% of cadmium.[17] In 1970s, the output of cadmium was 6.5 pounds per ton of zinc.[17] Zinc sulfide ores are roasted in the presence of oxygen, converting the zinc sulfide to the oxide. Zinc metal is produced either by smelting the oxide with carbon or by electrolysis in sulfuric acid. Cadmium is isolated from the zinc metal by vacuum distillation if the zinc is smelted, or cadmium sulfate is precipitated out of the electrolysis solution.[14][18]
Applications
Batteries

In 2009, 86% of all the cadmium is used in batteries, predominantly in rechargeable nickel-cadmium batteries. Nickel-cadmium cells have a nominal cell potential of 1.2 V. The cell consists of a positive nickel hydroxide electrode and a negative cadmium electrode plate separated by an alkaline electrolyte (potassium hydroxide). The European Union banned the use of cadmium in electronics in 2004 with several exceptions but reduced the allowed content of cadmium in electronics to 0.002%.[19]
Other uses


Most of cadmium which is not consumed in battery production is used mainly for cadmium pigments, coatings and plating. Examples of some uses include:
- In electroplating (6% cadmium).[20] Cadmium electroplating is widely used in aircraft industry due to the excellent corrosion resistance of cadmium-plated steel components. Cadmium provides cathodic protection to low-alloyed steels, since it is positioned lower in the galvanic series. The coating is usually passivated by chromate salts.
- Helium-cadmium lasers are a popular source of blue-ultraviolet laser light. They operate either at 325 or 422 nm and are used in fluorescence microscopes and various laboratory experiment.[21]
- Cadmium is used as a barrier to control neutrons in nuclear fission.[20]
- The pressurized water reactor designed by Westinghouse Electric Company uses an alloy consisting of 80% silver, 15% indium, and 5% cadmium.[20]
- Cadmium oxide in black and white television phosphors and in the blue and green phosphors for color television picture tubes.[22]
- Cadmium sulfide (CdS) as a photoconductive surface coating for photocopier drums.[23]
- In paint pigments, cadmium forms various salts, with CdS being the most common. This sulfide is used as a yellow pigment. Cadmium selenide can be used as red pigment, commonly called cadmium red. To painters who work with the pigment, cadmium yellows, oranges, and reds are the most brilliant and long-lasting colors to use. In fact, during production, these colors are significantly toned down before they are ground with oils and binders, or blended into watercolors, gouaches, acrylics, and other paint and pigment formulations. Since these pigments are potentially toxic, it is recommended to use a barrier cream on the hands to prevent absorption through the skin when working with them[24] even though the amount of cadmium absorbed into the body through the skin is usually reported to be less than 1%.
- Cadmium selenide quantum dots emit bright luminescence under UV excitation (He-Cd laser, for example). The color of this luminescence can be green, yellow or red depending on the particle size. Colloidal solutions of those particles are used for imaging of biological tissues and solutions with a fluorescence microscope.[25]
- Cadmium is a component of some compound semiconductors, such as cadmium sulfide, cadmium selenide, and cadmium telluride, which can be used for light detection or solar cells. HgCdTe is sensitive to infrared[20] light and therefore may be utilized as an infrared detector or switch for example in remote control devices.
- In PVC as heat, light, and weathering stabilizers[20][26] although cadmium stabilizers have now been almost completely replaced with barium-zinc, calcium-zinc and organo-tin stabilizers.
- In molecular biology, cadmium is used to block voltage-dependent calcium channels from fluxing calcium ions, as well as in hypoxia research to stimulate proteasome-dependent degradation of Hif-1α.[27]
Historic uses
- In many kinds of solder.[20]
- In bearing alloys, due to a low coefficient of friction and very good fatigue resistance.[20]
- In some of the lowest-melting alloys, such as Wood's metal.[28]
Biological role
A role for cadmium in biological systems has recently been found. A cadmium-dependent carbonic anhydrase has been found in marine diatoms. Cadmium performs the same function as zinc in other anhydrases, but the diatoms live in environments with very low zinc concentrations and thus the biological system has utilized cadmium in place of zinc to perform that function normally carried out by zinc. The discovery was made using X-ray absorption fluorescence spectroscopy (XAFS), and cadmium was characterized by noting the energy of the X-rays that were absorbed.[29][30]
Toxicity
The most dangerous form of occupational exposure to cadmium is inhalation of fine dust and fumes, or ingestion of highly soluble cadmium compounds[4]. Inhalation of cadmium-containing fumes can result initially in metal fume fever but may progress to chemical pneumonitis, pulmonary edema, and death.[31]
Cadmium is also a potential environmental hazard. Human exposures to environmental cadmium are primarily the result of fossil fuel combustion, phosphate fertilizers, natural sources, iron and steel production, cement production and related activities, nonferrous metals production, and municipal solid waste incineration.[4] However, there have been a few instances of general population toxicity as the result of long-term exposure to cadmium in contaminated food and water. In the decades leading up to World War II, Japanese mining operations contaminated the Jinzu River with cadmium and traces of other toxic metals. As a consequence, cadmium accumulated in the rice crops growing along the riverbanks downstream of the mines. Some members of the local agricultural communities consuming the contaminated rice developed itai-itai disease and renal abnormalities, including proteinuria and glucosuria.[32] The victims of this poisoning were almost exclusively post-menopausal women with low iron and other mineral body stores. Similar general population cadmium exposures in other parts of the world have not resulted in the same health problems as long as the populations maintained sufficient iron and other mineral levels. Thus, while cadmium is a major factor in the Itai Itai disease in Japan, most researchers have concluded that it was one of several factors[4]. Cadmium is one of six substances banned by the European Union's Restriction on Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, which bans certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment but allows for certain exemptions and exclusions from the scope of the law[33].
There has been research linking exposure to cadmium to lung and prostate cancer. However, there is still a substantial controversy about the carcinogenicity of cadmium in the scientific community. More recent studies suggest that arsenic rather than cadmium may lead to the increased lung cancer mortality rates. Furthermore, most data regarding the carcinogenicity of cadmium rely on research confounded by the presence of other carcinogenic substances[4].
Tobacco smoking is the most important single source of cadmium exposure in the general population. It has been estimated that about 10% of the cadmium content of a cigarette is inhaled through smoking. The absorption of cadmium from the lungs is much more effective than that from the gut, and as much as 50% of the cadmium inhaled via cigarette smoke may be absorbed.[34]
On average, smokers have 4-5 times higher blood cadmium concentrations and 2-3 times higher kidney cadmium concentrations than non-smokers. Despite the high cadmium content in cigarette smoke, there seems to be little exposure to cadmium from passive smoking. No significant effect on blood cadmium concentrations could be detected in children exposed to environmental tobacco smoke.[35]
Product recalls
Jewelry
Reports of high levels of cadmium use in children's jewelry in 2010 led to a US Consumer Product Safety Commission investigation. Twelve percent of the 103 items tested from New York, Ohio, Texas and California contained at least 10 percent cadmium, with a single item test claimed to be 91 percent cadmium. [36] The CPSC issued specific recall notices for cadmium content applying to jewelry sold by Claire's[37] and Wal-Mart[38] stores.
McDonald's drinking glasses
In June 2010 McDonald's voluntarily recalled more than 12 million promotional “Shrek Forever After 3D” Collectable Drinking Glasses due to concerns over cadmium levels in paint pigments used on the glassware. [39] The glasses were manufactured by ARC International, of Millville, NJ. [40]
See also
- Cadmium pigments
- Cadmium telluride
References
- ↑ Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds, in Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 81st edition, CRC press.
- ↑ Cotton, F. Albert Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 6th Edition, John Wiley and Sons (1999) Chapter 16: Survey of Transition-Metal Chemistry p. 633 ISBN 0471199575
- ↑ Cadmium in Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1999, revision to be published 2010
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, Article Cadmium
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils; (1985) (in German). Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (91–100 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1056–1057. ISBN 3-11-007511-3.
- ↑ Knoll, G.F. (1999). Radiation Detection and Measurement, 3rd edition. Wiley. p. 505. ISBN 978-0471073383.
- ↑ Hermann (1818). "Noch ein schreiben über das neue Metall(Another letter about the new metal)". Annalen der Physik 59: 113. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k150680/f125.chemindefer.
- ↑ Dunglison, Robley (1866). Medical Lexicon: A Dictionary of Medical Science. Henry C. Lea. pp. 159. http://books.google.com/?id=PmohO5jV2YsC.
- ↑ Burdun, G. D. (1958). "On the new determination of the meter" (pdf). Measurement Techniques 1 (3): 259–264. doi:10.1007/BF00974680. http://www.springerlink.com/content/tk70442064438147/fulltext.pdf?page=1.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Lansche, Arnold M.. "Minerals Yearbook 1956: Cadmium". United States Geological Survey. http://digicoll.library.wisc.edu/cgi-bin/EcoNatRes/EcoNatRes-idx?type=turn&entity=EcoNatRes.MinYB1956v1.p0289&id=EcoNatRes.MinYB1956v1&isize=XL&q1=cadmium. Retrieved 2008-04-21.
- ↑ "USGS Commodity Report cadmium". United States Geological Survey. http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/cadmium/. Retrieved 2009-08-08.
- ↑ Jiao, You; Grant, Cynthia A.; Bailey, Loraine D. (2004). "Effects of phosphorus and zinc fertilizer on cadmium uptake and distribution in flax and durum wheat". Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 84 (8): 777–785. doi:10.1002/jsfa.1648.
- ↑ Plachy, Jozef. "Annual Average Cadmium Price". USGS. http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/cadmium/140798.pdf. Retrieved 2010-06-16.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Fthenakis, V (2004). "Life cycle impact analysis of cadmium in CdTe PV production". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 8: 303. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2003.12.001.
- ↑ Fleischer, Michael (1980). "New Mineral Names". American Mineralogist 65: 1065–1070. http://www.minsocam.org/ammin/AM65/AM65_1065.pdf.
- ↑ "Cadmium". World Mineral Production 2002–06. British Geological Survey. p. 15. http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/3260/2/FINAL_WMP_2002_2006_COMPLETE_WEB.pdf. Retrieved 2009-07-07.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 National Research Council (U.S.), Panel on Cadmium, Committee on Technical Aspects of Critical and Strategic Material (1969). Trends in Usage of Cadmium: Report. National Research Council, National Academy of Sciences-National Academy of Engineering. pp. 1–3. http://books.google.com/?id=okArAAAAYAAJ.
- ↑ "Cadmium". WebElements.com. http://www.webelements.com/webelements/elements/text/Cd/key.html.
- ↑ "Battery collection;recycling, nature protected". European Union. http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?pubRef=-//EP//TEXT+IM-PRESS+20060628BRI09328+FULL-TEXT+DOC+XML+V0//EN. Retrieved 2008-11-04.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 20.6 Scoullos, Michael J.; Vonkeman, Gerrit H.; Thornton, Iain; Makuch, Zen (2001). Mercury, Cadmium, Lead: Handbook for Sustainable Heavy Metals Policy and Regulation. Springer. ISBN 9781402002243. http://books.google.com/?id=9yzN-QGag_8C.
- ↑ Helium-Cadmium Lasers, Olympus
- ↑ Lee, Ching-Hwa; Hsi, CS (2002). "Recycling of Scrap Cathode Ray Tubes". Environmental Science and Technology 36 (1): 69–75. doi:10.1021/es010517q. PMID 11811492.
- ↑ Miller, L. S.; Mullin, J. B. (1991). "Crystalline Cadmium Sulfide". Electronic materials: from silicon to organics. Springer. p. 273. ISBN 9780306436550. http://books.google.com/?id=8Yt6GzSEZRkC&pg=PR18.
- ↑ Buxbaum, Gunter; Pfaff, Gerhard (2005). "Cadmium Pigments". Industrial inorganic pigments. Wiley-VCH. pp. 121–123. ISBN 9783527303632. http://books.google.com/?id=_OrB0ew_HgAC&pg=PA121.
- ↑ "Cadmium Selenium Testing for Microbial Contaminants". NASA. http://mix.msfc.nasa.gov/abstracts.php?p=3906.
- ↑ Jennings, Thomas C. (2005). "Cadmium Environmental Concerns". PVC handbook. Hanser Verlag. p. 149. ISBN 9781569903797. http://books.google.com/?id=YUkJNI9QYsUC&pg=PA149.
- ↑ Park JW, Chun YS; Choi, E; Kim, GT; Choi, H; Kim, CH; Lee, MJ; Kim, MS; Park, JW (2000). "Cadmium blocks hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1-mediated response to hypoxia by stimulating the proteasome-dependent degradation of HIF-1alpha.". European Journal of Biochemistry 267 (13): 4198–4204. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01453.x. PMID 10866824.
- ↑ Brady, George Stuart; Brady, George S.; Clauser, Henry R.; Vaccari, John A. (2002). Materials handbook: an encyclopedia for managers, technical professionals, purchasing and production managers, technicians, and supervisors. McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 425. ISBN 9780071360760. http://books.google.com/?id=vIhvSQLhhMEC&pg=PA425.
- ↑ Lane, Todd W.; Morel, FM (2000). "A biological function for cadmium in marine diatoms". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 97 (9): 4627–4631. doi:10.1073/pnas.090091397. PMID 10781068. PMC 18283. http://www.pnas.org/content/97/9/4627.full.pdf+html.
- ↑ Lane, Todd W.; Saito, Mak A.; George, Graham N.; Pickering, Ingrid J.; Prince, Roger C.; Morel, François M. M. (2005). "A cadmium enzyme from a marine diatom". Nature 435 (42): 42. doi:10.1038/435042a. PMID 15875011. http://www.whoi.edu/cms/files/msaito/2005/5/LaneSaitoMorel_CdCA_Nature2005_2944.pdf.
- ↑ Hayes, Andrew Wallace (2007). Principles and Methods of Toxicology. Philadelphia: CRC Press. pp. 858–861. ISBN 9780849337789. http://books.google.com/?id=vgHXTId8rnYC&dq.
- ↑ Nogawa, Koji; Kobayashi, E; Okubo, Y; Suwazono, Y (2004). "Environmental cadmium exposure, adverse effects, and preventative measures in Japan". Biometals 17 (5): 581–587. doi:10.1023/B:BIOM.0000045742.81440.9c. PMID 15688869. http://www.springerlink.com/content/n0773057mw738u05/.
- ↑ European Commission Decision of 12 October 2006 amending, for the purposes of adapting to technical progress, the Annex to Directive 2002/95/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards exemptions for applications of lead and cadmium (notified under document number C(2006) 4790 http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:283:0048:0049:EN:PDF
- ↑ Friberg, L. (1983). "Cadmium". Annual Review of Public Health 4: 367–367. doi:10.1146/annurev.pu.04.050183.002055. PMID 6860444.
- ↑ Jarup, L. (1998). "Health effects of cadmium exposure—a review of the literature and a risk estimate". Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment and Health 24: 11–51.
- ↑ "U.S. to Develop Safety Standards for Toxic Metals". Business Week. 2010-01-12. http://www.businessweek.com/news/2010-01-12/u-s-to-develop-safety-standards-for-toxic-metals-update1-.html. Retrieved 2010-01-12.
- ↑ "Claire's Recalls Children's Metal Charm Bracelets Due to High Levels of Cadmium". U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. 2010-05-10. http://www.cpsc.gov/CPSCPUB/PREREL/prhtml10/10227.html. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
- ↑ "FAF Inc. Recalls Children's Necklaces Sold Exclusively at Walmart Stores Due to High Levels of Cadmium". U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. 2010-01-29. http://www.cpsc.gov/CPSCPUB/PREREL/prhtml10/10127.html. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
- ↑ "McDonald’s Recalls 12 Million ‘Shrek’ Glasses". New York Times. 2010-06-04. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/06/05/business/05recall.html. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
- ↑ "McDonald’s Recalls Movie Themed Drinking Glasses Due to Potential Cadmium Risk". U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. 2010-06-04. http://www.cpsc.gov/CPSCPUB/PREREL/prhtml10/10257.html. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
External links
- ATSDR Case Studies in Environmental Medicine: Cadmium Toxicity U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry’s (ATSDR) Toxicological Profile for Cadmium
- European Union Risk Assessment Reports on Cadmium Metal and Cadmium Oxide
- IARC Monograph "Cadmium and Cadmium Compounds"
- National Pollutant Inventory - Cadmium and compounds
- Cadmium exposure pathfinder
- WebElements.com - Cadmium
- Warning Moose and Deer Liver
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health - Cadmium Page
- NLM Hazardous Substances Databank – Cadmium, Elemental
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Uut | Uuq | Uup | Uuh | Uus | Uuo | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||
